Tumor necrosis factor receptor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
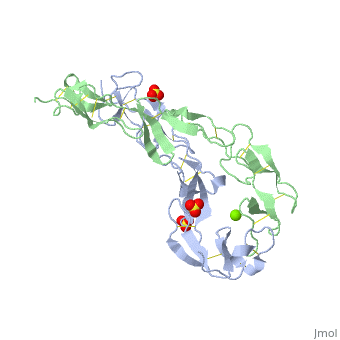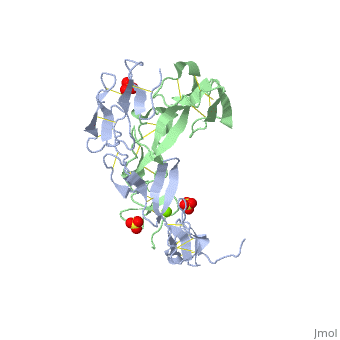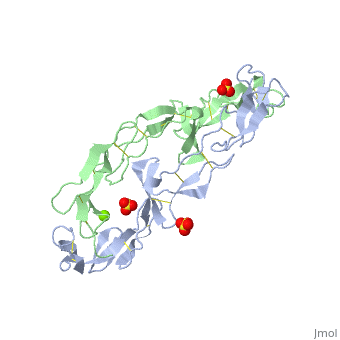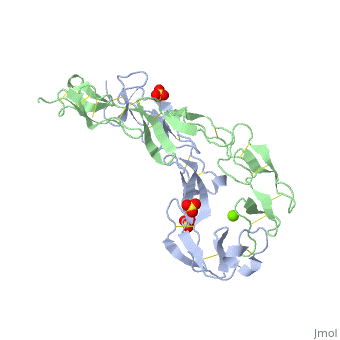
<StructureSection load=' | <StructureSection load='1ext' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human TNFR extracellular domain complex with sulfate and Mg+2 ion (green) (PDB code [[1ext]]).' scene='' pspeed='8'> | ||
__TOC__ | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Tumor necrosis factor receptor''' (TNFR) or '''death receptor''' is a trimeric cytokine receptor which binds TNF. TNFR family contains several members and superfamily (TNFRSF) members. | '''Tumor necrosis factor receptor''' (TNFR) or '''death receptor''' is a trimeric cytokine receptor which binds TNF<ref>PMID:10358762</ref>. TNFR family contains several members and superfamily ('''TNFRSF''') members. <br /> | ||
* '''TNFRSF 1''' is called '''Lymphotoxin-α or TNF-β'''<ref>PMID:20566898</ref>;<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 3''' is called '''TNFR-III''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 4''' is called '''OX40L receptor''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 5''' is called '''CD40L receptor''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 6''' is called '''Fas''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 9''' is called '''4-1BBL''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 10''' see [[TRAIL]];<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 10B''' is called '''Dr5''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 11A''' is called '''RANK''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 11B''' is called '''Osteoprotegerin''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 12''' is called '''TWEAK''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 12A''' is called '''TWEAKR''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 13B''' is called '''BAFF or sTALL-1''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 13C''' is called '''BAFF receptor''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 14''' is called '''LIGHT''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 16''' is called '''Low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor; p75NTR; p75 neurotrophin receptor''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 18''' is called '''GITRL''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 21''' is called '''Dr6''';<br /> | |||
* '''TNFRSF 25''' is called '''Dr3''';<br /> | |||
See also | |||
*[[Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily]] | |||
*[[Cytokine receptors]] | |||
*[[Receptor]] | |||
*[[Immune receptors]] | |||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
TRAPS - a condition characterized by recurrent episodes of fever is associated with TNFR<ref>PMID:24609716</ref>. | |||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
The extracellular domain of TNFR contains 2 to 6 cysteine-rich domains (CRD). The <scene name='59/590824/Cv/8'>CRD domains are ca. 40 amino-acid long and contain 4-6 cysteine residues</scene>. The CRDs are involved in binding of TNF<ref>PMID:8939750</ref>. <scene name='59/590824/Cv/9'>Mg coordination site</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | |||
==3D structures of tumor necrosis factor receptor== | ==3D structures of tumor necrosis factor receptor== | ||
[[Tumor necrosis factor receptor 3D structures]] | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 11:53, 20 August 2024
FunctionTumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) or death receptor is a trimeric cytokine receptor which binds TNF[1]. TNFR family contains several members and superfamily (TNFRSF) members.
See also RelevanceTRAPS - a condition characterized by recurrent episodes of fever is associated with TNFR[3]. Structural highlightsThe extracellular domain of TNFR contains 2 to 6 cysteine-rich domains (CRD). The . The CRDs are involved in binding of TNF[4]. . Water molecules are shown as red spheres. 3D structures of tumor necrosis factor receptorTumor necrosis factor receptor 3D structures
|
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Wallach D, Varfolomeev EE, Malinin NL, Goltsev YV, Kovalenko AV, Boldin MP. Tumor necrosis factor receptor and Fas signaling mechanisms. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:331-67. PMID:10358762 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.17.1.331
- ↑ Mounzer RH, Svendsen OS, Baluk P, Bergman CM, Padera TP, Wiig H, Jain RK, McDonald DM, Ruddle NH. Lymphotoxin-alpha contributes to lymphangiogenesis. Blood. 2010 Sep 23;116(12):2173-82. PMID:20566898 doi:10.1182/blood-2009-12-256065
- ↑ Lopalco G, Rigante D, Vitale A, Frediani B, Iannone F, Cantarini L. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome managed with the couple canakinumab-alendronate. Clin Rheumatol. 2015 Apr;34(4):807-9. doi: 10.1007/s10067-014-2556-8. Epub 2014, Mar 11. PMID:24609716 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2556-8
- ↑ Naismith JH, Devine TQ, Kohno T, Sprang SR. Structures of the extracellular domain of the type I tumor necrosis factor receptor. Structure. 1996 Nov 15;4(11):1251-62. PMID:8939750