Glucocorticoid receptor: Difference between revisions
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
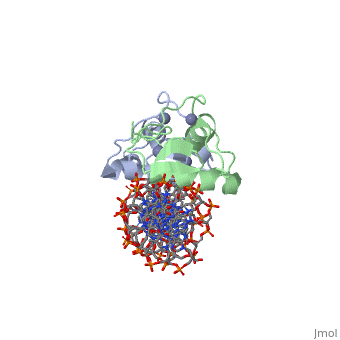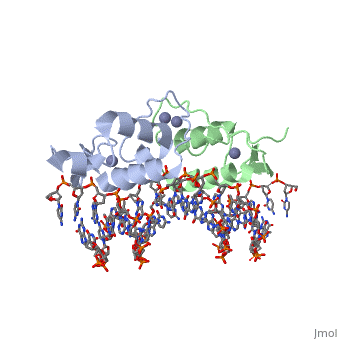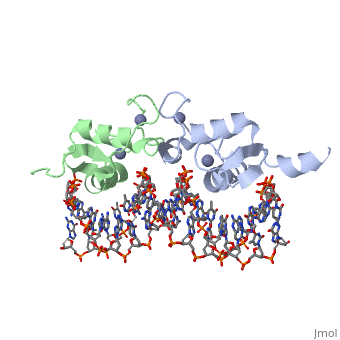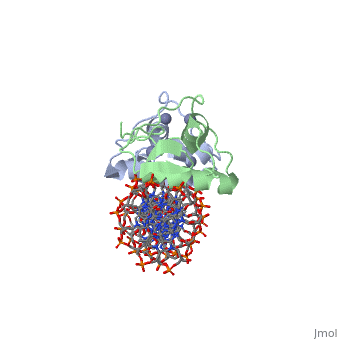
<StructureSection load='3g6r' size='350' side='right' caption='Rat glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain dimer complex with DNA and Zn+2 ions (grey) (PDB entry [[3g6r]])' scene=''> | |||
== Function == | |||
''' | |||
== | '''Glucocorticoid receptor''' (GCR) is the [[Nuclear receptors|nuclear receptor]] binding cortisol and [[glucocorticoids]]. GCR regulates genes involved in development, metabolism and immune response. GCR interacts with nuclear receptor coactivator 2 (NCOA2) which promotes DNA transcription by acylating histones<ref>PMID:17132855</ref>. | ||
See also: | |||
*[[Glucocorticoids]] | |||
*[[Intracellular receptors]] | |||
*[[Steroid Hormones and their receptors]]. | |||
== Relevance == | |||
The glucocorticoid-bound GCR can either up-regulate the expression of anti-inflammatory proteins (transactivation) or repress the expression of pro-inflammatory proteins (transrepression)<ref>PMID:24113652</ref>. | |||
== Disease == | |||
[[Budesonide]] is an agonist of GCR and is used as medication for asthma and inflammatory bowel diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease<ref>PMID:15641626</ref>. | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
GCR contains 5 domains: N terminal regulatory domain; DNA-binding domain (DBD) residues 417-506; hinge region; ligand-binding domain (LBD) residues 521-777 and C terminal domain. <scene name='89/895670/Cv/4'>Human glucocorticoid receptor ligand-binding domain bound to dexamethasone</scene> ([[1m2z]]). | |||
= | <scene name='96/962959/Tert/1'>Glucocorticoid Receptor in complex with budesonide</scene> ([[5nfp]]). | ||
<scene name='96/962959/Binding_site/1'>Budesonide binding site</scene>. Water molecule is shown as red sphere. | |||
= | <scene name='97/973067/Overall/1'>Crystal Structure of mometasone furoate-bound glucocorticoid receptor ligand binding domain</scene> ([[4p6w]]). | ||
<scene name='97/973067/Binding_site/1'>Mometasone furoate binding site</scene>. | |||
===Glucocorticoid receptor | ==3D structures of glucocorticoid receptor== | ||
[[Glucocorticoid receptor 3D structures]] | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:09, 16 January 2024
FunctionGlucocorticoid receptor (GCR) is the nuclear receptor binding cortisol and glucocorticoids. GCR regulates genes involved in development, metabolism and immune response. GCR interacts with nuclear receptor coactivator 2 (NCOA2) which promotes DNA transcription by acylating histones[1]. See also: RelevanceThe glucocorticoid-bound GCR can either up-regulate the expression of anti-inflammatory proteins (transactivation) or repress the expression of pro-inflammatory proteins (transrepression)[2]. DiseaseBudesonide is an agonist of GCR and is used as medication for asthma and inflammatory bowel diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[3]. Structural highlightsGCR contains 5 domains: N terminal regulatory domain; DNA-binding domain (DBD) residues 417-506; hinge region; ligand-binding domain (LBD) residues 521-777 and C terminal domain. (1m2z). (5nfp). . Water molecule is shown as red sphere. (4p6w). . 3D structures of glucocorticoid receptorGlucocorticoid receptor 3D structures
|
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Lu NZ, Wardell SE, Burnstein KL, Defranco D, Fuller PJ, Giguere V, Hochberg RB, McKay L, Renoir JM, Weigel NL, Wilson EM, McDonnell DP, Cidlowski JA. International Union of Pharmacology. LXV. The pharmacology and classification of the nuclear receptor superfamily: glucocorticoid, mineralocorticoid, progesterone, and androgen receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2006 Dec;58(4):782-97. PMID:17132855 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1124/pr.58.4.9
- ↑ Finsterwald C, Alberini CM. Stress and glucocorticoid receptor-dependent mechanisms in long-term memory: from adaptive responses to psychopathologies. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Jul;112:17-29. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.09.017. Epub, 2013 Oct 7. PMID:24113652 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2013.09.017
- ↑ Selroos O, Edsbäcker S, Hultquist C. Once-daily inhaled budesonide for the treatment of asthma: clinical evidence and pharmacokinetic explanation. J Asthma. 2004;41(8):771-90. PMID:15641626 doi:10.1081/jas-200038344