Tom Sandbox: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
[[2zta]] is composed of two identical 52 residue alpha helix chains that grouped together to form a dimer. The dimer binds through interlocking leucine amino acids in the C terminal ends, while pinching in on the major groove of DNA in the N terminal end. | |||
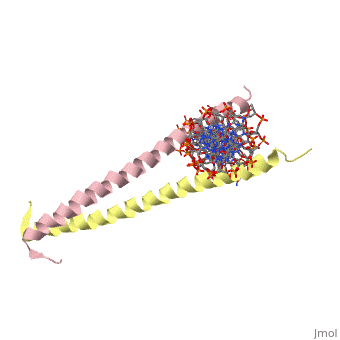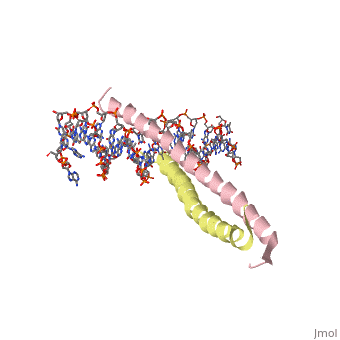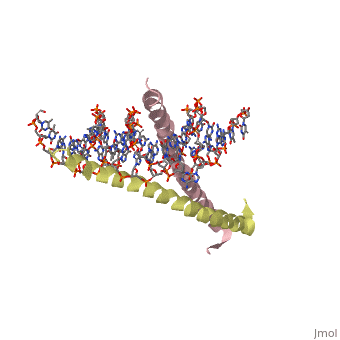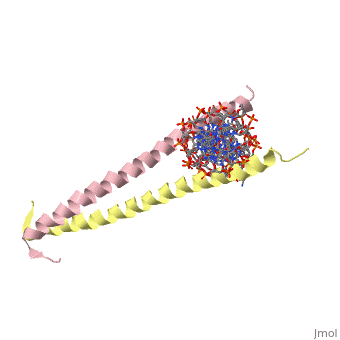
GCN4 (PDB [[2zta]] by itself, [[1ysa]] bound to DNA) is a eukaryotic transcription factor first isolated from yeast. It is composed of two identical 52 residue alpha helix chains that grouped together to form a dimer. The dimer binds through interlocking leucine amino acids in the C terminal ends, while pinching in on the major groove of DNA in the N terminal end. | |||
Revision as of 03:43, 9 November 2011
| |||||||
| 2zta, resolution 1.80Å () | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Standard Residues: | |||||||
| |||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
GCN4 - Leucine ZipperGCN4 - Leucine Zipper
Blah blah information about leucine zipper GCN4.
| |||||||||
| 1ysa, resolution 2.90Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
About this StructureAbout this Structure
GCN4 (PDB 2zta by itself, 1ysa bound to DNA) is a eukaryotic transcription factor first isolated from yeast. It is composed of two identical 52 residue alpha helix chains that grouped together to form a dimer. The dimer binds through interlocking leucine amino acids in the C terminal ends, while pinching in on the major groove of DNA in the N terminal end.