1xbr: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
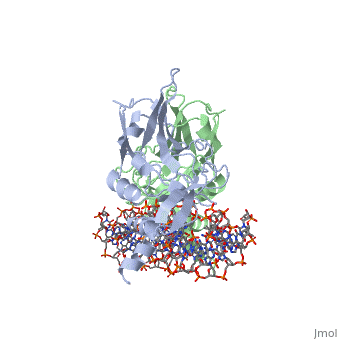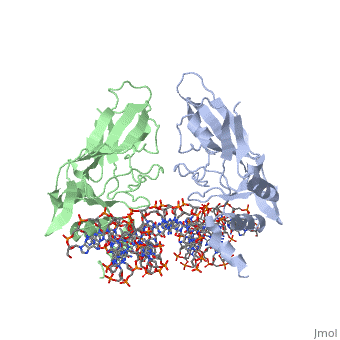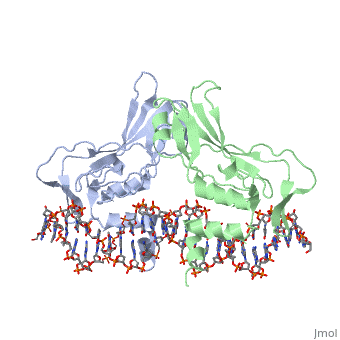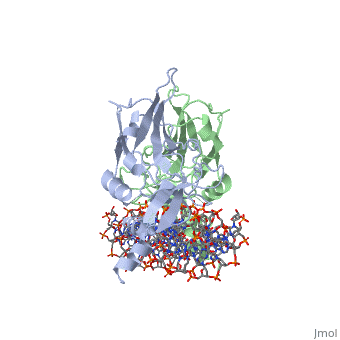
==T DOMAIN FROM XENOPUS LAEVIS BOUND TO DNA== | ==T DOMAIN FROM XENOPUS LAEVIS BOUND TO DNA== | ||
<StructureSection load='1xbr' size='340' side='right' caption='[[1xbr]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.50Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1xbr' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1xbr]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.50Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1xbr]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [ | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1xbr]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xenopus_laevis Xenopus laevis]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1XBR OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1XBR FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
</td></tr><tr id=' | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.5Å</td></tr> | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[ | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1xbr FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1xbr OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1xbr PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1xbr RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1xbr PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1xbr ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
[ | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/TBXT_XENLA TBXT_XENLA] Involved in the transcriptional regulation of genes required for mesoderm formation and differentiation (PubMed:11869292). Binds to the palindromic T site 5'-TTCACACCTAGGTGTGAA-3' DNA sequence (PubMed:11111039). Causes dorsal mesodermal differentiation of animal cap ectoderm when co-expressed with wnt8 and noggin (PubMed:7906224). None of these molecules causes dorsal mesoderm formation when expressed alone (PubMed:7906224). Establishes the left/right axis at early gastrula stage by directly up-regulating mesodermal expression of zic3 (PubMed:11869292).<ref>PMID:11111039</ref> <ref>PMID:11869292</ref> <ref>PMID:7906224</ref> | ||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1xbr ConSurf]. | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1xbr ConSurf]. | ||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| Line 35: | Line 26: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category: Xenopus laevis]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category: Muller CW]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:49, 14 February 2024
T DOMAIN FROM XENOPUS LAEVIS BOUND TO DNAT DOMAIN FROM XENOPUS LAEVIS BOUND TO DNA
Structural highlights
FunctionTBXT_XENLA Involved in the transcriptional regulation of genes required for mesoderm formation and differentiation (PubMed:11869292). Binds to the palindromic T site 5'-TTCACACCTAGGTGTGAA-3' DNA sequence (PubMed:11111039). Causes dorsal mesodermal differentiation of animal cap ectoderm when co-expressed with wnt8 and noggin (PubMed:7906224). None of these molecules causes dorsal mesoderm formation when expressed alone (PubMed:7906224). Establishes the left/right axis at early gastrula stage by directly up-regulating mesodermal expression of zic3 (PubMed:11869292).[1] [2] [3] Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||