1a32
RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN S15 FROM BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUSRIBOSOMAL PROTEIN S15 FROM BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS
Structural highlights
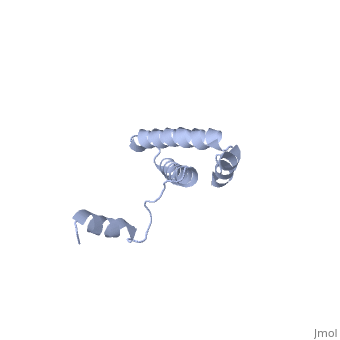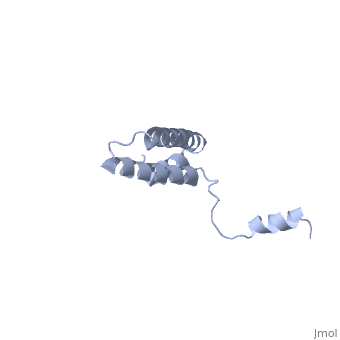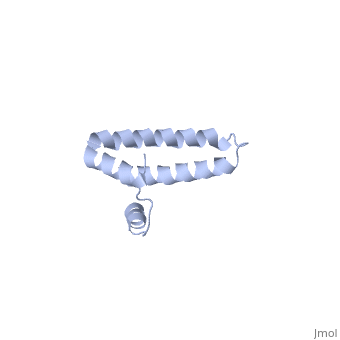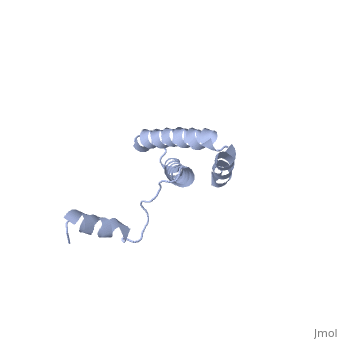
Function[RS15_GEOSE] One of the primary rRNA binding proteins, it binds directly to 16S rRNA where it helps nucleate assembly of the platform of the 30S subunit by binding and bridging several RNA helices of the 16S rRNA (By similarity).[HAMAP-Rule:MF_01343] Forms an intersubunit bridge (bridge B4) with the 23S rRNA of the 50S subunit in the ribosome (By similarity).[HAMAP-Rule:MF_01343] Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedBACKGROUND: Ribosomal protein S15 is a primary RNA-binding protein that binds to the central domain of 16S rRNA. S15 also regulates its own synthesis by binding to its own mRNA. The binding sites for S15 on both mRNA and rRNA have been narrowed down to less than a hundred nucleotides each, making the protein an attractive candidate for the study of protein-RNA interactions. RESULTS: The crystal structure of S15 from Bacillus stearothermophilus has been solved to 2.1 A resolution. The structure consists of four alpha helices. Three of these helices form the core of the protein, while the N-terminal helix protrudes out from the body of the molecule to make contacts with a neighboring molecule in the crystal lattice. S15 contains a large conserved patch of basic residues which could provide a site for binding 16S rRNA. CONCLUSIONS: The conformation of the N-terminal alpha helix is quite different from that reported in a recent NMR structure of S15 from Thermus thermophilus. The intermolecular contacts that this alpha helix makes with a neighboring molecule in the crystal, however, closely resemble the intramolecular contacts that occur in the NMR structure. This conformational variability of the N-terminal helix has implications for the range of possible S15-RNA interactions. A large, conserved basic patch at one end of S15 and a cluster of conserved but exposed aromatic residues at the other end provide two possible RNA-binding sites on S15. Conformational variability of the N-terminal helix in the structure of ribosomal protein S15.,Clemons WM Jr, Davies C, White SW, Ramakrishnan V Structure. 1998 Apr 15;6(4):429-38. PMID:9562554[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences |
| ||||||||||||||