Monooxygenase: Difference between revisions
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
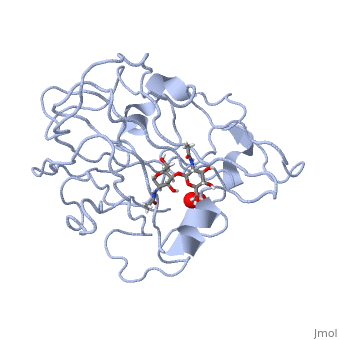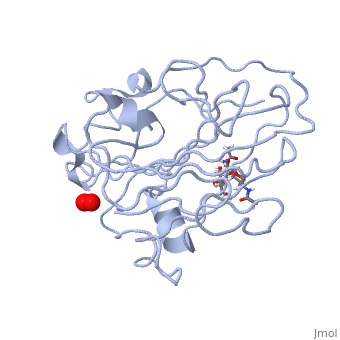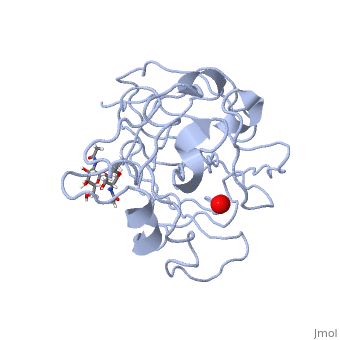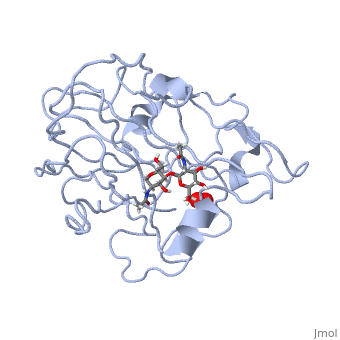
In recent years there has been a significant interest in describing the interactions of copper-containing enzymes with O<sub>2</sub>/H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>-derived species. The short-lived intermediates resulting from the activation of dioxygen are the key players in the mechanistic cycles in many metalloenzymes. In the enzyme <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/3'>peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM)</scene> various reduced Cu/oxygen species have been proposed to act as catalytically competent intermediates, yet their exact nature and their role in the enzymatic reaction is still unknown. | In recent years there has been a significant interest in describing the interactions of copper-containing enzymes with O<sub>2</sub>/H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>-derived species. The short-lived intermediates resulting from the activation of dioxygen are the key players in the mechanistic cycles in many metalloenzymes. In the enzyme <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/3'>peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM)</scene> various reduced Cu/oxygen species have been proposed to act as catalytically competent intermediates, yet their exact nature and their role in the enzymatic reaction is still unknown. | ||
Structural and other studies showed that peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) contains <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/4'>two non-equivalent copper sites (CuH and CuM)</scene>. CuM serves as an oxygen binding and hydrogen abstraction site, CuH is involved in electron transfer. In the structure of Cu(II)-PHM complexed with hydrogen peroxide determined to 1.98 Å resolution, <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/7'>(hydro)peroxide binds exclusively to CuM in a slightly asymmetric side-on mode</scene>. The <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/8'>interatomic O-O distance of the copper-bound ligand is 1.5, characteristic of peroxide/hydroperoxide species, and the copper-oxygen distances are 2.0 and 2.1</scene> Å. This Cu(II)-bound <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/9'>peroxo moiety interacts closely with a molecule of water</scene>, forming <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/10'>hydrogen bonds that stabilize the structure</scene>. DFT and QM/MM calculations indicate that this species is a Cu-bound doubly deprotonated peroxidate and that its energy is similar to that of its isomer Cu(I)-bound superoxide. | Structural and other studies showed that peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) contains <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/4'>two non-equivalent copper sites (CuH and CuM)</scene>. CuM serves as an oxygen binding and hydrogen abstraction site, CuH is involved in electron transfer. In the structure of Cu(II)-PHM complexed with hydrogen peroxide determined to 1.98 Å resolution, <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/7'>(hydro)peroxide binds exclusively to CuM in a slightly asymmetric side-on