Thrombin: Difference between revisions
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
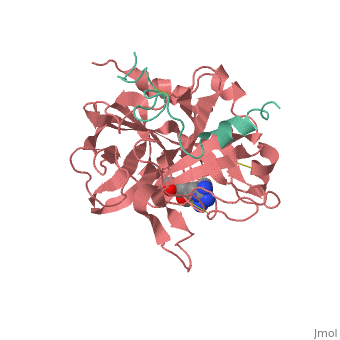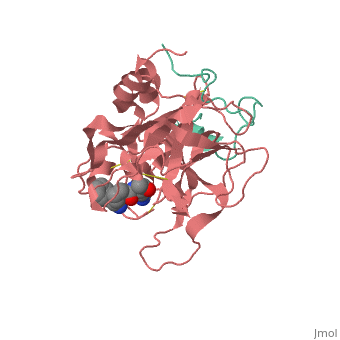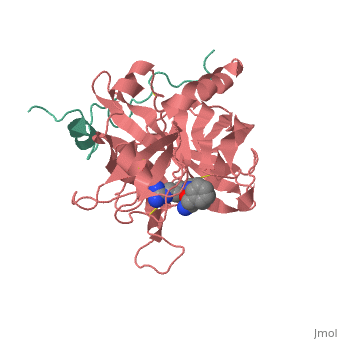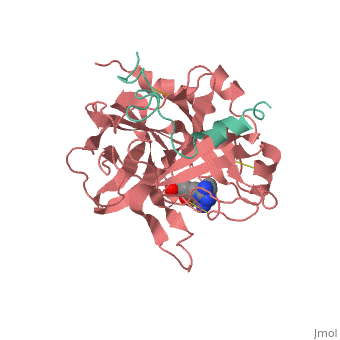
<StructureSection load='1ppb' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Human thrombin large (red) and small (aqua) subunits complex with prolinamide derivative (PDB code [[1ppb]])'> | <StructureSection load='1ppb' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Human thrombin large (red) and small (aqua) subunits complex with prolinamide derivative (PDB code [[1ppb]])'> | ||
'''Thrombin''' (Thr) is a serine protease. '''Prothrombin''' (PThr) is cleaved to form Thr in the coagulation cascade. The first step of the cleavage is at residue R320 and produces '''meizothrombin''' (MThr). Thr catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to the insoluble fibrin. Thr is composed of heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC). Prethrombin-1 lacks 155 N-terminal residues of PThr and is composed of a single polypeptide chain. '''Prethrombin-2''' is the product of proteolysis of '''prethrombin-1''' by trypsin or by active factor X. P-PACK Thr is a chemicaly modified Thr with inactivated catalytic site and active anion binding site. Hirudin is the most potent natural inhibitor of Thr ([[Sean Swale/Human Thrombin Inhibitor]]). For some more details see [[Serine Proteases]]. Prothrombin cleavage results in the creation of thrombin, a coagulative agent in plasma and is connected to fibrinolysis and platelet activation. During this process several peptides involved in the conversion are released into the plasma, and the remaining protein splits into two portions(http://www.uniprot.org/citations/3759958). It has been shown that prothrombin has a statistically significant connection to the occurrence of ischemic stroke with the presence of the G20210A mutation, though the cause was not isolated to prothrombin alone (http://www.uniprot.org/citations/15534175) (these links added by Connor Gramazio). | '''Thrombin''' (Thr) is a serine protease. '''Prothrombin''' (PThr) is cleaved to form Thr in the coagulation cascade. The first step of the cleavage is at residue R320 and produces '''meizothrombin''' (MThr). Thr catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to the insoluble fibrin. Thr is composed of heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC). Prethrombin-1 lacks 155 N-terminal residues of PThr and is composed of a single polypeptide chain. '''Prethrombin-2''' is the product of proteolysis of '''prethrombin-1''' by trypsin or by active factor X. P-PACK Thr is a chemicaly modified Thr with inactivated catalytic site and active anion binding site. Hirudin is the most potent natural inhibitor of Thr ([[Sean Swale/Human Thrombin Inhibitor]]). For some more details see [[Serine Proteases]]. Prothrombin cleavage results in the creation of thrombin, a coagulative