|
|
| Line 11: |
Line 11: |
| == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
|
| |
|
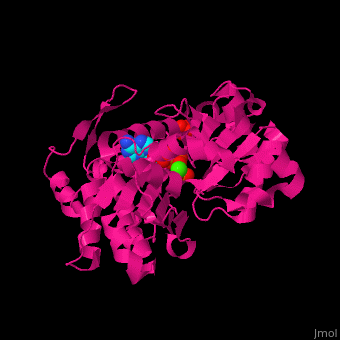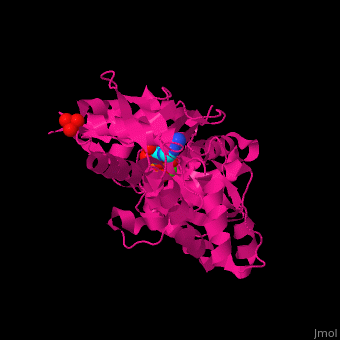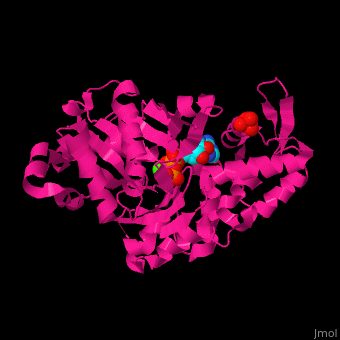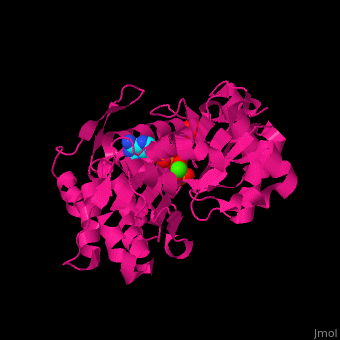
| <scene name='43/430015/Cv/10'>Actin binds ATP</scene> in a cleft. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='43/430015/Cv/11'>Click here to see Ca2+ ion coordination site</scene>.<ref>PMID:20540085</ref> It changes its conformation upon hydrolysis of its bound ATP to ADP. Actin filaments are polar. They are formed with all monomers having their clefts pointing in the same direction. | | <scene name='43/430015/Cv/10'>Actin binds ATP</scene> in a cleft. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='43/430015/Cv/13'>ATP and Ca2+ ion are located in cleft</scene>. <scene name='43/430015/Cv/11'>Click here to see Ca2+ ion coordination site</scene>.<ref>PMID:20540085</ref> It changes its conformation upon hydrolysis of its bound ATP to ADP. Actin filaments are polar. They are formed with all monomers having their clefts pointing in the same direction. |
| </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| == 3D Structures of Actin == | | == 3D Structures of Actin == |
Revision as of 13:35, 18 December 2018
FunctionActin is a protein found in all eukaryotic cells.[1] It is the monomer of two types of filaments: microfilaments which are part of the cytoskeleton and thin filaments which are part of muscles. Three isoforms of actin are identified: α (Aa) (or G-actin) found in muscle tissue, β (Ab) and γ (Ag) actins are components of the cytoskeleton. F-actin is Aa bound to ATP. For more details see:
*F-actin
*Non-polymerizable monomeric actin.
(PDB entries 1hlu and 2btf; morph was taken from Gallery of Morphs of the Yale Morph Server). Actin participates in muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis. Actin associated with myosin is responsible for most cell movements.
DiseaseMutations in α-actin found in skeletal striated muscles can cause myopathy. Mutations in α-actin found in smooth muscles can cause thoracic aortic aneurism. Mutations in α-actin found in heart muscles can cause heart malfunctioning.
