Calmodulin: Difference between revisions
New page: ==This is a placeholder== This is a placeholder text to help you get started in placing a Jmol applet on your page. At any time, click "Show Preview" at the bottom of this page to see how... |
No edit summary |
||
| (73 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | <StructureSection load='1cll' size='350' side='right' scene='39/398280/Cv/3' caption='Human calmodulin complex with ethanol and Ca+2 ions (green) (PDB code [[1cll]])'> | ||
__TOC__ | |||
==Function== | |||
[[Calmodulin]] (CaM) – calcium modulated protein – regulates various protein targets. It is used by various proteins as calcium sensor and signal transducer by binding to their calcium binding domain (CBD). It undergoes conformational change upon binding Ca++ via its 4 [[EF hand]] motives and can undergo post-translational modification. <scene name='39/398280/Cv/4'>Click here to see EF hand</scene> of Human calmodulin (PDB code [[1cll]]). <ref>PMID:1474585</ref> More details on apo-CaM [[Calcium-free Calmodulin]] and [[Calmodulin JMU]]. | |||
and | |||
{{ | {{Clear}} | ||
== [[Maximum Occurrence]] of Calmodulin Conformations == | |||
[[Maximum Occurrence]], a method for making rigorous numerical assessments about the maximum percent of time that a conformer of a flexible macromolecule can exist and still be compatible with the experimental data, was used to probe the conformational disorder of Calmodulin<ref>doi:10.1021/ja1063923</ref>.<br /> | |||
[[Image:Movie_MOforproteopedia.gif|thumb|center|400px|Figure 3: Orientation tensor representation for 400 conformational states of Calmodulin, color coded according to their MO values (from less than 5% in blue to more than 30% in red).To better explain their meaning, 10 randomly chosen models are shown as cartoons and then replaced by the three axes of their color-coded orientation tensors.]] <br /> | |||
It was shown that the open ([[1cll]]) and closed ([[1prw]]) conformers can have MO of only 15% and 5% respectively. | |||
== Calmodulin in Motion == | |||
The buttons below allow you to explore morphs <ref>The [[Jmol/Storymorph|Storymorph Jmol scripts]] creates the interpolated coordinates of the morph on the fly.</ref> between structures [[1prw]] and [[1cll]]. | |||
<jmol> | |||
<jmolButton> | |||
<script> | |||
script "/wiki/images/a/a2/Storymorph.spt"; | |||
load files "=1prw" "=1cll"; | |||
delete water; | |||
delete protein and not backbone; | |||
select all;cartoon only;cartoon off; | |||
select 4-147;cartoon on; | |||
model 1; | |||
center visible;color group; | |||
compare {2.1} {1.1} SUBSET{*.CA} ATOMS{4-138}{4-138} ROTATE TRANSLATE; | |||
</script> | |||
<text>Prepare Animation</text> | |||
</jmolButton> | |||
</jmol><jmol> | |||
<jmolButton> | |||
<script> | |||
model 2; | |||
display 4-147; | |||
backbone only; | |||
backbone 0.5 | |||
structures = [{1.1}, {2.1}]; | |||
my_recipe = [ | |||
[{79-147},{79-147}, {(79-138) and alpha}], | |||
