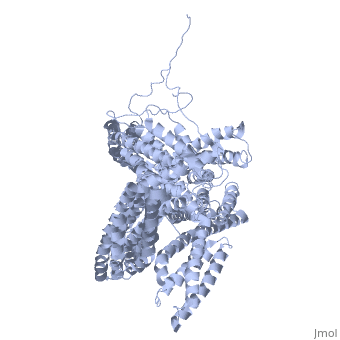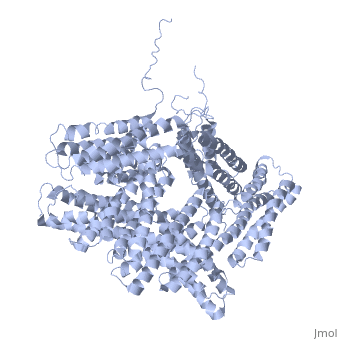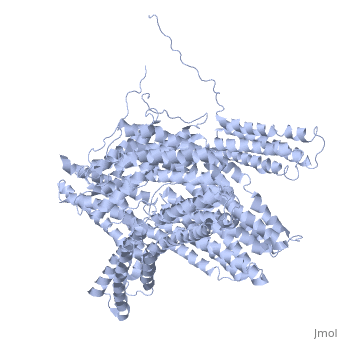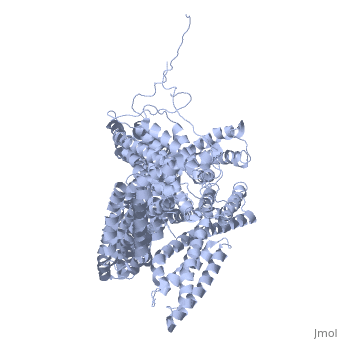
Vinculin
FunctionVinculins (VCLs) are involved in adhesion by linking integrin molecules to the actin cytoskeleton. Its head domain (Vd1) can bind to talin or to alpha-actinin at their respective VCL Binding Sites (VBS). A splice variant of vinculin is meta-vinculin (m-VCL). The protein raver1 RNA Recognition Motif (RRM) forms a complex with VCL or m-VCL. is achieved through a high affinity intramolecular interaction between tail (orange) and head (aqua) domains (1st6). Energetically, I997 is key to maintaining this autoinhibition. Metavinculin is a splice version of VCL containing an extra ca. 70 amino acids in the C-terminal domain. Structural highlightsis achieved through a high affinity intramolecular interaction between tail (orange) and head (aqua) domains (1st6). Energetically, I997 is key to maintaining this autoinhibition. |
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of Vinculin3D Structures of Vinculin
Updated on 13-December-2016
ReferencesReferences
- Created with the participation of Susan Craig.