agent in plasma and is connected to fibrinolysis and platelet activation. During this process several peptides involved in the conversion are released into the plasma, and the remaining protein splits into two portions(http://www.uniprot.org/citations/3759958). It has been shown that prothrombin has a statistically significant connection to the occurrence of ischemic stroke with the presence of the G20210A mutation, though the cause was not isolated to prothrombin alone (http://www.uniprot.org/citations/15534175) (these links added by Connor Gramazio). Some additional details in [[Ann Taylor 115]]. | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
Revision as of 13:30, 21 January 2014
Thrombin (Thr) is a serine protease. Prothrombin (PThr) is cleaved to form Thr in the coagulation cascade. The first step of the cleavage is at residue R320 and produces meizothrombin (MThr). Thr catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to the insoluble fibrin. Thr is composed of heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC). Prethrombin-1 lacks 155 N-terminal residues of PThr and is composed of a single polypeptide chain. Prethrombin-2 is the product of proteolysis of prethrombin-1 by trypsin or by active factor X. P-PACK Thr is a chemicaly modified Thr with inactivated catalytic site and active anion binding site. Hirudin is the most potent natural inhibitor of Thr (Sean Swale/Human Thrombin Inhibitor). For some more details see Serine Proteases. Prothrombin cleavage results in the creation of thrombin, a coagulative agent in plasma and is connected to fibrinolysis and platelet activation. During this process several peptides involved in the conversion are released into the plasma, and the remaining protein splits into two portions(http://www.uniprot.org/citations/3759958). It has been shown that prothrombin has a statistically significant connection to the occurrence of ischemic stroke with the presence of the G20210A mutation, though the cause was not isolated to prothrombin alone (http://www.uniprot.org/citations/15534175) (these links added by Connor Gramazio). Some additional details in Ann Taylor 115. StructureThrombin is a "trypsin-like" serine protease. Its structure (PDB code 1ppb) is shown here with a peptide chloroketone inhibitor (PPACK). The thrombin A chain (cleaved N terminal fragement) is shown in cyan and the B chain is shown in red. The is made up of a catalytic triad of Ser195, His57 and Asp102, backed up by Ser214. The peptide chloroketone inhibitor (PPACK) is shown in purple. A closeup shows the at which the sidechain of Asp194 makes a salt link with the N-terminus at residue 16, newly formed when the A chain is cleaved in the zymogen-to-enzyme activation process. The specificity pocket is on one side of the throat of the domain 2 beta barrel, and the activation site is close next to it. The B chain consists of . As is true for all of the "trypsin-like" serine proteases, each of the two thrombin domains consists mainly of a 6-stranded, antiparallel beta barrel. The specificity pocket (here filled with the Lys sidechain of the PPACK inhibitor) is in one side of the throat of the domain 2beta barrel, and the activation site is close next to it. |
