Transposase: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
**[[1muh]], [[1mus]], [[1mm8]], [[3ecp]], [[4dm0]] – EcTn5 (mutant) + DNA – ''Escherichia coli''<br /> | **[[1muh]], [[1mus]], [[1mm8]], [[3ecp]], [[4dm0]] – EcTn5 (mutant) + DNA – ''Escherichia coli''<br /> | ||
*Tn7 transposase | |||
**[[5d17]] – EcTn7 C terminal <br /> | |||
**[[5d16]] – EcTn7 C terminal (mutant) <br /> | |||
*Mos1 transposase | *Mos1 transposase | ||
**[[2f7t]] – DmMos1 catalytic domain (mutant) – ''Drosophila mauritiana''<br /> | **[[2f7t]] – DmMos1 catalytic domain (mutant) – ''Drosophila mauritiana''<br /> | ||
**[[4u7b]] – DmMos1 + DNA <br /> | **[[4u7b]], [[5hoo]] – DmMos1 + DNA <br /> | ||
**[[3hos]], [[3hot]], [[4r79]] – DmMos1 (mutant) + DNA <br /> | **[[3hos]], [[3hot]], [[4r79]] – DmMos1 (mutant) + DNA <br /> | ||
**[[4mda]], [[4mdb]] – DmMos1 catalytic domain (mutant) + drug<br /> | **[[4mda]], [[4mdb]] – DmMos1 catalytic domain (mutant) + drug<br /> | ||
| Line 59: | Line 64: | ||
**[[2a6m]] – HpOrfa – ''Helicobacter pylori''<br /> | **[[2a6m]] – HpOrfa – ''Helicobacter pylori''<br /> | ||
**[[2vhg]], [[2a6o]], [[2vic]], [[2vih]], [[2vju]], [[2vjv]] – HpOrfa + DNA <br /> | **[[2vhg]], [[2a6o]], [[2vic]], [[2vih]], [[2vju]], [[2vjv]] – HpOrfa + DNA <br /> | ||
*Sleeping beauty transposase | |||
**[[5cr4]] – SB catalytic domain – synthetic<br /> | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 13:25, 21 September 2016
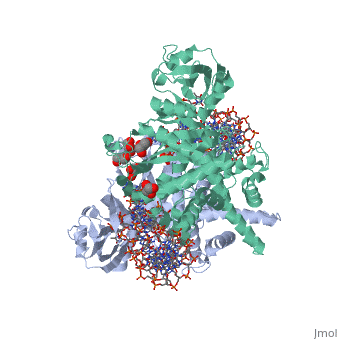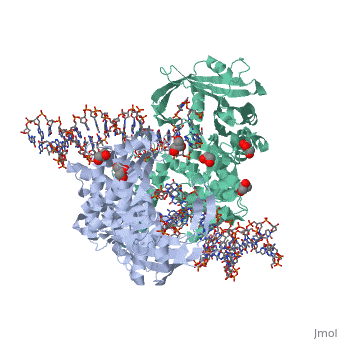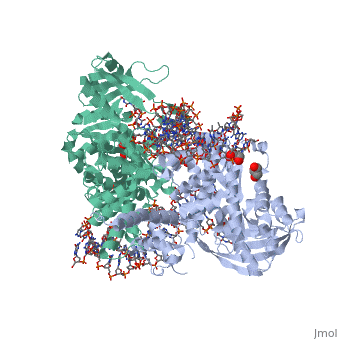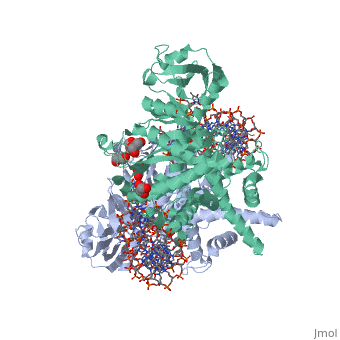
FunctionTransposases bind to the ends of a transposon and catalyze its movement to another part of the genome by a cut-and-paste mechanism[1].
Structural highlightsTransposase contains a DDE motif in its active site[8] enabling it to coordinate the binding of divalent metal ions. The metal ions affect transposase reactivity. The DDE motif is conserved in transposases and retroviral integrases and is essential for their activity. |
| ||||||||||
3D structures of transposase3D structures of transposase
Updated on 21-September-2016
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Ivics Z, Li MA, Mates L, Boeke JD, Nagy A, Bradley A, Izsvak Z. Transposon-mediated genome manipulation in vertebrates. Nat Methods. 2009 Jun;6(6):415-22. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1332. PMID:19478801 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1332
- ↑ Rice P, Mizuuchi K. Structure of the bacteriophage Mu transposase core: a common structural motif for DNA transposition and retroviral integration. Cell. 1995 Jul 28;82(2):209-20. PMID:7628012
- ↑ Park JM, Evertts AG, Levin HL. The Hermes transposon of Musca domestica and its use as a mutagen of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Methods. 2009 Nov;49(3):243-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2009.05.004. Epub 2009 May, 18. PMID:19450689 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2009.05.004
- ↑ Reznikoff WS. Transposon Tn5. Annu Rev Genet. 2008;42:269-86. PMID:18680433 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.42.110807.091656
- ↑ Wang W, Swevers L, Iatrou K. Mariner (Mos1) transposase and genomic integration of foreign gene sequences in Bombyx mori cells. Insect Mol Biol. 2000 Apr;9(2):145-55. PMID:10762422
- ↑ Colloms SD, van Luenen HG, Plasterk RH. DNA binding activities of the Caenorhabditis elegans Tc3 transposase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Dec 25;22(25):5548-54. PMID:7838706
- ↑ Ivics Z, Kaufman CD, Zayed H, Miskey C, Walisko O, Izsvak Z. The Sleeping Beauty transposable element: evolution, regulation and genetic applications. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2004 Jan;6(1):43-55. PMID:14632258
- ↑ Klenchin VA, Czyz A, Goryshin IY, Gradman R, Lovell S, Rayment I, Reznikoff WS. Phosphate coordination and movement of DNA in the Tn5 synaptic complex: role of the (R)YREK motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Oct;36(18):5855-62. Epub 2008 Sep 12. PMID:18790806 doi:10.1093/nar/gkn577