1ihr: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Crystal structure of the dimeric C-terminal domain of TonB== | |||
=== | <StructureSection load='1ihr' size='340' side='right' caption='[[1ihr]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 1.55Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1ihr]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli Escherichia coli]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1IHR OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1IHR FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=BR:BROMIDE+ION'>BR</scene><br> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">JM83 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=562 Escherichia coli])</td></tr> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1ihr FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1ihr OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1ihr RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1ihr PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | |||
<table> | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/ih/1ihr_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/chain_selection.php?pdb_ID=2ata ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
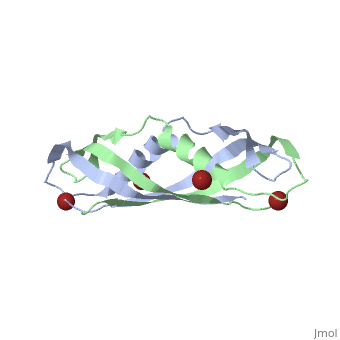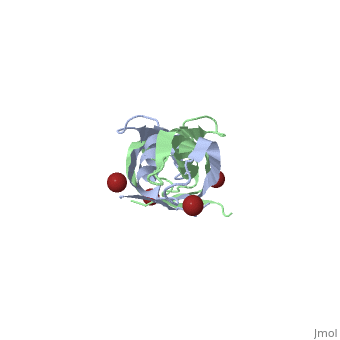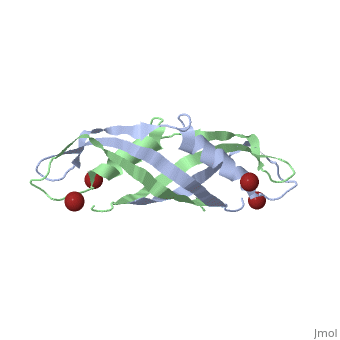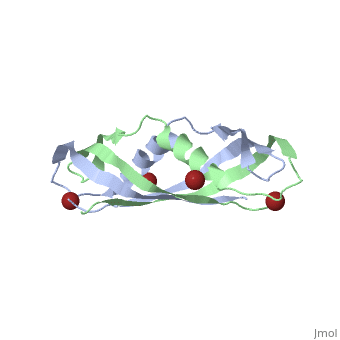
The TonB-dependent complex of Gram-negative bacteria couples the inner membrane proton motive force to the active transport of iron.siderophore and vitamin B(12) across the outer membrane. The structural basis of that process has not been described so far in full detail. The crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of TonB from Escherichia coli has now been solved by multiwavelength anomalous diffraction and refined at 1.55-A resolution, providing the first evidence that this region of TonB (residues 164-239) dimerizes. Moreover, the structure shows a novel architecture that has no structural homologs among any known proteins. The dimer of the C-terminal domain of TonB is cylinder-shaped with a length of 65 A and a diameter of 25 A. Each monomer contains three beta strands and a single alpha helix. The two monomers are intertwined with each other, and all six beta-strands of the dimer make a large antiparallel beta-sheet. We propose a plausible model of binding of TonB to FhuA and FepA, two TonB-dependent outer-membrane receptors. | |||
Crystal structure of the dimeric C-terminal domain of TonB reveals a novel fold.,Chang C, Mooser A, Pluckthun A, Wlodawer A J Biol Chem. 2001 Jul 20;276(29):27535-40. Epub 2001 Apr 27. PMID:11328822<ref>PMID:11328822</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[TonB|TonB]] | *[[TonB|TonB]] | ||
== References == | |||
== | <references/> | ||
< | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Escherichia coli]] | [[Category: Escherichia coli]] | ||
[[Category: Chang, C.]] | [[Category: Chang, C.]] | ||
Revision as of 19:59, 29 September 2014
Crystal structure of the dimeric C-terminal domain of TonBCrystal structure of the dimeric C-terminal domain of TonB
Structural highlights
Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe TonB-dependent complex of Gram-negative bacteria couples the inner membrane proton motive force to the active transport of iron.siderophore and vitamin B(12) across the outer membrane. The structural basis of that process has not been described so far in full detail. The crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of TonB from Escherichia coli has now been solved by multiwavelength anomalous diffraction and refined at 1.55-A resolution, providing the first evidence that this region of TonB (residues 164-239) dimerizes. Moreover, the structure shows a novel architecture that has no structural homologs among any known proteins. The dimer of the C-terminal domain of TonB is cylinder-shaped with a length of 65 A and a diameter of 25 A. Each monomer contains three beta strands and a single alpha helix. The two monomers are intertwined with each other, and all six beta-strands of the dimer make a large antiparallel beta-sheet. We propose a plausible model of binding of TonB to FhuA and FepA, two TonB-dependent outer-membrane receptors. Crystal structure of the dimeric C-terminal domain of TonB reveals a novel fold.,Chang C, Mooser A, Pluckthun A, Wlodawer A J Biol Chem. 2001 Jul 20;276(29):27535-40. Epub 2001 Apr 27. PMID:11328822[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||