To get started:
- Click the edit this page tab at the top. Save the page after each step, then edit it again.
- Click the 3D button (when editing, above the wikitext box) to insert Jmol.
- show the Scene authoring tools, create a molecular scene, and save it. Copy the green link into the page.
- Add a description of your scene. Use the buttons above the wikitext box for bold, italics, links, headlines, etc.
More help: Help:Editing
For more help, look at this link:
http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Help:Getting_Started_in_Proteopedia
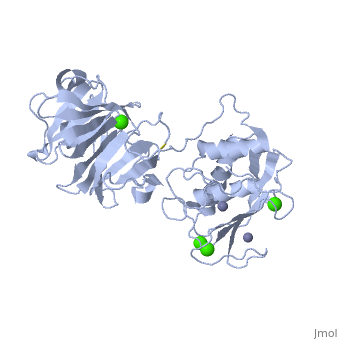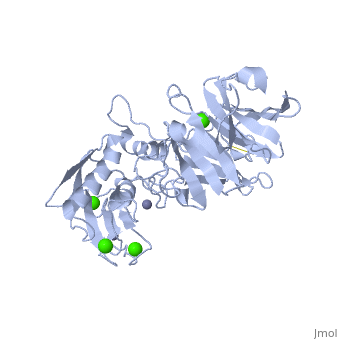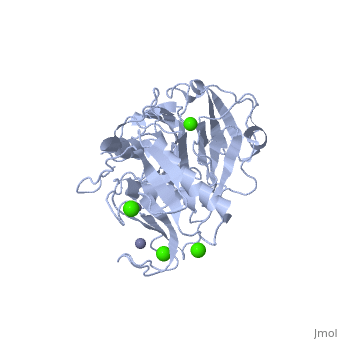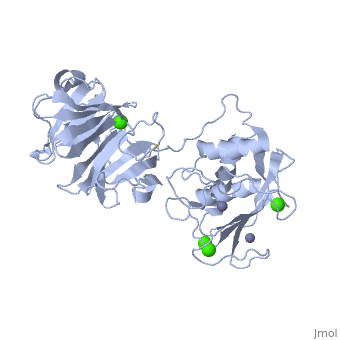
Matrix Metalloproteinase 1(MMP1) also known as Interstitial collagenase is a zinc-dependent protease that degrades extracellular matrix proteins. Collagenases are enzymes, which cleave bonds in collagen. MMP1 belongs to the Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP) family, which are involved in the regulation of cell-matrix composition by the breakdown of the extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes. These physiological processes many include disease activities such as arthritis and metastasis as well as normal human reproduction and embryonic development.
|
|
| 2clt, resolution 2.67Å ()
|
| Ligands:
|
,
|
| Activity:
|
Interstitial collagenase, with EC number 3.4.24.7
|
| Related:
|
1ayk, 1cge, 1cgf, 1cgl, 1hfc, 1su3, 2ayk, 2tcl, 3ayk, 4ayk, 966c
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Resources:
|
FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum
|
| Coordinates:
|
save as pdb, mmCIF, xml
|
StructureStructure
The Structure of MMP-1 and all other members of the Metalloproteinase family for that matter are formed from three domains. The structure comprises of the N-terminal catalytic domain, the linker region and the C-terminal hemopexin domain. The structure of human MMP-1 was determined with X-Ray Crystallography at a resolution of 2.67A to have two monomers (chains A and B). The catalytic domain of one monomer contacts the hemopexin domain of the other monomer. An interesting observation that has been noted is that the contact site used by the two monomers in the asymmetric unit to form the dimer is not the same as the dimerization site observed in the structure of the MMP-9 hemopexin domain. This difference shows that not all members of the Matrix Metalloproteinase family behave the same in their dimerization processes.
Catalytic DomainCatalytic Domain
klklm
lkm
lkm
Linker RegionLinker Region
asdflkafalkfna;lkdf
adfa
fa
fa
Hemopexin-like DomainHemopexin-like Domain
adlskflam
adfafdaf
afa
f
Mechanism of ActionMechanism of Action
sdfglkmsdfsd
fasdf
a
sdf
asf
ads
ff
Medical ImplicationsMedical Implications
lkmlml;kmlm
ReferencesReferences
|