2a9i: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image: | ==Molecular Structure of the Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase-4 Death Domain== | ||
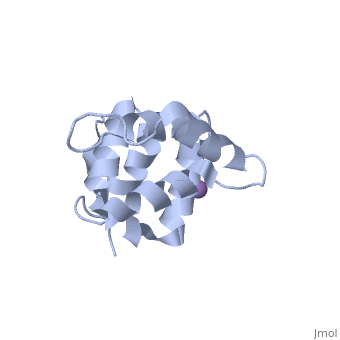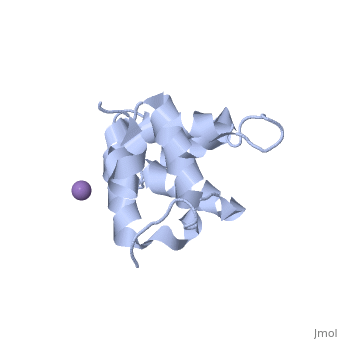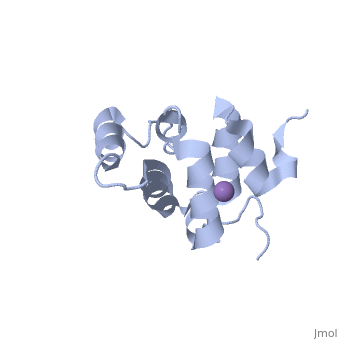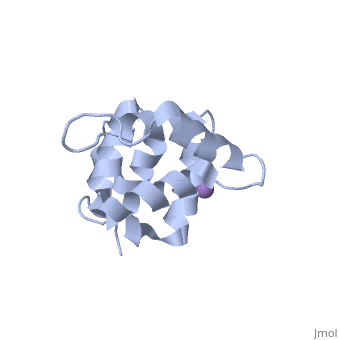
<StructureSection load='2a9i' size='340' side='right' caption='[[2a9i]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 1.70Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2a9i]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mus_musculus Mus musculus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2A9I OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2A9I FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=MN:MANGANESE+(II)+ION'>MN</scene><br> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">Irak4 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=10090 Mus musculus])</td></tr> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-specific_serine/threonine_protein_kinase Non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=2.7.11.1 2.7.11.1] </span></td></tr> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2a9i FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2a9i OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2a9i RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2a9i PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | |||
<table> | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/a9/2a9i_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/chain_selection.php?pdb_ID=2ata ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
IL-1R-associated kinase (IRAK) 4 is an essential component of innate immunity. IRAK-4 deficiency in mice and humans results in severe impairment of IL-1 and TLR signaling. We have solved the crystal structure for the death domain of Mus musculus IRAK-4 to 1.7 A resolution. This is the first glimpse of the structural details of a mammalian IRAK family member. The crystal structure reveals a six-helical bundle with a prominent loop, which among IRAKs and Pelle, a Drosophila homologue, is unique to IRAK-4. This highly structured loop contained between helices two and three, comprises an 11-aa stretch. Although innate immune domain recognition is thought to be very similar between Drosophila and mammals, this structural component points to a drastic difference. This structure can be used as a framework for future mutation and deletion studies and potential drug design. | |||
Cutting edge: molecular structure of the IL-1R-associated kinase-4 death domain and its implications for TLR signaling.,Lasker MV, Gajjar MM, Nair SK J Immunol. 2005 Oct 1;175(7):4175-9. PMID:16177054<ref>PMID:16177054</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4|Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4]] | *[[Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4|Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4]] | ||
== References == | |||
== | <references/> | ||
< | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Mus musculus]] | [[Category: Mus musculus]] | ||
[[Category: Non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase]] | [[Category: Non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase]] | ||
Revision as of 07:47, 29 September 2014
Molecular Structure of the Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase-4 Death DomainMolecular Structure of the Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase-4 Death Domain
Structural highlights
Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedIL-1R-associated kinase (IRAK) 4 is an essential component of innate immunity. IRAK-4 deficiency in mice and humans results in severe impairment of IL-1 and TLR signaling. We have solved the crystal structure for the death domain of Mus musculus IRAK-4 to 1.7 A resolution. This is the first glimpse of the structural details of a mammalian IRAK family member. The crystal structure reveals a six-helical bundle with a prominent loop, which among IRAKs and Pelle, a Drosophila homologue, is unique to IRAK-4. This highly structured loop contained between helices two and three, comprises an 11-aa stretch. Although innate immune domain recognition is thought to be very similar between Drosophila and mammals, this structural component points to a drastic difference. This structure can be used as a framework for future mutation and deletion studies and potential drug design. Cutting edge: molecular structure of the IL-1R-associated kinase-4 death domain and its implications for TLR signaling.,Lasker MV, Gajjar MM, Nair SK J Immunol. 2005 Oct 1;175(7):4175-9. PMID:16177054[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences |
| ||||||||||||||||||||