[{4-78}, {79}, {(8-78) and alpha}], | |||
]; | |||
morph(20, structures, my_recipe); | |||
</script> | |||
<text>Open</text> | |||
</jmolButton> | |||
</jmol><jmol> | |||
<jmolButton> | |||
<script> | |||
model 1 | |||
display 4-147; | |||
backbone only; | |||
backbone 0.5 | |||
structures = [{2.1}, {1.1}]; | |||
my_recipe = [ | |||
[{79-147},{79-147}, {(79-138) and alpha}], | |||
[{4-78}, {79}, {(8-78) and alpha}], | |||
]; | |||
morph(20, structures, my_recipe); | |||
</script> | |||
<text>Close</text> | |||
</jmolButton> | |||
</jmol> | |||
The following morph is between [[1prw]] and [[1cll]] after superposition of residues 79-138. This shows the subtle conformational changes in that domain more clearly. | |||
<jmol> | |||
<jmolButton> | |||
<script> | |||
script "/wiki/images/a/a2/Storymorph.spt"; | |||
load files "=1prw" "=1cll"; | |||
delete water; | |||
delete protein and not backbone; | |||
select all;cartoon only;cartoon off; | |||
select 4-147;cartoon on; | |||
model 1; | |||
center visible;color group; | |||
compare {2.1} {1.1} SUBSET{*.CA} ATOMS{79-138}{79-138} ROTATE TRANSLATE; | |||
</script> | |||
<text>Prepare Animation</text> | |||
</jmolButton> | |||
</jmol><jmol> | |||
<jmolButton> | |||
<script> | |||
model 2; | |||
display 4-147; | |||
backbone only; | |||
backbone 0.5 | |||
structures = [{1.1}, {2.1}]; | |||
my_recipe = [ | |||
[{79-147},{79-147}, {(79-138) and alpha}], | |||
[{4-78}, {79}, {(8-78) and alpha}], | |||
]; | |||
morph(20, structures, my_recipe); | |||
</script> | |||
<text>Open</text> | |||
</jmolButton> | |||
</jmol><jmol> | |||
<jmolButton> | |||
<script> | |||
model 1 | |||
display 4-147; | |||
backbone only; | |||
backbone 0.5 | |||
structures = [{2.1}, {1.1}]; | |||
my_recipe = [ | |||
[{79-147},{79-147}, {(79-138) and alpha}], | |||
[{4-78}, {79}, {(8-78) and alpha}], | |||
]; | |||
morph(20, structures, my_recipe); | |||
</script> | |||
<text>Close</text> | |||
</jmolButton> | |||
</jmol> | |||
The following morph is between [[1prw]] and [[1cll]] after superposition of residues 8-78. This shows the subtle conformational changes in that domain more clearly. | |||
<jmol> | |||
<jmolButton> | |||
<script> | |||
script "/wiki/images/a/a2/Storymorph.spt"; | |||
load files "=1prw" "=1cll"; | |||
delete water; | |||
delete protein and not backbone; | |||
select all;cartoon only;cartoon off; | |||
select 4-147;cartoon on; | |||
model 1; | |||
center visible;color group; | |||
compare {2.1} {1.1} SUBSET{*.CA} ATOMS{8-78}{8-78} ROTATE TRANSLATE; | |||
</script> | |||
<text>Prepare Animation</text> | |||
</jmolButton> | |||
</jmol><jmol> | |||
<jmolButton> | |||
<script> | |||
model 2; | |||
display 4-147; | |||
backbone only; | |||
backbone 0.5 | |||
structures = [{1.1}, {2.1}]; | |||
my_recipe = [ | |||
[{4-78}, {4-78}, {(8-78) and alpha}], | |||
[{79-147},{78}, {(79-138) and alpha}], | |||
]; | |||
morph(20, structures, my_recipe); | |||
</script> | |||
<text>Open</text> | |||
</jmolButton> | |||
