Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
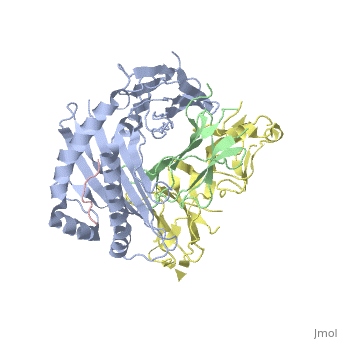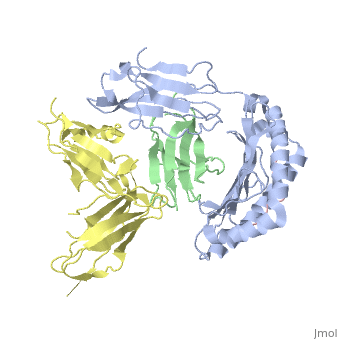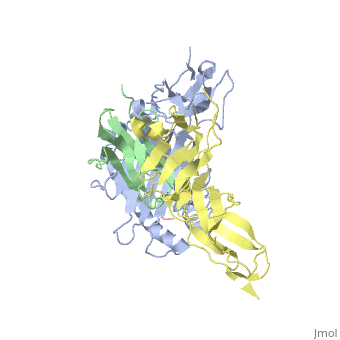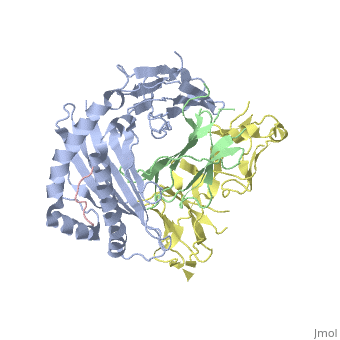
<StructureSection load='1p7q' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor ligand-binding domain (yellow) complex with class I MHC (grey), β-2 microglobulin (green) and POL polyprotein peptide (pink) (PDB entry [[1p7q]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1p7q' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor ligand-binding domain (yellow) complex with class I MHC (grey), β-2 microglobulin (green) and POL polyprotein peptide (pink) (PDB entry [[1p7q]])' scene=''> | ||
'''Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors''' (LIR) or '''CD85''' have extracellular immunoglobulin domains. LIR modulates a variety of immune cells. LIR interacts with class I MHC molecules. | '''Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors''' (LIR) or '''CD85''' have extracellular immunoglobulin domains. LIR modulates a variety of immune cells. LIR interacts with class I MHC molecules<ref>PMID:19548123</ref>. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
**[[3d2u]] – hLIR ligand-binding domain + herpesvirus UL18 + β-2 microglobulin + actin peptide<br /> | **[[3d2u]] – hLIR ligand-binding domain + herpesvirus UL18 + β-2 microglobulin + actin peptide<br /> | ||
}} | }} | ||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Revision as of 12:29, 11 April 2016
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors (LIR) or CD85 have extracellular immunoglobulin domains. LIR modulates a variety of immune cells. LIR interacts with class I MHC molecules[1]. |
| ||||||||||
3D structures of leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor3D structures of leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor
Updated on 11-April-2016
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Thomas R, Matthias T, Witte T. Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors as new players in autoimmunity. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2010 Apr;38(2-3):159-62. doi:, 10.1007/s12016-009-8148-8. PMID:19548123 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12016-009-8148-8