mode</scene>. The <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/8'>interatomic O-O distance of the copper-bound ligand is 1.5, characteristic of peroxide/hydroperoxide species, and the copper-oxygen distances are 2.0 and 2.1</scene> Å. This Cu(II)-bound <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/9'>peroxo moiety interacts closely with a molecule of water</scene>, forming <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/10'>hydrogen bonds that stabilize the structure</scene>. DFT and QM/MM calculations indicate that this species is a Cu-bound doubly deprotonated peroxidate and that its energy is similar to that of its isomer Cu(I)-bound superoxide. | ||
==3D structures of monooxygenase== | |||
[[Monooxygenase 3D structures]] | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 56: | Line 60: | ||
*'''Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO)''' | *'''Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO)''' | ||
**[[5x68]] – hKMO + FAD - human<br /> | |||
**[[4j2w]], [[4j31]], [[4j33]], [[4j34]] – yKMO + FAD – yeast<br /> | **[[4j2w]], [[4j31]], [[4j33]], [[4j34]] – yKMO + FAD – yeast<br /> | ||
**[[4j36]], [[5x64]] – yKMO + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | **[[4j36]], [[5x64]] – yKMO + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[5x6q]] – yKMO (mutant) + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | **[[5x6q]] – yKMO (mutant) + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[5na5]], [[5x6p]] – PfKMO (mutant) + FAD – ''Pseudomonas fluorescens''<br /> | **[[5na5]], [[5x6p]] – PfKMO (mutant) + FAD – ''Pseudomonas fluorescens''<br /> | ||
**[[5y7a]], [[5y77]] – PfKMO + FAD + kynurenine <br /> | **[[5y7a]], [[5y77]], [[6fox]] – PfKMO + FAD + kynurenine <br /> | ||
**[[5nak]] – PfKMO (mutant) + FAD + kynurenine <br /> | **[[5nak]] – PfKMO (mutant) + FAD + kynurenine <br /> | ||
**[[5y66]] – PfKMO + FAD + kynurenine + inhibitor<br /> | **[[5y66]] – PfKMO + FAD + kynurenine + inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[6fph]], [[6fp1]], [[6fp0]], [[6foz]], [[6foy]] – PfKMO + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | |||
**[[5nah]], [[5nag]], [[5nae]], [[5nab]], [[5n7t]], [[5mzk]], [[5mzi]], [[5mzc]], [[5fn0]] – PfKMO (mutant) + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | **[[5nah]], [[5nag]], [[5nae]], [[5nab]], [[5n7t]], [[5mzk]], [[5mzi]], [[5mzc]], [[5fn0]] – PfKMO (mutant) + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| Line 74: | Line 79: | ||
**[[5pah]], [[6pah]] – hFMO catalytic domain + inhibitor <br /> | **[[5pah]], [[6pah]] – hFMO catalytic domain + inhibitor <br /> | ||
*Phenylalanine 4-monooxygenase or phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase | |||
See [[Hydroxylase]] | |||
*'''ActVA-Orf6 monooxygenase (AOMO)''' | *'''ActVA-Orf6 monooxygenase (AOMO)''' | ||
| Line 81: | Line 90: | ||
**[[1n5s]], [[1n5t]] – ScAOMO + acetyl dithranol<br /> | **[[1n5s]], [[1n5t]] – ScAOMO + acetyl dithranol<br /> | ||
**[[1n5v]] – ScAOMO + nanaomycine <br /> | **[[1n5v]] – ScAOMO + nanaomycine <br /> | ||
*Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase (BVMO) | |||
**[[6jdk]] – BVMO – ''Parvibaculum lavamentivorans''<br /> | |||
*'''Flavin-containing monooxygenase''' | *'''Flavin-containing monooxygenase''' | ||
| Line 88: | Line 101: | ||
