1ihr
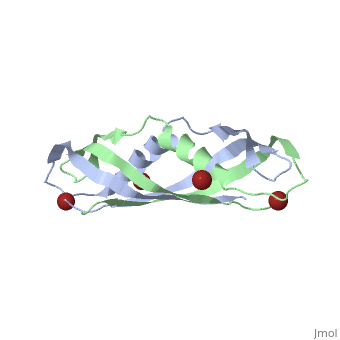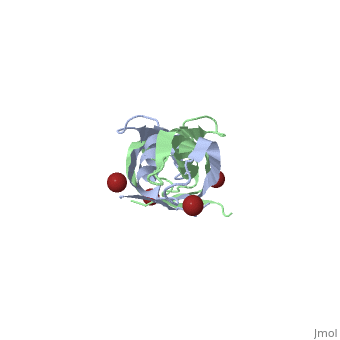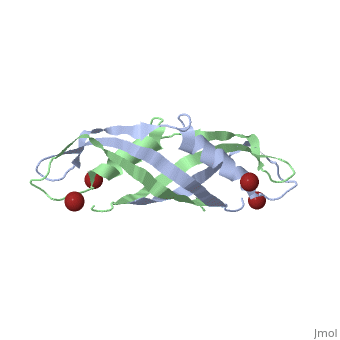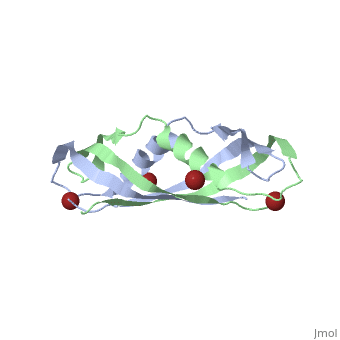
Crystal structure of the dimeric C-terminal domain of TonBCrystal structure of the dimeric C-terminal domain of TonB
Structural highlights
Function[TONB_ECOLI] Interacts with outer membrane receptor proteins that carry out high-affinity binding and energy dependent uptake into the periplasmic space of specific substrates such as cobalamin, and various iron compounds (such as iron dicitrate, enterochelin, aerobactin, etc.). In the absence of TonB these receptors bind their substrates but do not carry out active transport. TonB also interacts with some colicins and is involved in the energy-dependent, irreversible steps of bacteriophages phi 80 and T1 infection. It could act to transduce energy from the cytoplasmic membrane to specific energy-requiring processes in the outer membrane, resulting in the release into the periplasm of ligands bound by these outer membrane proteins. Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe TonB-dependent complex of Gram-negative bacteria couples the inner membrane proton motive force to the active transport of iron.siderophore and vitamin B(12) across the outer membrane. The structural basis of that process has not been described so far in full detail. The crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of TonB from Escherichia coli has now been solved by multiwavelength anomalous diffraction and refined at 1.55-A resolution, providing the first evidence that this region of TonB (residues 164-239) dimerizes. Moreover, the structure shows a novel architecture that has no structural homologs among any known proteins. The dimer of the C-terminal domain of TonB is cylinder-shaped with a length of 65 A and a diameter of 25 A. Each monomer contains three beta strands and a single alpha helix. The two monomers are intertwined with each other, and all six beta-strands of the dimer make a large antiparallel beta-sheet. We propose a plausible model of binding of TonB to FhuA and FepA, two TonB-dependent outer-membrane receptors. Crystal structure of the dimeric C-terminal domain of TonB reveals a novel fold.,Chang C, Mooser A, Pluckthun A, Wlodawer A J Biol Chem. 2001 Jul 20;276(29):27535-40. Epub 2001 Apr 27. PMID:11328822[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||