Structural highlights in a cleft. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. . .[2] It changes its conformation upon hydrolysis of its bound ATP to ADP. Actin filaments are polar. They are formed with all monomers having their clefts pointing in the same direction.
| |
3D Structures of Actin3D Structures of Actin
Updated on 18-December-2018
{"openlevels":0}
- α actin 1 (Aa)
- 3hbt, 2zwh, 1nwk, 1j6z, 3g37, 2y83 – rAa – rabbit
- 2q1n, 2q31, 2a5x, 1rdw, 1rfq, 1lcu – rAa – dimer
- 3mfp, 4a7n, 3jbj, 6bnu – rAa + ADP – Cryo EM
- 2hmp – rAa – protease cleaved
- 2zwh, 2gwj, 2gwk – rAa-ATP
- 3j8i, 3j8j, 3j8k, 6bno, 6avb, 6av9, 5mvy, 5mva – rAa + ADP – Cryo EM
- 3b5u – rAa filament – fiber diffraction
- α actin 1 complex with gelsolin
- 1mdu – cAa+hGelsolin - chicken
- 2ff3 - rAa+ hGelsolin +domains of hWASP
- 1eqy, 3cjb, 1p8z, 3ffk, 3tu5, 4pkg, 4pkh, 4pki – rAa+hGelsolin
- 1rgi - rAa+hoGelsolin – horse (ho)
- 1t44 - rAa+hGelsolin/mThymosin β-4
- 4z94 - rAa+hGelsolin/tropomodulin/leiomodin
- 2ff6 - rAa+DmCiboulot+hGelsolin
- 4cbu, 5mvv – PfAa + gelsolin – Plasmodium falciparum
- 4cbw – PbAa + gelsolin – Plasmodium berghei
- α actin 1 complex with small molecule
- 2q36, 1qz5 – rAa+kabiramide C + ATP – dimer
- 2vyp – rAa+myxobacterial rhizopodin + ATP
- 1ijj - rAa+latrunculin A
- 2fxu – rAa+bistramide A
- 1wua – rAa+alpyronine A
- 2asm, 2asp – rAa+reidispongiolide
- 2aso – rAa+sphinxolide B
- 1yxq – rAa+swinholide A
- 4k41, 1qz6, 1s22, 4k42, 4k43 - rAa+ macrolide
- 1s22 – rAa+ulapualide A
- 1qz6 – rAa+jaspisamide A
- 3m6g – rAa+lobophorolide
- 5ogw – PfAa + jasplakinolide + ADP – Cryo EM
- α actin 1 complex with protein
- 2w49 – cAa +troponin C+ troponin T+ troponin I+ tropomyosin α-1
- 3j4k - cAa + tropomyosin
- 3j8a - mAa + tropomyosin - mouse
- 4a7f, 4a7h, 4a7l, 5h53, 5kg8 – rAa + tropomyosin α-1 + myosin heavy chain (mutant) – Cryo EM
- 5nol, 5noj, 5nog – Aa + tropomyosin alpha-1 + ADP – pig - Cryo EM
- 5jlf, 3j8a – rAa + tropomyosin alpha-1 + ADP – Cryo EM
- 6c1h, 6c1g, 6c1d - rAa + myosin + calmodulin
- 6bnv - rAa + myosin + calmodulin – Cryo EM
- 6bnw, 6bnp - rAa + myosin – Cryo EM
- 6bnq - rAa + myosin + ADP – Cryo EM
- 2v51, 2v52, 2yje, 2yjf – rAa+mMKL/Myocardin-like protein
- 2vcp – rAa+ neural wiskott-aldrich syndrome protein (hWASP) – human (h)
- 2a3z, 2a40, 2a41 – rAa+cDNase I+domains of hWASP – cow (c)
- 2a42 – rAa+cDNase I
- 4eah – rAa + formin-like protein 3 FH2 domain
- 3daw – rAa+mTwinfilin-1
- 3buz – rAa+Iota toxin component IA
- 4b1u, 4b1v, 4b1w, 4b1x, 4b1y, 4b1z – rAa + phosphatase and actin regulator
- 4pl8 - rAa+ Thymosin β-4
- 3u8x - rAa+DmThymosin β-4 - Drosophila melanogaster
- 1esv - rAa+hGelsolin+ latrunculin A
