1cma: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<StructureSection load='1cma' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1cma]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.80Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1cma' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1cma]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.80Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1cma]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [ | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1cma]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli Escherichia coli]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1CMA OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1CMA FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
</td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=SAM:S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE'>SAM</scene></td></tr> | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=SAM:S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE'>SAM</scene></td></tr> | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[ | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1cma FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1cma OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1cma PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1cma RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1cma PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1cma ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
[[ | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/METJ_ECOLI METJ_ECOLI]] This regulatory protein, when combined with SAM (S-adenosylmethionine) represses the expression of the methionine regulon and of enzymes involved in SAM synthesis. It is also autoregulated.[HAMAP-Rule:MF_00744] | ||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Met repressor|Met repressor]] | *[[Met repressor|Met repressor]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 13:37, 14 July 2021
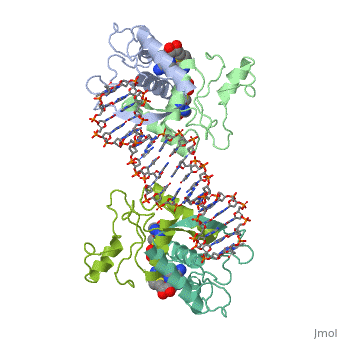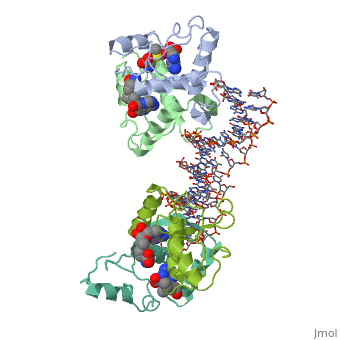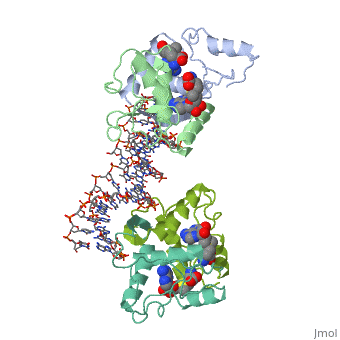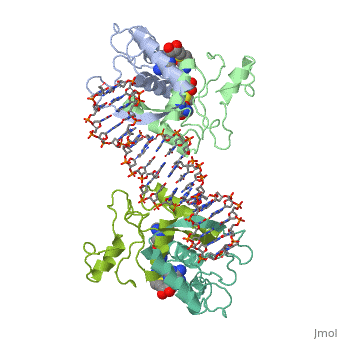
MET REPRESSOR/DNA COMPLEX + S-ADENOSYL-METHIONINEMET REPRESSOR/DNA COMPLEX + S-ADENOSYL-METHIONINE
Structural highlights
Function[METJ_ECOLI] This regulatory protein, when combined with SAM (S-adenosylmethionine) represses the expression of the methionine regulon and of enzymes involved in SAM synthesis. It is also autoregulated.[HAMAP-Rule:MF_00744] Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe crystal structure of the met repressor-operator complex shows two dimeric repressor molecules bound to adjacent sites 8 base pairs apart on an 18-base-pair DNA fragment. Sequence specificity is achieved by insertion of double-stranded antiparallel protein beta-ribbons into the major groove of B-form DNA, with direct hydrogen-bonding between amino-acid side chains and the base pairs. The repressor also recognizes sequence-dependent distortion or flexibility of the operator phosphate backbone, conferring specificity even for inaccessible base pairs. Crystal structure of the met repressor-operator complex at 2.8 A resolution reveals DNA recognition by beta-strands.,Somers WS, Phillips SE Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):387-93. PMID:1406951[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||