ExbB: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
ExbB is essential for TonB-dependent energy transduction as the absence of ExbB prevents TonB responding to the proton motive force, as well as the change of the high-affinity association of TonB for the outer membrane to the cytoplasmic membrane | <StructureSection load='5zfu' size='350' side='right' caption='ExbB pentamer complex with ExbD peptide (red) (PDB code [[5zfu]])' scene=''> | ||
[[Image:ExbB.jpg|300px|right|thumb| The Structure of ExbB<ref name='Kampfenkel'>PMID: 8449962</ref>]] | |||
== Structure== | |||
'''ExbB''' consists of three transmembrane domains (spanning from residues 16-39, 128-155 and 162-194), with two large portions of the protein representing the majority of the protein in the cytoplasm and two smaller portions in the periplasm<ref name='Kampfenkel'>PMID: 8449962</ref>. | |||
ExbB can exist in the [[TonB]] system either in a complex with [[ExbD]] (to a ratio of 3.5:1) or on its own (where no ExbD is present), which has been suggested to play a part in the diverse roles of TonB<ref name='Held'>PMID: 12193634</ref>. | |||
ExbB has a similar sequence and physiological structure to [[TolQ]] and is therefore thought to be evolutionarily linked<ref name='Braun'>PMID: 15205446</ref>. | |||
==Function== | |||
ExbB is essential for TonB-dependent energy transduction as the absence of ExbB prevents TonB responding to the proton motive force, as well as the change of the high-affinity association of TonB for the outer membrane to the cytoplasmic membrane<ref name='Held'>PMID: 12193634</ref>. | |||
ExbB can | Loss of ExbB function can be partially replaced by TolQ and vice versa - reduced activities of either of these proteins via a mutant form can be reversed by introducing double mutants<ref name='Braun'>PMID: 15205446</ref>. | ||
</StructureSection> | |||
==3D structures of ExbB== | |||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | |||
ExbB | [[5zfu]], [[5zfv]] – EcExbB + ExbD peptide – ''Escherichia coli'' – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
[[6tyi]] – EcExbB + ExbD – Cryo EM<br /> | |||
[[5sv1]] – ExbB + ExbD peptide <br /> | |||
[[5sv0]], [[5zfp]] – EcExbB <br /> | |||
[[6ye4]] – SmExbB – ''Serratia marsescens'' - Cryo EM<br /> | |||
[[7ajq]] – SmExbB + ExbD - Cryo EM<br /> | |||
== References== | == References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:29, 26 February 2023
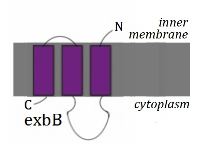 StructureExbB consists of three transmembrane domains (spanning from residues 16-39, 128-155 and 162-194), with two large portions of the protein representing the majority of the protein in the cytoplasm and two smaller portions in the periplasm[1]. ExbB can exist in the TonB system either in a complex with ExbD (to a ratio of 3.5:1) or on its own (where no ExbD is present), which has been suggested to play a part in the diverse roles of TonB[2]. ExbB has a similar sequence and physiological structure to TolQ and is therefore thought to be evolutionarily linked[3]. FunctionExbB is essential for TonB-dependent energy transduction as the absence of ExbB prevents TonB responding to the proton motive force, as well as the change of the high-affinity association of TonB for the outer membrane to the cytoplasmic membrane[2]. Loss of ExbB function can be partially replaced by TolQ and vice versa - reduced activities of either of these proteins via a mutant form can be reversed by introducing double mutants[3]. |
| ||||||||||
3D structures of ExbB3D structures of ExbB
Updated on 26-February-2023
5zfu, 5zfv – EcExbB + ExbD peptide – Escherichia coli – Cryo EM
6tyi – EcExbB + ExbD – Cryo EM
5sv1 – ExbB + ExbD peptide
5sv0, 5zfp – EcExbB
6ye4 – SmExbB – Serratia marsescens - Cryo EM
7ajq – SmExbB + ExbD - Cryo EM
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kampfenkel K, Braun V. Topology of the ExbB protein in the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):6050-7. PMID:8449962
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Held KG, Postle K. ExbB and ExbD do not function independently in TonB-dependent energy transduction. J Bacteriol. 2002 Sep;184(18):5170-3. PMID:12193634
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Braun V, Herrmann C. Point mutations in transmembrane helices 2 and 3 of ExbB and TolQ affect their activities in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 2004 Jul;186(13):4402-6. PMID:15205446 doi:10.1128/JB.186.13.4402-4406.2004