</jmol><jmol> | |||
<jmolButton> | |||
<script> | |||
model 1 | |||
display 4-147; | |||
backbone only; | |||
backbone 0.5 | |||
structures = [{2.1}, {1.1}]; | |||
my_recipe = [ | |||
[{4-78}, {4-78}, {(8-78) and alpha}], | |||
[{79-147},{78}, {(79-138) and alpha}], | |||
]; | |||
morph(20, structures, my_recipe); | |||
</script> | |||
<text>Close</text> | |||
</jmolButton> | |||
</jmol> | |||
== 3D Structures of Calmodulin == | |||
[[Calmodulin 3D structures]] | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calmodulin Calmodulin at Wikipedia] | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calmodulin Calmodulin at Wikipedia] | ||
* [http://www.pdb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/pdb44_1.html Molecule of the Month (08/2003) at RCSB PDB] | |||
== Bibliography == | |||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:03, 7 July 2023
FunctionCalmodulin (CaM) – calcium modulated protein – regulates various protein targets. It is used by various proteins as calcium sensor and signal transducer by binding to their calcium binding domain (CBD). It undergoes conformational change upon binding Ca++ via its 4 EF hand motives and can undergo post-translational modification. of Human calmodulin (PDB code 1cll). [1] More details on apo-CaM Calcium-free Calmodulin and Calmodulin JMU. Maximum Occurrence of Calmodulin ConformationsMaximum Occurrence, a method for making rigorous numerical assessments about the maximum percent of time that a conformer of a flexible macromolecule can exist and still be compatible with the experimental data, was used to probe the conformational disorder of Calmodulin[2]. 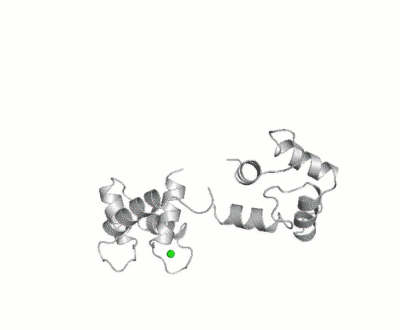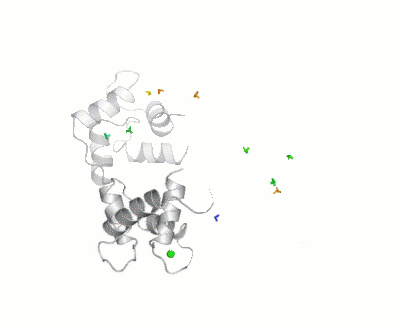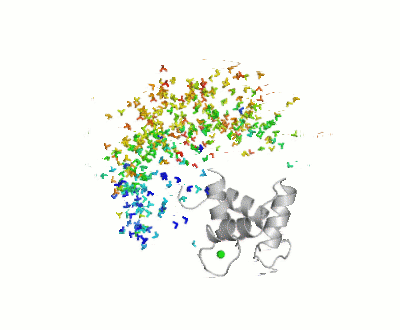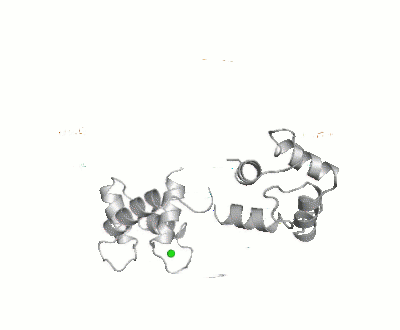
It was shown that the open (1cll) and closed (1prw) conformers can have MO of only 15% and 5% respectively. Calmodulin in MotionThe buttons below allow you to explore morphs [3] between structures 1prw and 1cll.
The following morph is between 1prw and 1cll after superposition of residues 79-138. This shows the subtle conformational changes in that domain more clearly.
The following morph is between 1prw and 1cll after superposition of residues 8-78. This shows the subtle conformational changes in that domain more clearly.
3D Structures of Calmodulin
|
| ||||||||||
See AlsoSee Also
BibliographyBibliography
- ↑ Chattopadhyaya R, Meador WE, Means AR, Quiocho FA. Calmodulin structure refined at 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 20;228(4):1177-92. PMID:1474585
- ↑ Bertini I, Giachetti A, Luchinat C, Parigi G, Petoukhov MV, Pierattelli R, Ravera E, Svergun DI. Conformational Space of Flexible Biological Macromolecules from Average Data. J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Sep 7. PMID:20822180 doi:10.1021/ja1063923
- ↑ The Storymorph Jmol scripts creates the interpolated coordinates of the morph on the fly.