**[[4a9w]] – SmMO + FAD – ''Stenotrophomonas maltophilia''<br /> | **[[4a9w]] – SmMO + FAD – ''Stenotrophomonas maltophilia''<br /> | ||
**[[4c5o]] – SmMO (mutant) + FAD <br /> | **[[4c5o]] – SmMO (mutant) + FAD <br /> | ||
**[[5wan]] – | **[[5wan]] – EcMO + FMN + uracil – Escherichia coli<br /> | ||
**[[5iq4]], [[5iq1]], [[5ipy]] – RnMO (mutant) + FAD + NAP – ''Roseovarius nubinhibens'' <br /> | **[[5iq4]], [[5iq1]], [[5ipy]] – RnMO (mutant) + FAD + NAP – ''Roseovarius nubinhibens'' <br /> | ||
**[[5gsn]] – RnMO (mutant) + FAD + NAP + methimazole <br /> | **[[5gsn]] – RnMO (mutant) + FAD + NAP + methimazole <br /> | ||
| Line 153: | Line 166: | ||
**[[4q4k]] – PaMO + FMN <br /> | **[[4q4k]] – PaMO + FMN <br /> | ||
**[[6e2a]] – PaMO + FMN + NAD<br /> | |||
**[[5lsm]] – MO + FMN – ''Shewanella oneidensis''<br /> | **[[5lsm]] – MO + FMN – ''Shewanella oneidensis''<br /> | ||
**[[6bka]] – MO + FMN – ''Cyberlyndnera mrakii''<br /> | **[[6bka]] – MO + FMN – ''Cyberlyndnera mrakii''<br /> | ||
| Line 165: | Line 179: | ||
*4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-monooxygenase | *4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-monooxygenase | ||
**[[4ira]] – BmMO + FAD – Brucella melitensis<br /> | **[[4ira]] – BmMO + FAD – ''Brucella melitensis''<br /> | ||
**[[3cb0]] – BmMO + FMN<br /> | **[[3cb0]] – BmMO + FMN<br /> | ||
**[[6eb0]] – EcMO oxygenase subunit<br /> | |||
**[[6b1b]] – EcMO oxygenase subunit (mutant)<br /> | |||
*Ornithine N(5)-monooxygenase | *Ornithine N(5)-monooxygenase | ||
| Line 186: | Line 202: | ||
*Cyclohexanone monooxygenase | *Cyclohexanone monooxygenase | ||
**[[5m10]] – TmMO + FAD + NAP + nicotinamide – ''Thermocripsum municipale | **[[5m10]] – TmMO + FAD + NAP + nicotinamide – ''Thermocripsum municipale''<br /> | ||
**[[5m0z]] – TmMO + FAD + NADP derivative <br /> | **[[5m0z]] – TmMO + FAD + NADP derivative <br /> | ||
**[[4rg4]], [[4rg3]], [[3gwf]], [[3gwd]] – RhMO + FAD + NAP + caprolactone | **[[6gqi]] – TmMO + FAD + NADP + hexanic acid <br /> | ||
**[[6era]], [[6er9]] – RhMO + FAD + NADP – ''Rhodococcus''<br /> | |||
**[[4rg4]], [[4rg3]], [[3gwf]], [[3gwd]] – RhMO + FAD + NAP + caprolactone <br /> | |||
**[[3ucl]] – RhMO + FAD + NADP + cyclohexanone <br /> | **[[3ucl]] – RhMO + FAD + NADP + cyclohexanone <br /> | ||
| Line 228: | Line 246: | ||
**[[5mw0]], [[5wkw]] – rMO <br /> | **[[5mw0]], [[5wkw]] – rMO <br /> | ||
**[[1yjl]] – rMO (mutant)<br /> | |||
**[[3mib]], [[3mic]], [[3mid]], [[3mie]], [[3mif]], [[3mig]], [[3mih]], [[3mlj]], [[3mlk]], [[3mll]], [[1opm]] – rMO + Cu + Ni <br /> | **[[3mib]], [[3mic]], [[3mid]], [[3mie]], [[3mif]], [[3mig]], [[3mih]], [[3mlj]], [[3mlk]], [[3mll]], [[1opm]] – rMO + Cu + Ni <br /> | ||
**[[6ao6]], [[5wja]] – rMO (mutant) + Cu + Ni<br /> | |||
**[[1sdw]] – rMO + Cu + Ni + O2 + threonine derivative<br /> | **[[1sdw]] – rMO + Cu + Ni + O2 + threonine derivative<br /> | ||
**[[1yjk]], [[1yip]], [[1phm]] – rMO + Cu<br /> | **[[1yjk]], [[1yip]], [[1phm]] – rMO + Cu<br /> | ||
**[[1yi9]], [[6ay0]], [[6an3]], [[6amp]], [[6alv]], [[6ala]] – rMO (mutant) + Cu<br /> | **[[1yi9]], [[6ay0]], [[6an3]], [[6amp]], [[6alv]], [[6ala]] – rMO (mutant) + Cu<br /> | ||
**[[3fw0]] – rMO + Hg<br /> | **[[3fw0]] – rMO + Hg<br /> | ||
**[[3fvz]] – rMO + Zn + Fe<br /> | **[[3fvz]] – rMO + Zn + Fe<br /> | ||
| Line 249: | Line 267: | ||