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of thrombin3D Structures of thrombin
Updated on 21-January-2014
ThrombinThrombin
3pmb - bThr HC + LC – bovine
3qgn - hThr HC (mutant) + LC – human
3r3g - hThr HC + LC
2hnt– hThr-γ HC + LC
3jz1, 3jz2, 2od3 - hThr HC + LC (mutant)
3gic - hThr HC + LC
3ee0, 2a0q, 1sg8, 1sgi, 1jou - hThr HC (mutant) + LC
3edx, 3hk3, 3hk6 - mThr HC (mutant) + LC – mouse
2ocv - mThr HC + LC
Thrombin complexesThrombin complexes
3pma – bThr HC + LC residues 336-364 + sucrose octasulfate
1dlk - bThr HC + LC + peptide inhibitor
3hki - mThr HC (mutant) + LC + proteinase-activated receptor 1 peptide
3hkj - hThr HC (mutant) + LC + proteinase-activated receptor 1 peptide
2pux - mThr HC + LC + proteinase-activated receptor 3 peptide
2pv9 - mThr HC (mutant) + LC + proteinase-activated receptor 4 peptide
1dm4 - mThr HC (mutant) + LC + fibrinogen peptide
1ycp, 1bbr – bThr-ε HC + LC + fibrinogen peptide
1ucy - bThr HC + LC + fibrinogen peptide
1fph - hThr HC + LC + fibrinogen peptide
3bv9 - hThr HC (mutant) + LC + peptide inhibitor
2a2x, 1eb1, 1h8i, 1h8d, 1dit, 1hbt, 3u8t - hThr HC + LC + peptide inhibitor
1g37, 1eoj, 1eol, 1nrn, 1nro, 1nrp, 1nrq, 1nrr, 1nrs - hThr HC + peptide inhibitor
1hlt - hThr HC + LC + thrombomodulin peptide
2ank - hThr HC + LC + peptide + inhibitor
1bhx, 1abj, 1ppb - hThr HC + LC + inhibitor
1uvs, 1uvt, 1uvu - bThr HC + LC + inhibitor
1etr, 1ets, 1ett – bThr-ε HC + LC + inhibitor
3dd2 - hThr HC + LC + RNA
1hao, 1hap, 1hut - hThr HC + LC + DNA
3bf6 - hThr HC + LC + suramin
1xmn - hThr HC + LC + heparin
2h9t - hThr HC + LC + suramin + PPACK
1z8i, 1z8j - hThr HC + LC (mutant) + PPACK
1sfq, 1shh, 2thf, 1thp, 1b7x - hThr HC (mutant) + LC + PPACK
1ook - hThr HC + LC + PPACK
2hpp, 2hpq - hThr HC + LC + PThr residues 214-292 + PPACK
Thrombin complexes containing hirudinThrombin complexes containing hirudin
3c27, 2zc9, 2zda, 2zdv, 3egk, 2r2m, 2v3h, 2v3o, 2pks, 3eq0, 3dt0, 3dux, 3da9, 3dhk, 2znk, 2zo3, 3d49, 2zhe, 2zhf, 2zhw, 2zg0, 2zfq, 2zfr, 2zhq, 2zi2, 2ziq, 2zff, 2zfp, 2zgb, 2zgx, 2zf0, 3biu, 3biv, 2uuj, 2uuk, 2jh0, 2jh5, 2jh6, 2gde, 2bxt, 2bxu, 2bvr, 2bvs, 2bvx, 2bdy, 2feq, 2c8w, 2c8x, 2c8y, 2c8z, 2c90, 2c93, 2cf8, 2cf9, 2anm, 2w7g, 2fes, 1ype, 1ypg, 1ypj, 1ypk, 1ypl, 1ypm, 1vzq, 1way, 1wbg, 1riw, 1mu6, 1mu8, 1mue, 1nzq, 1o0d, 1oyt, 1o2g, 1gj4, 1gj5, 1kts, 1ktt, 1ghv, 1ghw, 1ghx, 1ghy, 1c5n, 1c5o, 1c4y, 1d3d, 1d3p, 1d3q, 1d3t, 1c4u, 1c4v, 1c1u, 1c1v, 1c1w, 1qj1, 1qj6, 1qj7, 1qhr, 1qur, 1d4p, 1ba8, 1bb0, 1ca8, 1awf, 1awh, 1bcu, 1a61, 1a3b, 1a3e, 1a46, 1a5g, 1b5g, 1tbz, 1a4w, 1ay6, 1ae8, 1afe, 1ad8, 1ai8, 1aix, 1bmm, 1bmn, 1lhc, 1lhd, 1lhe, 1lhf, 1lhg, 1uma, 1aht, 1fpc, 1w7g, 3ldx, 3p17, 3qto, 3qtv, 3qwc, 3qx5, 3rlw, 3rly, 3rm0, 3rm2, 3rml, 3rmm, 3rmn, 3rmo, 3t5f, 3sv2, 3si3, 3si4, 3sha, 3shc, 3u98, 3u9a, 3uwj, 4e7r - hThr HC + LC + hirudin peptide + inhibitor
