Tom Sandbox

| |||||||
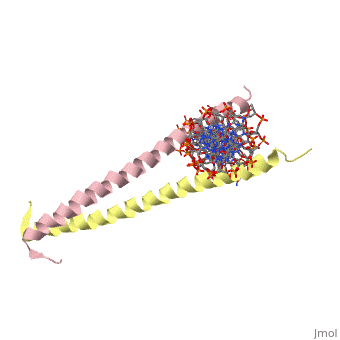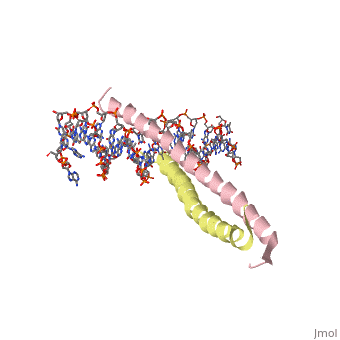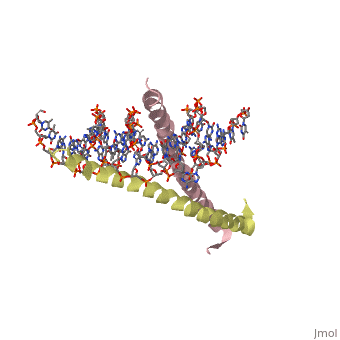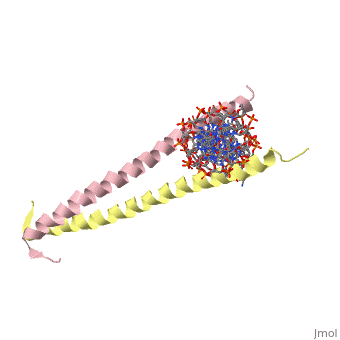
| 2zta, resolution 1.80Å () | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Standard Residues: | |||||||
| |||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
GCN4 - The Leucine ZipperGCN4 - The Leucine Zipper
Blah blah information about leucine zipper GCN4.
| |||||||||
| 1ysa, resolution 2.90Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
StructureStructure
GCN4 (PDB 2zta by itself, 1ysa bound to DNA) is a eukaryotic transcription factor first isolated from yeast. It is composed of two identical 52 residue alpha helix chains that grouped together to form a dimer. The dimer binds through interlocking leucine amino acids in the C terminal ends, while pinching in on the major groove of DNA in the N terminal end. The X-ray structure of the 33-residue polypeptide corresponding to the leucine zipper of GCN4 was determined by Peter Kim and Thomas Alber[1].
BindingBinding
The Leucine ZipperThe Leucine Zipper
Binding with DNABinding with DNA
FunctionFunction
See AlsoSee Also
ReferenceReference
- ↑ Voet, Donald; Voet, Judith G.; Pratt, Charlotte W. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. 3rd Ed. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2008.