**[[5f5l]] – MiMO – ''Micromonospora'' <br /> | **[[5f5l]] – MiMO – ''Micromonospora'' <br /> | ||
**[[5f5n]] – MiMO + NAD + substrate <br /> | **[[5f5n]] – MiMO + NAD + substrate <br /> | ||
*Monooxygenase TROPB | |||
**[[6nes]] – TsMO + FAD – ''Talaromyces stipitatus''<br /> | |||
**[[6nev]], [[6neu]] – TsMO (mutant) + FAD <br /> | |||
**[[6net]] – TsMO + FAD + dihydroxy dimethylbenzaldehyde<br /> | |||
*Lactate 2-monooxygenase or lactate oxydase | |||
**[[6dvi]] – MsLMO + FMN – ''Mycobacterium smegmatis''<br /> | |||
**[[6dvh]] – MsLMO (mutant) + FMN <br /> | |||
*Squalene monooxygenase or squalene epoxidase | |||
**[[6c6r]], [[6c6p]], [[6c6n]] – hSMO + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | |||
*Dimethyl-sulfide monooxygenase | |||
**[[6ak1]] – DMOA – ''Hyphomicrobium sulfonivorans''<br /> | |||
*Salicylate 1-monooxygenase or salicylate hydroxylase | |||
See [[Hydroxylase]] | |||
'''Methane monooxygenase''' See [[Methane monooxygenase]] | '''Methane monooxygenase''' See [[Methane monooxygenase]] | ||
Revision as of 14:10, 3 November 2019
FunctionMonooxygenases (MO) catalyzes the incorporation of a hydroxyl group into a variety of substrates. MO catalyzes the reduction of O2 to H2O while oxidating NADPH. Peptidylglycine α-Hydroxylating Monooxygenase (PHM)-coordination of peroxide to CuM center. Structural and computational study [1]In recent years there has been a significant interest in describing the interactions of copper-containing enzymes with O2/H2O2-derived species. The short-lived intermediates resulting from the activation of dioxygen are the key players in the mechanistic cycles in many metalloenzymes. In the enzyme various reduced Cu/oxygen species have been proposed to act as catalytically competent intermediates, yet their exact nature and their role in the enzymatic reaction is still unknown. Structural and other studies showed that peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) contains . CuM serves as an oxygen binding and hydrogen abstraction site, CuH is involved in electron transfer. In the structure of Cu(II)-PHM complexed with hydrogen peroxide determined to 1.98 Å resolution, . The Å. This Cu(II)-bound , forming . DFT and QM/MM calculations indicate that this species is a Cu-bound doubly deprotonated peroxidate and that its energy is similar to that of its isomer Cu(I)-bound superoxide. 3D structures of monooxygenase
|
| ||||||||||
3D structures of monooxygenase3D structures of monooxygenase
Updated on 03-November-2019
See Hydroxylase
- ActVA-Orf6 monooxygenase (AOMO)
- Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase (BVMO)
- 6jdk – BVMO – Parvibaculum lavamentivorans
- 6jdk – BVMO – Parvibaculum lavamentivorans
- Flavin-containing monooxygenase
- 2gv8 – fyMO + FAD + NADP – fission yeast
- 2gvc – fyMO + FAD + NADP + methimazole
- 4a9w – SmMO + FAD – Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
- 4c5o – SmMO (mutant) + FAD
- 5wan – EcMO + FMN + uracil – Escherichia coli
- 5iq4, 5iq1, 5ipy – RnMO (mutant) + FAD + NAP – Roseovarius nubinhibens
- 5gsn – RnMO (mutant) + FAD + NAP + methimazole
- 4usr – PsMO + FAD
- 3rp6 – KpMO + FAD – Klebsiella pneumoniae
- 3rp8 – KpMO (mutant) + FAD
- 3rp7 – KpMO + FAD + uric acid
- 3c96, 2rgj – PaMO + FAD – Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- 2xvf, 2xve – MaMO + FAD – Methylophaga aminisulfidivorans
- 2xvj – MaMO (mutant) + FAD + indole
- 2xvi – MaMO (mutant) + FAD + O2
- 2vqb – MaMO (mutant) + FAD + NADP + O2
