Complement C5
FunctionComplement C5 (CC5) is the fifth component of the complement system. The complement system is part of the innate immune system. CC5 is composed of α chain (C5a) and β chain (C5b). Proteoplytic degradation of CC5 produces anaphylatoxin which is a mediator of local inflammatory process. The C terminal domain of CC5 (residues 1530-1676) is homologous to a domain in netrins and is named C345C. Activation of CC5 by C5 convertase initiates the assembly of the C5 to C9 components into the membrane attack complex. [1] DiseaseMutations in CC5 cause a deficiency leading to severe recurrent infections and are linked to liver fibrosis, Leiner's disease and rheumatoid arthritis. |
| ||||||||||
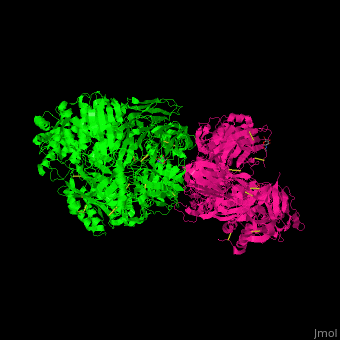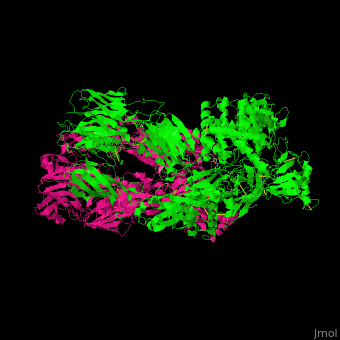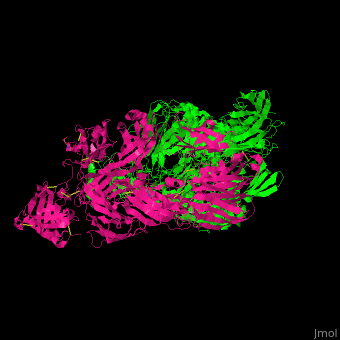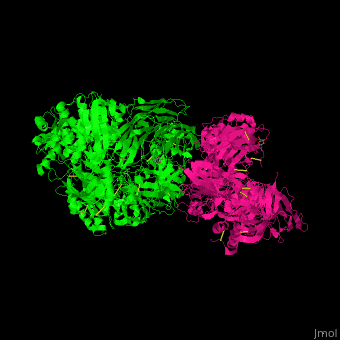
3D Structures of complement C53D Structures of complement C5
Updated on 20-December-2015
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Fredslund F, Laursen NS, Roversi P, Jenner L, Oliveira CL, Pedersen JS, Nunn MA, Lea SM, Discipio R, Sottrup-Jensen L, Andersen GR. Structure of and influence of a tick complement inhibitor on human complement component 5. Nat Immunol. 2008 Jul;9(7):753-60. Epub 2008 Jun 8. PMID:18536718 doi:10.1038/ni.1625