5hz2
Crystal structure of PhaC1 from Ralstonia eutrophaCrystal structure of PhaC1 from Ralstonia eutropha
Structural highlights
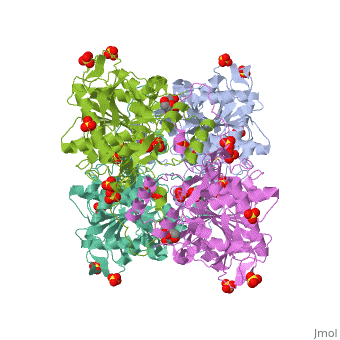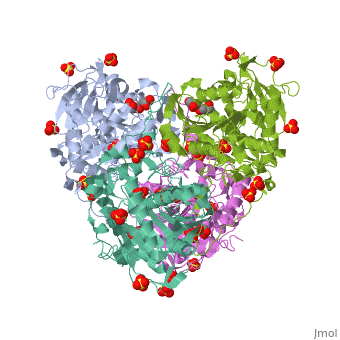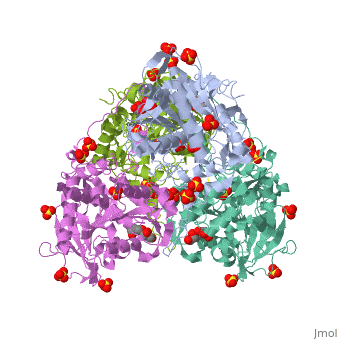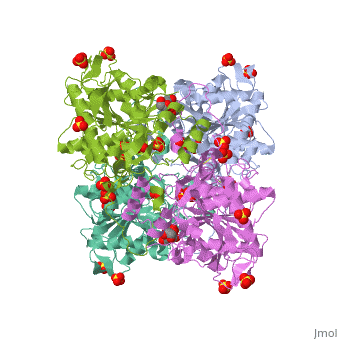
FunctionPHAC_CUPNH Polymerizes (R)-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA to create polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) which consists of thousands of hydroxybutyrate molecules linked end to end. PHB serves as an intracellular energy reserve material when cells grow under conditions of nutrient limitation.[1] Publication Abstract from PubMedPolyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) are natural polyesters synthesized by numerous microorganisms as energy and reducing power storage materials, and have attracted much attention as substitutes for petroleum-based plastics. Here, we report the first crystal structure of Ralstonia eutropha PHA synthase at 1.8 A resolution and structure-based mechanisms for PHA polymerization. RePhaC1 contains two distinct domains, the N-terminal (RePhaC1ND ) and C-terminal domains (RePhaC1CD ), and exists as a dimer. RePhaC1CD catalyzes polymerization via non-processive ping-pong mechanism using a Cys-His-Asp catalytic triad. Molecular docking simulation of 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA to the active site of RePhaC1CD reveals residues involved in the formation of 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA binding pocket and substrate binding tunnel. Comparative analysis with other polymerases elucidates how different classes of PHA synthases show different substrate specificities. Furthermore, we attempted structure-based protein engineering and developed a RePhaC1 mutant with enhanced PHA synthase activity. Crystal structure of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase C-terminal domain and reaction mechanisms.,Kim J, Kim YJ, Choi SY, Lee SY, Kim KJ Biotechnol J. 2016 Nov 3. doi: 10.1002/biot.201600648. PMID:27808482[2] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||