2hue
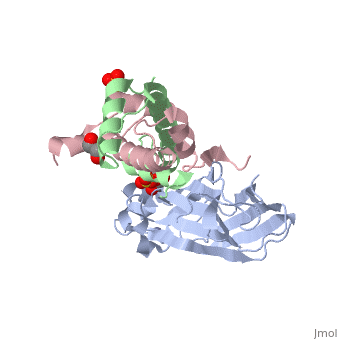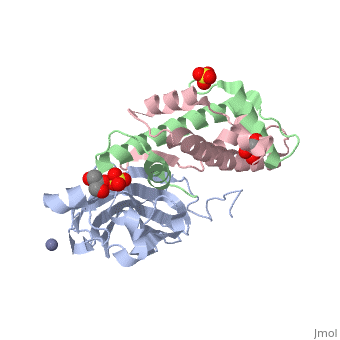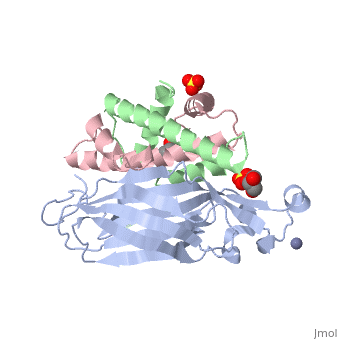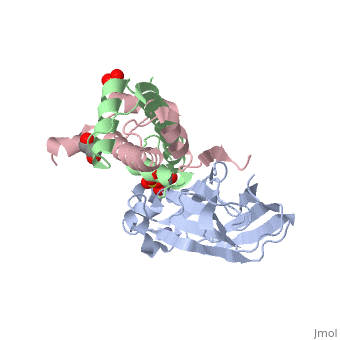
Structure of the H3-H4 chaperone Asf1 bound to histones H3 and H4Structure of the H3-H4 chaperone Asf1 bound to histones H3 and H4
Structural highlights
Evolutionary ConservationCheck, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedAnti-silencing function 1 (Asf1) is a highly conserved chaperone of histones H3/H4 that assembles or disassembles chromatin during transcription, replication, and repair. The structure of the globular domain of Asf1 bound to H3/H4 determined by X-ray crystallography to a resolution of 1.7 Angstroms shows how Asf1 binds the H3/H4 heterodimer, enveloping the C terminus of histone H3 and physically blocking formation of the H3/H4 heterotetramer. Unexpectedly, the C terminus of histone H4 that forms a mini-beta sheet with histone H2A in the nucleosome undergoes a major conformational change upon binding to Asf1 and adds a beta strand to the Asf1 beta sheet sandwich. Interactions with both H3 and H4 were required for Asf1 histone chaperone function in vivo and in vitro. The Asf1-H3/H4 structure suggests a "strand-capture" mechanism whereby the H4 tail acts as a lever to facilitate chromatin disassembly/assembly that may be used ubiquitously by histone chaperones. Structural basis for the histone chaperone activity of Asf1.,English CM, Adkins MW, Carson JJ, Churchill ME, Tyler JK Cell. 2006 Nov 3;127(3):495-508. PMID:17081973[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||