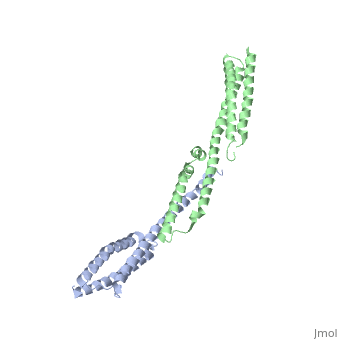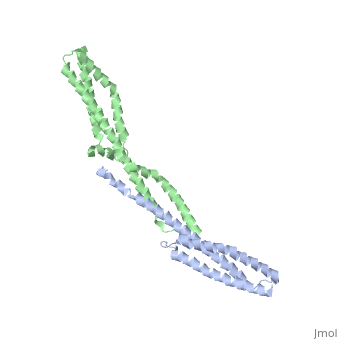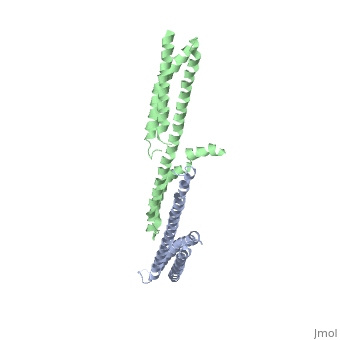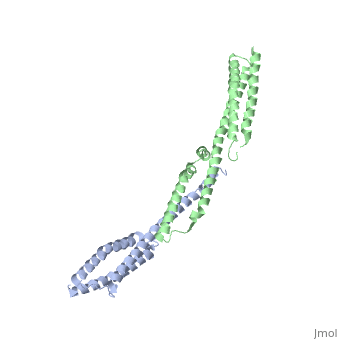
Spectrin
FunctionSpectrin forms scaffolding in plasma membranes and cytoskeletal structure. It interacts with actin at either end of its tetramer[1]. The SPT dimer is formed by association of α1 and β1 monomers. In invertebrates there are SPT α, β and βH. In vertebrates there are SPT α1 (SPTA1), α2 (SPTA2) and β1 (SPTB1) to β5. SPT contains an SRC Homology 3 domain (SH3), a Pleckstrin Homology (PH) domain and a Calponin Homology (CH) domain. DiseaseMutations in SPT α are found in patients with hereditary elliptocytosis[2]. SPT β deficiency is found in hereditary spherocytosis[3]. 3D Structures of Spectrin |
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of Spectrin3D Structures of Spectrin
Updated on 07-April-2022
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Das A, Base C, Dhulipala S, Dubreuil RR. Spectrin functions upstream of ankyrin in a spectrin cytoskeleton assembly pathway. J Cell Biol. 2006 Oct 23;175(2):325-35. PMID:17060500 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200602095
- ↑ Coetzer T, Palek J, Lawler J, Liu SC, Jarolim P, Lahav M, Prchal JT, Wang W, Alter BP, Schewitz G, et al.. Structural and functional heterogeneity of alpha spectrin mutations involving the spectrin heterodimer self-association site: relationships to hematologic expression of homozygous hereditary elliptocytosis and hereditary pyropoikilocytosis. Blood. 1990 Jun 1;75(11):2235-44. PMID:2346784
- ↑ Dhermy D, Galand C, Bournier O, Cynober T, Mechinaud F, Tchemia G, Garbarz M. Hereditary spherocytosis with spectrin deficiency related to null mutations of the beta-spectrin gene. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 1998 Jun;24(2):251-61. PMID:9714702 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/bcmd.1998.0190