Amyloid precursor protein: Difference between revisions
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
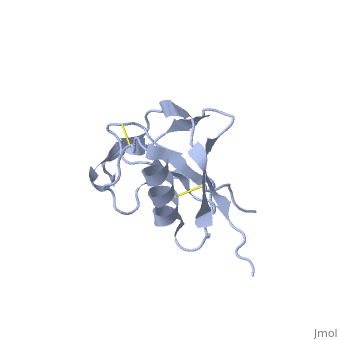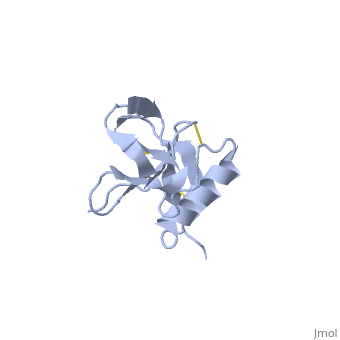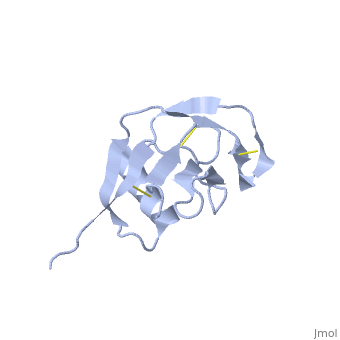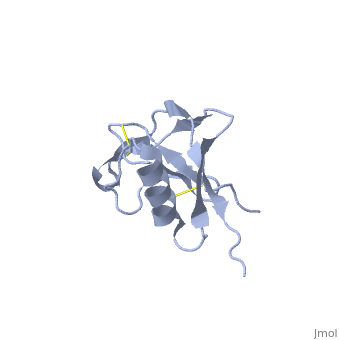
{{STRUCTURE_1mwp| PDB=1mwp | SIZE=400| SCENE= |right| CAPTION=Human amyloid precursor protein heparin-binding domain [[1mwp]] }} | |||
'''Amyloid precursor protein''' (APP) is thought to regulate transcription. APP is cleaved by β-secretase and the resulting N terminal peptide which is ca. 40 amino acid long is called hAPP β-peptide. | == Function == | ||
'''Amyloid precursor protein''' (APP) is a transmembranal protein which is thought to regulate transcription. APP plays a role in synaptic formation and repair. | |||
== Disease == | |||
APP is cleaved by β-secretase and the resulting N terminal peptide which is ca. 40 amino acid long is called hAPP β-peptide. The aggregation of the hAPP β-peptide is the cause of Alzheimer’s Disease. For detailed discussion see<br /> | |||
* [[Human APP]]<br /> | * [[Human APP]]<br /> | ||
* [[Human APP Intracellular Domain Complex with Fe65-PTB2]]<br /> | * [[Human APP Intracellular Domain Complex with Fe65-PTB2]]<br /> | ||
* [[Amyloid beta]]. | * [[Amyloid beta]]. | ||
== Structural highlights == | |||
The extracellular region of APP contains several domains named E1 (residues 1-189) and E2 (residues 346-551). The E1 domain contains a growth factor-like or heparin-binding (residues 28-123) and Cu-binding (residues 124-189) subdomains. Additional domains are: Kunitz-type protease inhibitor (residues 287-344) and Zn-binding (residues 672-687). The Z-binding domain is involved in the oligomerizatin of APP. | |||
==3D structures of amyloid precursor protein== | ==3D structures of amyloid precursor protein== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 30: | ||
**[[1rw6]] - hAPP residues 346-551<BR /> | **[[1rw6]] - hAPP residues 346-551<BR /> | ||
**[[1tkn]] - hAPP residues 460-569 - NMR<BR /> | **[[1tkn]] - hAPP residues 460-569 - NMR<BR /> | ||
**[[1mwp]] - hAPP heparin-binding domain<br /> | **[[1mwp]] - hAPP heparin-binding domain<br /> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 36: | ||
**[[1z0q]], [[2beg]] – hAPP β-peptide residues 1-42 – NMR<br /> | **[[1z0q]], [[2beg]] – hAPP β-peptide residues 1-42 – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1amb]], [[1amc]] – hAPP β-peptide residues 1-28 – NMR<br /> | **[[1amb]], [[1amc]] – hAPP β-peptide residues 1-28 – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1qcm]], [[ | **[[1qcm]], [[1qyt]], [[1qwp]], [[1qxc]] – hAPP β-peptide residues 25-35 – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1ba4]], [[1ba6]], [[2lnq]] – hAPP β-peptide residues 1-40 – NMR<br /> | **[[1ba4]], [[1ba6]], [[2lnq]] – hAPP β-peptide residues 1-40 – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1bjb]], [[1bjc]] – hAPP β-peptide residues 1-28 (mutant) – NMR<br /> | **[[1bjb]], [[1bjc]] – hAPP β-peptide residues 1-28 (mutant) – NMR<br /> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 49: | ||
**[[1ze9]] - hAPP zinc-binding domain + Zn – NMR<BR /> | **[[1ze9]] - hAPP zinc-binding domain + Zn – NMR<BR /> | ||
**[[2fk1]], [[2fk2]], [[2fk3]], [[2fkl]] - hAPP residues 133-189 + Cu<BR /> | **[[2fk1]], [[2fk2]], [[2fk3]], [[2fkl]] - hAPP residues 133-189 + Cu<BR /> | ||
**[[3jti]], [[3gci]] – hAPP peptide + phospholipase A2<BR /> | **[[3jti]], [[3gci]] – hAPP peptide residues 699-706 + phospholipase A2<BR /> | ||
**[[3l81]] - hAPP peptide + AP-4 complex subunit μ-1<BR /> | **[[3l81]] - hAPP peptide residues 761-767 + AP-4 complex subunit μ-1<BR /> | ||
**[[3ifl]], [[3ifn]], [[3ifo]], [[3ifp]], [[2r0w]] - hAPP peptide + antibody<BR /> | **[[3ifl]], [[3ifn]], [[3ifo]], [[3ifp]], [[2r0w]] - hAPP peptide residues 672-711 + antibody<BR /> | ||
**[[2wk3]] - hAPP residues | **[[2wk3]] - hAPP residues 672-713 + insulin degrading enzyme<BR /> | ||
**[[3dxc]] - hAPP residues 739-770 + Fe65-PTB2<BR /> | **[[3dxc]] - hAPP residues 739-770 + Fe65-PTB2<BR /> | ||
**[[3dxd]], [[3dxe]] - hAPP residues 739-770 (mutant) + Fe65-PTB2<BR /> | **[[3dxd]], [[3dxe]] - hAPP residues 739-770 (mutant) + Fe65-PTB2<BR /> | ||
**[[2roz]] - hAPP peptide + Fe65 C terminal<BR /> | **[[2roz]] - hAPP peptide residues 582-704 + Fe65 C terminal<BR /> | ||
**[[2otk]] - hAPP residues 672-711 + ZAB3 affibody dimer - NMR<BR /> | **[[2otk]] - hAPP residues 672-711 + ZAB3 affibody dimer - NMR<BR /> | ||
**[[3l3t]] - hAPP residues 211-267 + mesotrypsin<br /> | **[[3l3t]] - hAPP residues 211-267 + mesotrypsin<br /> | ||
Revision as of 14:04, 1 November 2015
| |||||||||
| Human amyloid precursor protein heparin-binding domain 1mwp | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
FunctionFunction
Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is a transmembranal protein which is thought to regulate transcription. APP plays a role in synaptic formation and repair.
DiseaseDisease
APP is cleaved by β-secretase and the resulting N terminal peptide which is ca. 40 amino acid long is called hAPP β-peptide. The aggregation of the hAPP β-peptide is the cause of Alzheimer’s Disease. For detailed discussion see
Structural highlightsStructural highlights
The extracellular region of APP contains several domains named E1 (residues 1-189) and E2 (residues 346-551). The E1 domain contains a growth factor-like or heparin-binding (residues 28-123) and Cu-binding (residues 124-189) subdomains. Additional domains are: Kunitz-type protease inhibitor (residues 287-344) and Zn-binding (residues 672-687). The Z-binding domain is involved in the oligomerizatin of APP.
3D structures of amyloid precursor protein3D structures of amyloid precursor protein
Updated on 01-November-2015