- 2xvh, 2xlu, 2xlt – MaMO + FAD + NADP derivative
- 2xls, 2xlr, 2xlp, 2vq7 – MaMO (mutant) + FAD + NADP
- 5nmw – ZvMO + FAD – Zonocerus variegatus
- 5nmx – ZvMO + FAD + NADP
- 2gv8 – fyMO + FAD + NADP – fission yeast
- 2,4,6-trichlorophenol 4-monooxygenase
- 4g5e – MO – Cupriavidus necator
- 4g5e – MO – Cupriavidus necator
- Chlorophenol 4-monooxygenase
- Phenylacetone monooxygenase
- 6-hydroxynicotinate 3-monooxygenase
- 5eow – PpMO + FAD – Pseudomonas putida
- 5eow – PpMO + FAD – Pseudomonas putida
- Styrene monooxygenase
- Tryptophan 2-monooxygenase
- 4iv9 – MO + FAD – Pseudomonas savastanoi
- 4iv9 – MO + FAD – Pseudomonas savastanoi
- Tryptophan 5-monooxygenase
- 1mlw – hMO + Fe + dihydrobiopterin
- 1mlw – hMO + Fe + dihydrobiopterin
- Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase
- Nitronate monooxygenase
- 2-hydroxbiphenyl 3-monooxygenase
- 4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-monooxygenase
- Ornithine N(5)-monooxygenase
- 5cku – MO + FAD + NADP + ornithine – Neosartorya fumigata
- 4nzh, 4b69 – AfMO + FAD + ornithine – Aspergillus fumigatus
- 4b65 – AfMO + FAD + NADP
- 4b68, 4b66 – AfMO + FAD + NAP + arginine
- 4b67, 4b63 – AfMO + FAD + NADP + ornithine
- 4b64 – AfMO + FAD + NADP + lysine
- 3s61 – PaMO + FAD + NADP + ornithine derivative
- 5cku – MO + FAD + NADP + ornithine – Neosartorya fumigata
- Steroid monooxygenase
- Cyclohexanone monooxygenase
- Lysine 6-monooxygenase
- EDTA monooxygenase
- 5dqp – MO – Chelativorans
- 5dqp – MO – Chelativorans
- Rifampicin monooxygenase or Pentachlorophenol 4-monooxygenase
- 3,6-diketocamphane 1,6 monooxygenase
- Lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase
- 5tki, 5foh, 4qi8 – NcMO-2 + Cu – Neurospora crassa'Italic text
- 5tkh, 5tkg, 5tkf, 4eir – NcMO-2 + Cu + O2
- 4eis – NcMO-3 + Cu + peroxide
- 5iju – MO + Cu – Bacillus amyloliquefaciens
- 5acj, 5aci, 5ach, 5acg, 5acf – MO + Cu – Lentinus similis
- 4mai – moMO + Cu – mold
- 4mah – moMO + Zn
- 5no7 – MO – Pycnoporus cinnabarinus
- 5tki, 5foh, 4qi8 – NcMO-2 + Cu – Neurospora crassa'Italic text
- Peptidyl-glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase
- 5mw0, 5wkw – rMO
- 1yjl – rMO (mutant)
- 3mib, 3mic, 3mid, 3mie, 3mif, 3mig, 3mih, 3mlj, 3mlk, 3mll, 1opm – rMO + Cu + Ni
- 6ao6, 5wja – rMO (mutant) + Cu + Ni
- 1sdw – rMO + Cu + Ni + O2 + threonine derivative
- 1yjk, 1yip, 1phm – rMO + Cu
- 1yi9, 6ay0, 6an3, 6amp, 6alv, 6ala – rMO (mutant) + Cu
- 3fw0 – rMO + Hg
- 3fvz – rMO + Zn + Fe
- 5mw0, 5wkw – rMO
- Antibiotic biosynthesis monooxygenase
- Monooxygenase
- Monooxygenase TROPB
- Lactate 2-monooxygenase or lactate oxydase
- Squalene monooxygenase or squalene epoxidase
- Dimethyl-sulfide monooxygenase
- 6ak1 – DMOA – Hyphomicrobium sulfonivorans
- 6ak1 – DMOA – Hyphomicrobium sulfonivorans
- Salicylate 1-monooxygenase or salicylate hydroxylase
See Hydroxylase
Methane monooxygenase See Methane monooxygenase Camphor 5-monooxygenase See Cytochrome P450 Luciferin 4-monooxygenase and Alkanal monooxygenase See Luciferase
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Rudzka K, Moreno DM, Eipper B, Mains R, Estrin DA, Amzel LM. Coordination of peroxide to the Cu(M) center of peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM): structural and computational study. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2012 Dec 18. PMID:23247335 doi:10.1007/s00775-012-0967-z