Phage integrase
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
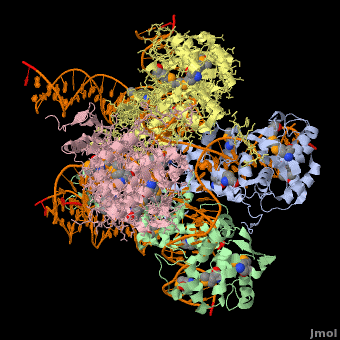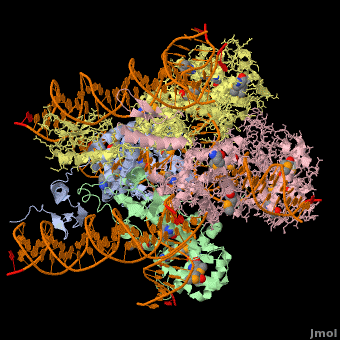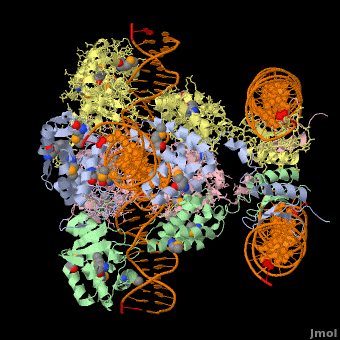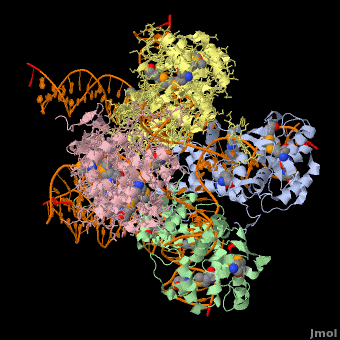
Phage integrase (PIN) mediates recombination between DNA recognition sequences - the phage attachment site attP and the bacterial attachment site attB[1]. The Tyrosine family PIN uses a catalytic tyrosine to mediate strand cleavage while the Serine family PIN uses a serine residue. The High-Pathogenicity Island (HPI) is a genomic island essential for virulence of the family of Enterobacteria.
|
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of phage integrase see Retroviral Integrase3D Structures of phage integrase see Retroviral Integrase
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Groth AC, Calos MP. Phage integrases: biology and applications. J Mol Biol. 2004 Jan 16;335(3):667-78. PMID:14687564 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0022283603013561