Phage integrase: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
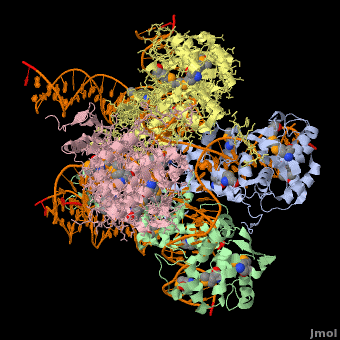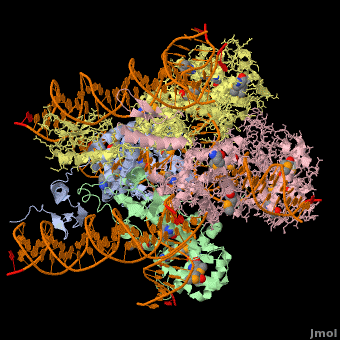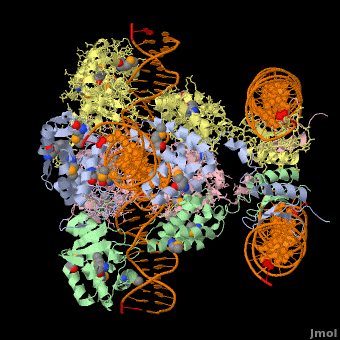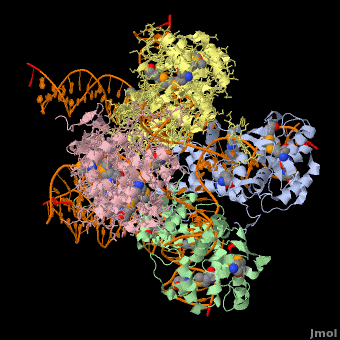
<StructureSection load='' size='400' side='right' scene='44/443479/Cv/2' caption='Se-Met Enterobacteria phage λ integrase:DNA tetramer complex (Holiday Junction) [[1z1g]]' pspeed='8'> | |||
'''Phage integrase''' (PIN) mediates recombination between DNA recognition sequences - the phage attachment site attP and the bacterial attachment site attB<ref>PMID:14687564</ref>. The '''Tyrosine family PIN''' uses a catalytic tyrosine to mediate strand cleavage while the '''Serine family PIN''' uses a serine residue. The High-Pathogenicity Island (HPI) is a genomic island essential for virulence of the family of Enterobacteria. | |||
*The biological assembly of Enterobacteria phage λ integrase is <scene name='44/443479/Cv/3'>homotetramer</scene>. | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
== 3D Structures of phage integrase see [[Retroviral Integrase]]== | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
== | |||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:20, 5 September 2018
Phage integrase (PIN) mediates recombination between DNA recognition sequences - the phage attachment site attP and the bacterial attachment site attB[1]. The Tyrosine family PIN uses a catalytic tyrosine to mediate strand cleavage while the Serine family PIN uses a serine residue. The High-Pathogenicity Island (HPI) is a genomic island essential for virulence of the family of Enterobacteria.
|
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of phage integrase see Retroviral Integrase3D Structures of phage integrase see Retroviral Integrase
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Groth AC, Calos MP. Phage integrases: biology and applications. J Mol Biol. 2004 Jan 16;335(3):667-78. PMID:14687564 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0022283603013561