Stimulator of interferon genes: Difference between revisions
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
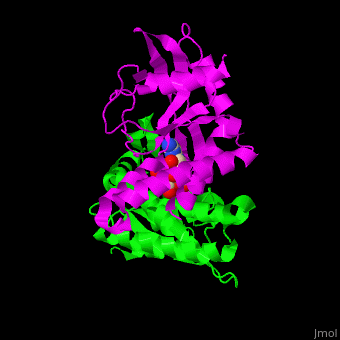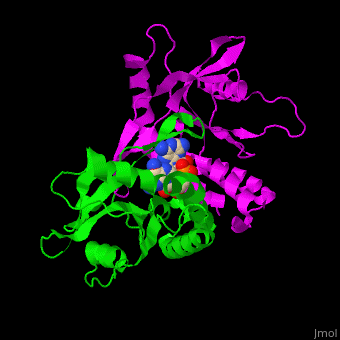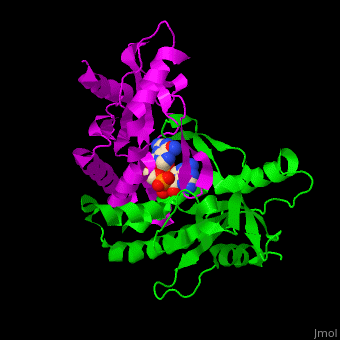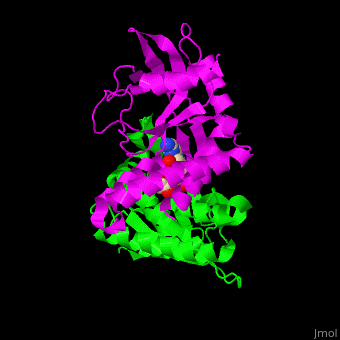
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human STING CTD complex with c-GMP-AMP (PDB entry [[4loh]])' scene='57/573101/Cv/1'> | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human STING CTD complex with c-GMP-AMP (PDB entry [[4loh]])' scene='57/573101/Cv/1'> | ||
'''Stimulator of interferon genes''' (STING) | == Function == | ||
'''Stimulator of interferon genes protein''' or '''transmembrane protein 173''' (STING) is an ER-associated membrane protein. STING signals immune responses in human and other animals. STING is activated by cyclic GMP-AMP produced by [[Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase]] whose activity is triggered by infections of DNA-containing pathogens<ref>PMID:30842659</ref>. A PLPLRT/SD conserved motif at the STING C-terminal plays a critical role in turning on the immune system to fight against viral infections<ref>PMID:31118511</ref>. | |||
== Disease == | |||
STING mutations are associated with autoimmune diseases<ref>PMID:26235147</ref>. | |||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
The | The 3D structure of the complex between human STING and cyclic GMP-AMP shows the dinucleotide bound by the symmetric dimer of STING. The U-shaped cleft between the 2 subunits makes numerous interactions with the U-shaped ligand. A Tyr residue from each monomer stacks against each of the purine moieties while an Arg residue from each monomer forms hydrogen bonds to the dinucleotide <ref>PMID:23910378</ref>. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of stimulator of interferon genes protein== | |||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | |||
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
*Stimulator of interferon genes protein; domains - C-di-GMP-binding 154-341; PLPLRT/SD motif 342-379 | |||
**[[6nt5]] – hSTING - human - Cryo EM<br /> | |||
**[[4ef5]], [[4f5w]], [[4f9e]] – hSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain<br /> | |||
**[[4f5e]], [[6mx0]] – hSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain (mutant)<br /> | |||
**[[6iyf]] – pSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain - pig<br /> | |||
**[[6nt5]] – hSTING | **[[4kc0]] – mSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain - mouse<br /> | ||
**[[4ef5]], [[4f5w]], [[4f9e]] – hSTING | **[[5gs5]] – rSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain - rat<br /> | ||
**[[4f5e]] – hSTING | **[[6nt6]] – cSTING - chicken - Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[ | **[[5cfo]], [[5cfr]] – aSTING – anemone<br /> | ||
**[[6nt6]] – cSTING | |||
**[[5cfo]], [[5cfr]] – | |||
*Stimulator of interferon genes complex | *Stimulator of interferon genes protein complex | ||
**[[4ef4]], [[4f5y]], [[4f9g]], [[ | **[[4ef4]], [[4emt]], [[4emu]], [[4f5y]], [[4f9g]], [[6rm0]], [[6s86]] – hSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + GMP derivative<br /> | ||
**[[4f5d]] – hSTING | **[[4f5d]] – hSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain (mutant) + GMP derivative <br /> | ||
**[[ | **[[6cff]], [[6cy7]] – hSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + AMP derivative <br /> | ||
**[[4ksy]], [[4loh]], [[5bqx]], [[6dnk]], [[6xnp]], [[6s26]], [[6s27]] – hSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + GMP-AMP derivative <br /> | |||
**[[4loh]], [[ | **[[4loi]], [[6mx3]], [[6mxe]] – hSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain (mutant) + GMP-AMP derivative <br /> | ||
**[[ | **[[6dxg]], [[6dxl]], [[6ukm]], [[6uku]], [[6ukv]], [[6ukw]], [[6ukx]], [[6uky]], [[6ukz]], [[6ul0]] – hSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + agonist <br /> | ||
**[[ | **[[4qxo]] – hSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + drug <br /> | ||
**[[4qxp]], [[4qxq]], [[4qxr]] – hSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain (mutant) + drug <br /> | |||
**[[5jej]] – hSTING PLPLRT/SD motif + IRF-3 CTD <br /> | |||
**[[ | **[[6o8b]], [[6o8c]] – hSTING PLPLRT/SD motif (mutant) + TBK1 <br /> | ||
**[[ | **[[6a03]], [[6a04]], [[6a05]], [[6a06]] – pSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + ligand <br /> | ||
**[[ | **[[4kby]] – mSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain+ GMP derivative<br /> | ||
**[[ | **[[4loj]], [[4lok]], [[4yp1]] – mSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + GMP-AMP derivative <br /> | ||
**[[ | **[[6xnn]] – mSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + GMP-AMP derivative <br /> | ||
**[[4kby]] – mSTING | **[[4lol]] – mSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + drug <br /> | ||
**[[4loj]], [[4lok]] – mSTING | **[[4jc5]] – mSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + immune activator <br /> | ||
**[[ | **[[5grm]] – rSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + GMP-AMP derivative <br /> | ||
**[[4lol]] – mSTING | **[[6nt7]], [[6nt8]] – cSTING + GMP-AMP derivative - Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[ | **[[6nt9]] – cSTING + TBK1 - Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[6nt7]], [[6nt8]] – cSTING + GMP-AMP | **[[5cfl]], [[5cfm]], [[5cfq]] – aSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + GMP derivative <br /> | ||
**[[6nt9]] – cSTING + TBK1 | **[[5cfp]] – aSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain (mutant) + GMP derivative<br /> | ||
**[[5cfl]] | **[[5cfn]] – aSTING C-di-GMP-binding domain + AMP derivative <br /> | ||
**[[ | |||
**[[5cfn]] – | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 14:22, 29 January 2021
FunctionStimulator of interferon genes protein or transmembrane protein 173 (STING) is an ER-associated membrane protein. STING signals immune responses in human and other animals. STING is activated by cyclic GMP-AMP produced by Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase whose activity is triggered by infections of DNA-containing pathogens[1]. A PLPLRT/SD conserved motif at the STING C-terminal plays a critical role in turning on the immune system to fight against viral infections[2]. DiseaseSTING mutations are associated with autoimmune diseases[3]. Structural highlightsThe 3D structure of the complex between human STING and cyclic GMP-AMP shows the dinucleotide bound by the symmetric dimer of STING. The U-shaped cleft between the 2 subunits makes numerous interactions with the U-shaped ligand. A Tyr residue from each monomer stacks against each of the purine moieties while an Arg residue from each monomer forms hydrogen bonds to the dinucleotide [4].
|
| ||||||||||
3D structures of stimulator of interferon genes protein3D structures of stimulator of interferon genes protein
Updated on 29-January-2021
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Shang G, Zhang C, Chen ZJ, Bai XC, Zhang X. Cryo-EM structures of STING reveal its mechanism of activation by cyclic GMP-AMP. Nature. 2019 Mar 6. pii: 10.1038/s41586-019-0998-5. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-019-0998-5. PMID:30842659 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0998-5
- ↑ Zhao B, Du F, Xu P, Shu C, Sankaran B, Bell SL, Liu M, Lei Y, Gao X, Fu X, Zhu F, Liu Y, Laganowsky A, Zheng X, Ji JY, West AP, Watson RO, Li P. A conserved PLPLRT/SD motif of STING mediates the recruitment and activation of TBK1. Nature. 2019 May;569(7758):718-722. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1228-x. Epub 2019 May, 22. PMID:31118511 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1228-x
- ↑ Dobbs N, Burnaevskiy N, Chen D, Gonugunta VK, Alto NM, Yan N. STING Activation by Translocation from the ER Is Associated with Infection and Autoinflammatory Disease. Cell Host Microbe. 2015 Aug 12;18(2):157-68. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.07.001., Epub 2015 Jul 30. PMID:26235147 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2015.07.001
- ↑ Gao P, Ascano M, Zillinger T, Wang W, Dai P, Serganov AA, Gaffney BL, Shuman S, Jones RA, Deng L, Hartmann G, Barchet W, Tuschl T, Patel DJ. Structure-Function Analysis of STING Activation by c[G(2',5')pA(3',5')p] and Targeting by Antiviral DMXAA. Cell. 2013 Aug 15;154(4):748-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.023. Epub 2013 Aug, 1. PMID:23910378 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.023