1eqq: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1eqq]] is a 6 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli Escherichia coli]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1EQQ OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1EQQ FirstGlance]. <br> | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1eqq]] is a 6 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli Escherichia coli]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1EQQ OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1EQQ FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
</td></tr><tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Non-Standard_Residue|NonStd Res:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=5MU:5-METHYLURIDINE+5-MONOPHOSPHATE'>5MU</scene></td></tr> | </td></tr><tr id='NonStdRes'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Non-Standard_Residue|NonStd Res:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=5MU:5-METHYLURIDINE+5-MONOPHOSPHATE'>5MU</scene></td></tr> | ||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1qvc|1qvc]]</td></tr> | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1qvc|1qvc]]</td></tr> | ||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1eqq FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1eqq OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1eqq RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1eqq PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1eqq FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1eqq OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1eqq RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1eqq PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | ||
<table> | </table> | ||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: Escherichia coli]] | [[Category: Escherichia coli]] | ||
[[Category: Matsumoto, T | [[Category: Matsumoto, T]] | ||
[[Category: Morimoto, Y | [[Category: Morimoto, Y]] | ||
[[Category: Shibata, N | [[Category: Shibata, N]] | ||
[[Category: Shimamoto, N | [[Category: Shimamoto, N]] | ||
[[Category: Yasuoka, N | [[Category: Yasuoka, N]] | ||
[[Category: Beta barrel]] | [[Category: Beta barrel]] | ||
[[Category: Protein-dna complex]] | [[Category: Protein-dna complex]] | ||
[[Category: Replication-rna complex]] | [[Category: Replication-rna complex]] | ||
Revision as of 02:04, 23 December 2014
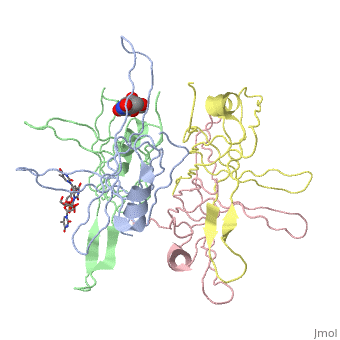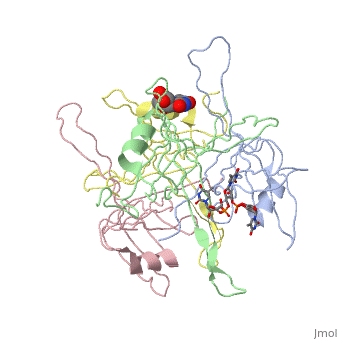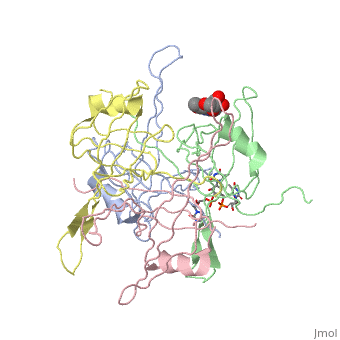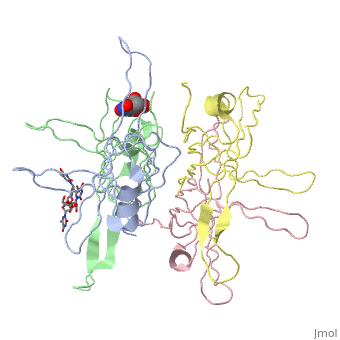
SINGLE STRANDED DNA BINDING PROTEIN AND SSDNA COMPLEXSINGLE STRANDED DNA BINDING PROTEIN AND SSDNA COMPLEX
Structural highlights
Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) binding protein from Escherichia coli (EcoSSB) plays a central role in DNA replication, recombination and repair. The tertiary structure of EcoSSB was determined at 2.2 A resolution. This is rather higher resolution than previously reported. Crystals were grown from the homogeneous intact protein but the EcoSSB tetramer in the crystals contains truncated subunits lacking a part of the C-terminal. The structure determined includes biologically important flexible loops and C-terminal regions, and revealed the existence of concavities. These concavities include the residues important for ssDNA binding. An ssDNA can be fitted on the concavities and further stabilized through interactions with the loops forming flexible lids. It seems likely to play a central role in the binding of ssDNA. Roles of functional loops and the C-terminal segment of a single-stranded DNA binding protein elucidated by X-Ray structure analysis.,Matsumoto T, Morimoto Y, Shibata N, Kinebuchi T, Shimamoto N, Tsukihara T, Yasuoka N J Biochem. 2000 Feb;127(2):329-35. PMID:10731701[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences |
| ||||||||||||||||||