Calmodulin
FunctionCalmodulin (CaM) – calcium modulated protein – regulates various protein targets. It is used by various proteins as calcium sensor and signal transducer by binding to their calcium binding domain (CBD). It undergoes conformational change upon binding Ca++ via its 4 EF hand motives and can undergo post-translational modification. of Human calmodulin (PDB code 1cll). [1] More details on apo-CaM Calcium-free Calmodulin and Calmodulin JMU. Maximum Occurrence of Calmodulin ConformationsMaximum Occurrence, a method for making rigorous numerical assessments about the maximum percent of time that a conformer of a flexible macromolecule can exist and still be compatible with the experimental data, was used to probe the conformational disorder of Calmodulin[2]. 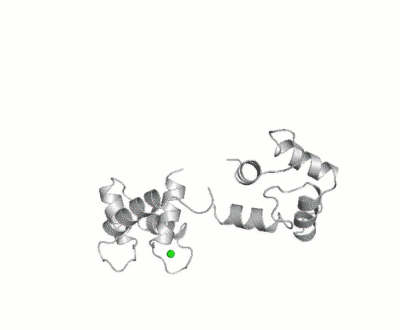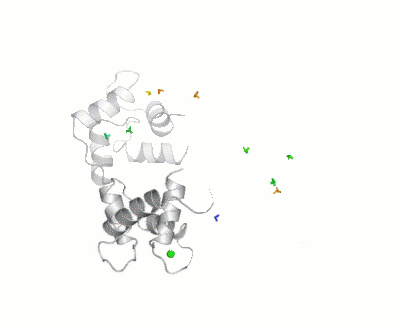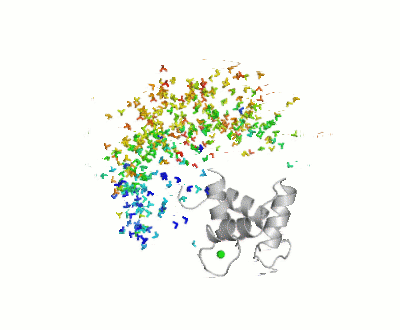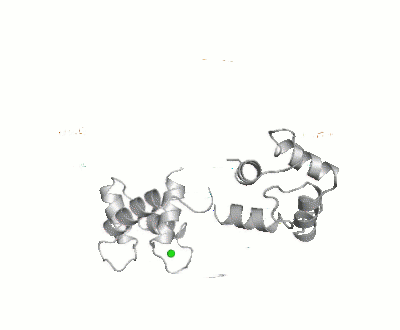
It was shown that the open (1cll) and closed (1prw) conformers can have MO of only 15% and 5% respectively. Calmodulin in MotionThe buttons below allow you to explore morphs [3] between structures 1prw and 1cll.
The following morph is between 1prw and 1cll after superposition of residues 79-138. This shows the subtle conformational changes in that domain more clearly.
The following morph is between 1prw and 1cll after superposition of residues 8-78. This shows the subtle conformational changes in that domain more clearly.
3D Structures of Calmodulin
|
| ||||||||||
See AlsoSee Also
BibliographyBibliography
- ↑ Chattopadhyaya R, Meador WE, Means AR, Quiocho FA. Calmodulin structure refined at 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 20;228(4):1177-92. PMID:1474585
- ↑ Bertini I, Giachetti A, Luchinat C, Parigi G, Petoukhov MV, Pierattelli R, Ravera E, Svergun DI. Conformational Space of Flexible Biological Macromolecules from Average Data. J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Sep 7. PMID:20822180 doi:10.1021/ja1063923
- ↑ The Storymorph Jmol scripts creates the interpolated coordinates of the morph on the fly.