Vinculin: Difference between revisions
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
*Vinculin | *Vinculin; Domains - Vd1 140-327; tail 878-1066 | ||
**[[1tr2]] – hVCL - human<br /> | **[[1tr2]], [[6fuy]] – hVCL - human<br /> | ||
**[[1qkr]] – hVCL tail domain<br /> | **[[1qkr]] – hVCL tail domain<br /> | ||
**[[3h2v]] - hVCL tail domain + raver1 RRM<br /> | **[[3h2v]] - hVCL tail domain + raver1 RRM<br /> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
**[[3s90]] - hm-VCL head domain + mTalin-1 peptide<br /> | **[[3s90]] - hm-VCL head domain + mTalin-1 peptide<br /> | ||
**[[4dj9]] - hm-VCL head domain + hTalin-1 peptide <br /> | **[[4dj9]] - hm-VCL head domain + hTalin-1 peptide <br /> | ||
**[[6fq4]] - hm-VCL head domain + TARP peptide <br /> | |||
**[[3tj5]] - hm-VCL head domain + Sca-family protein peptide<br /> | **[[3tj5]] - hm-VCL head domain + Sca-family protein peptide<br /> | ||
**[[3tj6]] - hm-VCL head domain + protein Ps 120 peptide<br /> | **[[3tj6]] - hm-VCL head domain + protein Ps 120 peptide<br /> | ||
**[[4ehp]] - hm-VCL head domain + catenin α-1 residues 277-382<br /> | **[[4ehp]], [[5y04]] - hm-VCL head domain + catenin α-1 residues 277-382<br /> | ||
**[[3vf0]] – hm-VCL residues 856-1134 + ribonucleoprotein PTB-binding<br /> | **[[3vf0]] – hm-VCL residues 856-1134 + ribonucleoprotein PTB-binding<br /> | ||
**[[2gdc]] – cm-VCL Vd1+SfInvasin C-terminal <br /> | **[[2gdc]] – cm-VCL Vd1+SfInvasin C-terminal <br /> | ||
Revision as of 00:55, 6 October 2018
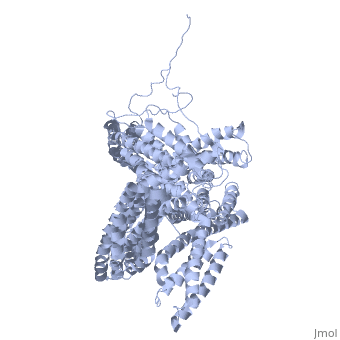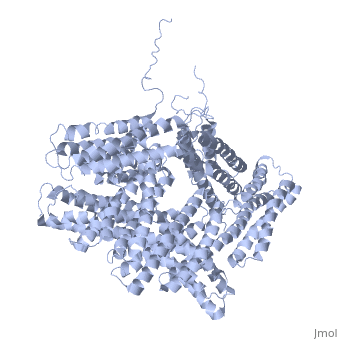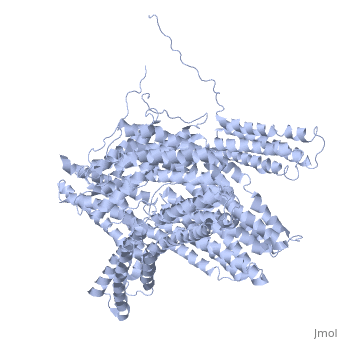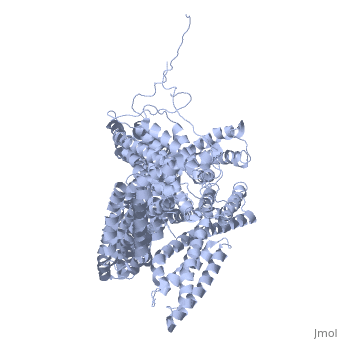
FunctionVinculins (VCLs) are involved in adhesion by linking integrin molecules to the actin cytoskeleton. Its head domain (Vd1) can bind to talin or to alpha-actinin at their respective VCL Binding Sites (VBS)[1]. The protein raver1 RNA Recognition Motif (RRM) forms a complex with VCL or m-VCL. Metavinculin (m-VCL) is a splice version of VCL containing an extra ca. 70 amino acids in the C-terminal domain. RelevanceLoss of VCL could be used as a prognostic factor for colorectal cancer se it promotes metastasis[2]. DiseaseMutation in m-VCL can yield cardiomyopathic phenotype[3]. Structural highlightsis achieved through a high affinity intramolecular interaction between tail (orange) and head (aqua) domains (1st6). Energetically, I997 is key to maintaining this autoinhibition. |
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of Vinculin3D Structures of Vinculin
Updated on 06-October-2018
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Palovuori R, Eskelinen S. Role of vinculin in the maintenance of cell-cell contacts in kidney epithelial MDBK cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;79(12):961-74. PMID:11152287 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1078/0171-9335-00120
- ↑ Li T, Guo H, Song Y, Zhao X, Shi Y, Lu Y, Hu S, Nie Y, Fan D, Wu K. Loss of vinculin and membrane-bound beta-catenin promotes metastasis and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 2014 Dec 11;13:263. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-263. PMID:25496021 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-13-263
- ↑ Vasile VC, Will ML, Ommen SR, Edwards WD, Olson TM, Ackerman MJ. Identification of a metavinculin missense mutation, R975W, associated with both hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy. Mol Genet Metab. 2006 Feb;87(2):169-74. Epub 2005 Oct 19. PMID:16236538 doi:S1096-7192(05)00258-1
- Created with the participation of Susan Craig.