1zgi, 1zgv, 1zrb, 1z71, 1xm1, 1sl3, 1ta2, 1ta6, 1nm6, 1nt1, 1doj, 1d9i, 1d6w, 1qbv, 1tmu, 1dwb, 1dwc, 1dwd, 1dwe, 4baq, 4bao, 4ban, 4bak, 4bam, 4bah- hThr HC + hirudin peptide + inhibitor
1ny2, 8kme, 7kme, 1a2c, 1tom, 1hdt, 1tmt, 1tmb, 3u8o, 3u8r - hThr HC + LC + hirudin peptide + peptide inhibitor
3hat - hThr HC + LC + hirudin peptide + fibrinogen peptide
2uuf, 2pw8, 1no9, 1c5l, 1vr1, 4thn, 5gds, 1hxf, 1hxe, 1abi, 1hgt, 1ihs, 1iht, 1thr, 1ths, 2hgt, 3utu, 4ayv, 4ayy, 4az2 - hThr HC + LC + hirudin peptide
1vit - bThr HC + LC + hirudin peptide
Thrombin complex with proteinThrombin complex with protein
2a45 - hThr HC + LC + fibrinogen α, β, γ chains
2a1d, 1nu7 – bThr HC + LC + staphylocoagulase
1tb6 - hThr HC + LC (mutant) + antithrombin
2b5t - hThr HC (mutant) + LC + antithrombin III (mutant)
4dt7 - hThr HC (mutant) + LC + vitamin K-dependent protein C peptide
1jmo - hThr HC (mutant) + LC + heparin cofactor II
1e0f - hThr HC + LC + haemadin
1dx5 - hThr HC + LC + thrombomodulin
3p6z, 3p70 - hThr HC + LC + coagulation factor V
1de7 - hThr HC + LC + factor XIII activation peptide
3pmh - hThr HC + LC + platelet glycoprotein IB α chain
3b23 - hThr HC + LC + variegin
1avg - bThr HC + LC + triabin
1bth - bThr HC (mutant) + LC (mutant) + BPTI
1toc - bThr HC + LC + ornithodorin
1tbq, 1tbr - bThr HC + LC + rhodniin
1hrt - bThr HC + LC + hirudin
3htc, 4htc - hThr HC + LC + hirudin
ProthrombinProthrombin
3e6p, 2afq, 3u69 - hPThr HC + LC
3s7h, 3s7k– hPThr HC + LC (mutant)
3bei, 2pgb, 2gp9, 1tq0, 1rd3, 4hzh, 4h6t, 4h6s - hPThr HC (mutant) + LC
1mh0 - hPThr HC (mutant)
1nl1, 1nl2, 2spt, 2pf1, 2pf2 – bPThr residues 1-156
Prothrombin complexesProthrombin complexes
3qdz – hPThr HC (mutant) + LC + proteinase-activated receptor 4 peptide
3lu9, 3bef - hPThr HC + LC (mutant) + proteinase-activated receptor 1 peptide
1sr5 - hPThr HC + LC + antithrombin III
3k65 - hPThr HC residues 315-622 (mutant) + LC residues 199-314
3f68 - hPThr HC residues 364-622 + LC residues 328-363 + hirudin peptide
1jwt, 3c1k - hPThr HC + inhibitor
4hfy, 4hfp - hPThr HC (mutant) + LC + inhibitor
2pgq, 1tq7 - hPThr HC (mutant) + LC + PPACK
2cn0, 1t4u, 1t4v, 1sb1, 1k21, 1k22, 1g30, 1g32, 1o5g, 3tu7 - hPThr HC + LC + hirudin peptide + inhibitor
1twx - hPThr HC (mutant) + LC + hirudin peptide
2hwl - hPThr HC (mutant) + LC + fibrinogen γ’ peptide
Prothrombin complex with proteinProthrombin complex with protein
1id5 - hPThr HC + LC + ecotin
1p8v - hPThr HC + LC + platelet glycoprotein IB α chain
3gis - hPThr HC residues 364-622 (mutant) + LC residues 315-363 + thrombomodulin
3b9f - hPThr HC (mutant) + LC + protein C inhibitor
2ody - hPThr HC + LC + boophilin
Prethrombin-1Prethrombin-1
3nxp - hThr residues 199-622
Prethrombin-2Prethrombin-2
1nu9 – hThr + staphylocoagulase
1mkw, 1mkx – hThr + bThr HC + LC
1hag, 1hah – hThr + hirudin peptide
1hai – hThr + inhibitor
3sqe, 3sqh - hThr (mutant)
MeizothrombinMeizothrombin
1a0h - bMThr