4ivt: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
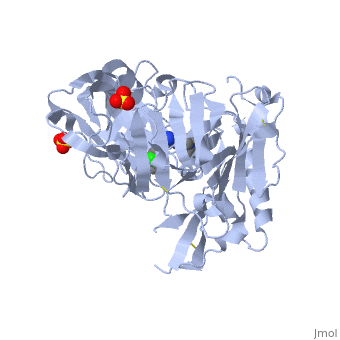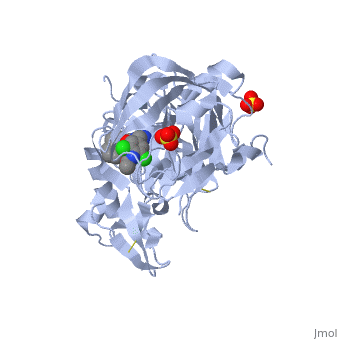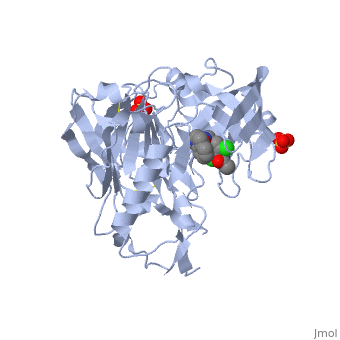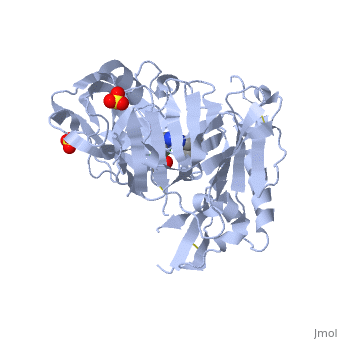
==Crystal structure of BACE1 with its inhibitor== | |||
=== | <StructureSection load='4ivt' size='340' side='right' caption='[[4ivt]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 1.60Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4ivt]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4IVT OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4IVT FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=SO4:SULFATE+ION'>SO4</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=VTI:N-{N-[4-(ACETYLAMINO)-3,5-DICHLOROBENZYL]CARBAMIMIDOYL}-2-(1H-INDOL-1-YL)ACETAMIDE'>VTI</scene></td></tr> | |||
<tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[4ivs|4ivs]]</td></tr> | |||
<tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">BACE1 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 HUMAN])</td></tr> | |||
<tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Memapsin_2 Memapsin 2], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=3.4.23.46 3.4.23.46] </span></td></tr> | |||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4ivt FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4ivt OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4ivt RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4ivt PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
Proteolytic cleavage of amyloid precursor protein by beta-secretase (BACE1) is a key step in generating the N-terminal of beta-amyloid (Abeta), which further forms into amyloid plaques that are considered as the hallmark of Alzheimer's disease. Inhibitors of BACE1 can reduce the levels of Abeta and thus have a therapeutic potential for treating the disease. We report here the identification of a series of small molecules bearing an indole acylguanidine core structure as potent BACE1 inhibitors. The initial weak fragment was discovered by virtual screening, and followed with a hit-to-lead optimization. With the aid of co-crystal structures of two discovered inhibitors (compounds 19 and 25) with BACE1, we explored the SAR around the indole and aryl groups, and obtained several BACE1 inhibitors about 1,000-fold more potent than the initial fragment hit. Accompanying the lead optimization, a previously under-explored sub-site opposite the flap loop was redefined as a potential binding site for later BACE1 inhibitor design. | |||
Virtual screening and structure-based discovery of indole acylguanidines as potent beta-secretase (BACE1) inhibitors.,Zou Y, Li L, Chen W, Chen T, Ma L, Wang X, Xiong B, Xu Y, Shen J Molecules. 2013 May 16;18(5):5706-22. doi: 10.3390/molecules18055706. PMID:23681056<ref>PMID:23681056</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Beta secretase|Beta secretase]] | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Human]] | |||
[[Category: Memapsin 2]] | [[Category: Memapsin 2]] | ||
[[Category: Chen, T T | [[Category: Chen, T T]] | ||
[[Category: Chen, W Y | [[Category: Chen, W Y]] | ||
[[Category: Li, L | [[Category: Li, L]] | ||
[[Category: Xu, Y C | [[Category: Xu, Y C]] | ||
[[Category: Hydrolase]] | [[Category: Hydrolase]] | ||
[[Category: Hydrolase-hydrolase inhibitor complex]] | [[Category: Hydrolase-hydrolase inhibitor complex]] | ||
Revision as of 15:09, 21 December 2014
Crystal structure of BACE1 with its inhibitorCrystal structure of BACE1 with its inhibitor
Structural highlights
Publication Abstract from PubMedProteolytic cleavage of amyloid precursor protein by beta-secretase (BACE1) is a key step in generating the N-terminal of beta-amyloid (Abeta), which further forms into amyloid plaques that are considered as the hallmark of Alzheimer's disease. Inhibitors of BACE1 can reduce the levels of Abeta and thus have a therapeutic potential for treating the disease. We report here the identification of a series of small molecules bearing an indole acylguanidine core structure as potent BACE1 inhibitors. The initial weak fragment was discovered by virtual screening, and followed with a hit-to-lead optimization. With the aid of co-crystal structures of two discovered inhibitors (compounds 19 and 25) with BACE1, we explored the SAR around the indole and aryl groups, and obtained several BACE1 inhibitors about 1,000-fold more potent than the initial fragment hit. Accompanying the lead optimization, a previously under-explored sub-site opposite the flap loop was redefined as a potential binding site for later BACE1 inhibitor design. Virtual screening and structure-based discovery of indole acylguanidines as potent beta-secretase (BACE1) inhibitors.,Zou Y, Li L, Chen W, Chen T, Ma L, Wang X, Xiong B, Xu Y, Shen J Molecules. 2013 May 16;18(5):5706-22. doi: 10.3390/molecules18055706. PMID:23681056[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||