- 3cjc - rAa+hGelsolin+cDNase I
- 2d1k - rAa+hWH2 domain of MIN+cDNase I
- 2pbd – rAa+hProfilin-1
- 2pav - rAa+hProfilin-1+hVASP
- 2q97 – rAa+toxofilin – Toxoplasma gondii
- 2q0r – rAa+pectenotoxin-2
- 2q0u - rAa+pectenotoxin-2+latrunculin B
- 1y64 – rAa+yBNI1 domain FH2 - yeast
- 1sqk – rAa+DmCiboulot
- 3sjh, 3u9d, 3u9z - rAa+DmCiboulot thymosin β-4 domain
- 3mn5 – rAa+ DmSpire WH2 domain
- 1lot, 1kxp, 1ma9 – rAa+hVitamin D binding protein
- 3m1f – rAa+VOPL WH2 domain
- 3m3n – rAa+mN-WASP
- 3tpq – rAa + MAL RPEL domain
- 3ue5 – rAa + spire domain D
- 4gy2 – rAa + ι toxin component IA
- 3jbi – rAa + vinculin - CryoEM
- 3jbk – rAa + metavinculin + ADP - CryoEM
- 4wyb – rAa + BUD6
- 4v0u – rAa + protein phosphatase 1 +serine/threonine protein phosphatase
- 4h0t – rAa + ι toxin component IA + ADPR
- 4h03, 4h0v, 4h0x, 4h0y – rAa + ι toxin component IA + NAD
- 4jhd – DmAa + protein cordon-bleu WH2 domain
- 5i9e – yAa + actin-related protein 4 + helicase
- 5ce3, 4ci6 – Aa + protein kinase YopO – fall armyworm
- β actin (Ab)
- 3lue – hAb+hAlpha-actinin
- 3byh – hAb+hFimbrin ABD2 – Cryo EM
- 3j82 – hAb + DNGR-1 - CryoEM
- 6anu – hAb + spectrin – Cryo EM
- 2oan – cAb
- 3j0s – cAb + cofilin 2
- 3u4l, 3ub5 – Ab + profilin-1 - bovine
- 4cbx – PbAb + gelsolin
- γ 1 actin (Ag)
- 1atn – rAg+cDNase I
- 3chw – Major DdAg+hProfilin+poly-Pro repeat – Dictyostelium discoideum
- 3ci5, 3cip, 1nmd - Major DdAg+hGelsolin
- 3a5l, 3a5m, 3a5n, 3a5o - Major DdAg+hGelsolin (mutant)
- 1c0g, 1dej – DdAg:tetrahymenatA+hGelsolin
- 1nm1 - DdAg+hGelsolin+Mg-ATP
- 1nlv, 1c0f – DdAg+hGelsolin
- 1d4x – Ag 1/3+hGelsolin – C. elegans
- 1h1v – hAg+rGelsolin
- 5jlh – hAg + myosin-14 + tropomyosin alpha-3 – Cryo-EM
- 1hlu, 2btf – cAg+cProfilin
- 1o1g, 1o1a, 1o1b, 1o1c, 1o1d, 1o1e, 1o1f, 1o18, 1o19, 1mvw, 1m8q –cAg+cMyosin II - tomography
- 3eks – DmAg 5c (mutant)
- 3eku – DmAg 5c (mutant)+cytochalasin D
- 3el2, 2hf4 - DmAg 5c (mutant)+Ca-ATP
- 2hf3 - DmAg 5c (mutant)+Ca-ADP
- 3w3d – cAg + DNase I
- 3b63 – actin filament – Limulus polyphemus
- 1yvn – yA (mutant)+hGelsolin
- 1yag - yA+hGelsolin
- 3mmv – DmA-5C+spire WH2 domain
- 3mn6, 3mn7, 3mn9 - DmA-5C (mutant)+spire
- Actin 5C (A5C)
- 4rwt, 5wfn – DmA5C + leiomodin
- 4efh – A + spire domains C,D – Acanthamoeba castellanii
ReferenceReference
- ↑ Otterbein LR, Graceffa P, Dominguez R. The crystal structure of uncomplexed actin in the ADP state. Science. 2001 Jul 27;293(5530):708-11. PMID:11474115 doi:10.1126/science.1059700
- ↑ Wang H, Robinson RC, Burtnick LD. The structure of native G-actin. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2010 Jul;67(7):456-65. PMID:20540085 doi:10.1002/cm.20458