Stepler sandbox STAT3
STAT3STAT3
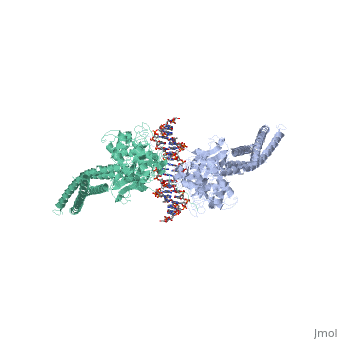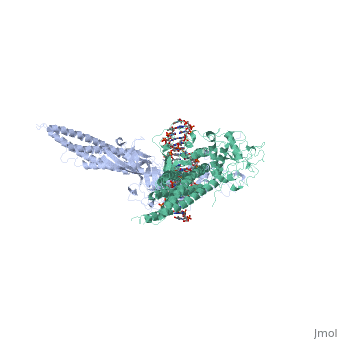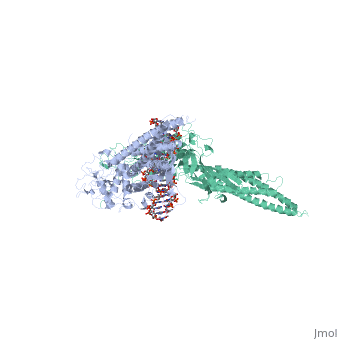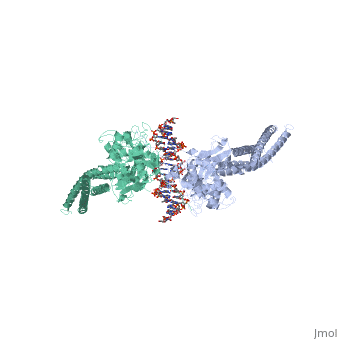
STAT3 (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3) is one of a family of seven homologous STAT proteins that differentially regulate gene expression. STAT 3 is important in both the development of embryos and many functions in adult organisms. [1] StructureThe STAT3 protein is composed of several structures and its quaternary structure consists of two STAT3 proteins with themselves. [2] RegulationSTAT3 plays a large role in differential gene regulation. One way that STAT3 can regulate gene expression is through protein-protein interactions with other transcription factors. One major protein-protein interaction for STAT3 is the interaction with nF-κB p65. [3] is characterized by the β-pleated sheet structures. Other protein transcription factors have been shown to interact with STAT3 in similar ways at different locations. STAT3 can also be regulated by phosphorylation. There is a at the C-terminal that plays a large role in transcriptional activation during regulatory events. Phosphorylation of the transcription activating domain's Y residue can be used as a regulatory process. Alternatively, other sites can also be phosphorylated causing other regulatory pathways to occur, such as serine phosphorylation and oncogene activity from STAT3. [4] DNA-Protein InteractionsThe by "clamping" around it. by interacting with the major groove of it. STAT3 (along with other STAT family members) bind to specific DNA sequences. [5] STAT3 has a binding domain with sequences like . is then what interacts with the STAT3 protein. As shown in the scene, the DNA is bound by the protein in its major groove. Positively charged glutamines and lysines interact with the negatively charged phosphates of the DNA. This is what allows to the protein to bind in the major groove.
|
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Horvath CM. STAT proteins and transcriptional responses to extracellular signals. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000 Oct;25(10):496-502. PMID:11050435
- ↑ Becker S, Groner B, Muller CW. Three-dimensional structure of the Stat3beta homodimer bound to DNA. Nature. 1998 Jul 9;394(6689):145-51. PMID:9671298 doi:10.1038/28101
- ↑ Yu Z, Kone BC. The STAT3 DNA-binding domain mediates interaction with NF-kappaB p65 and inducible nitric oxide synthase transrepression in mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004 Mar;15(3):585-91. PMID:14978160
- ↑ Sakaguchi M, Oka M, Iwasaki T, Fukami Y, Nishigori C. Role and regulation of STAT3 phosphorylation at Ser727 in melanocytes and melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 2012 Jul;132(7):1877-85. doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.45. Epub 2012, Mar 15. PMID:22418867 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/jid.2012.45
- ↑ Horvath CM. STAT proteins and transcriptional responses to extracellular signals. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000 Oct;25(10):496-502. PMID:11050435