Sandbox Reserved 561
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 05/22/2012, through 07/22/2012 for use in the course "BIOL 414" taught by Greg Buhrman at the North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 551 through Sandbox Reserved 590. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Hi Lakshmi, Here is your very own Proteopedia Page for pdb code: 1PUF. Your presentation is scheduled for: June 4.
Have Fun!
Greg Buhrman

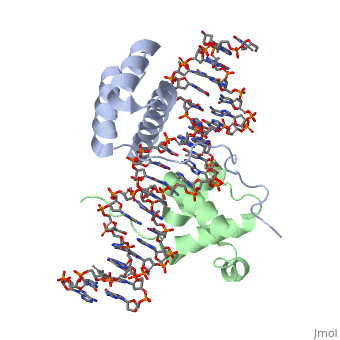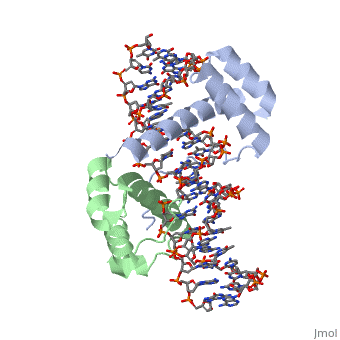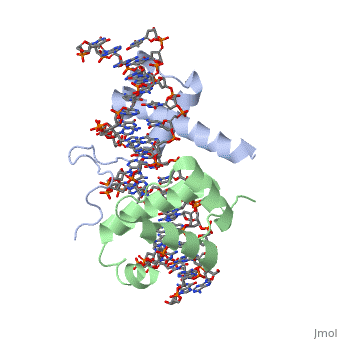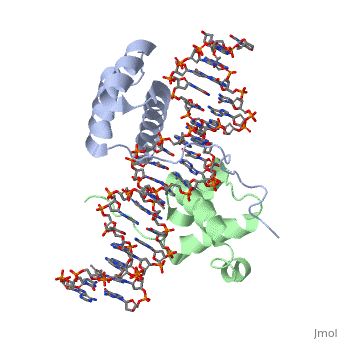
Crystal Structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 homeodomains bound to DNACrystal Structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 homeodomains bound to DNA
The HOX/HOM superfamily of homeodomain proteins controls cell fate and segmental embryonic patterning by a mechanism that is conserved in all metazoans. The linear arrangement of the Hox genes on the chromosome correlates with the spatial distribution of HOX protein expression along the anterior-posterior axis of the embryo. Most HOX proteins bind DNA cooperatively with members of the PBC family of TALE-type homeodomain proteins, which includes human Pbx1. Cooperative DNA binding between HOX and PBC proteins requires a residue N-terminal to the HOX homeodomain termed the hexapeptide, which differs significantly in sequence between anterior- and posterior-regulating HOX proteins. We report here the 1.9-A-resolution structure of a posterior HOX protein, HoxA9, complexed with Pbx1 and DNA, which reveals that the posterior Hox hexapeptide adopts an altered conformation as compared with that seen in previously determined anterior HOX/PBC structures. The additional nonspecific interactions and altered DNA conformation in this structure account for the stronger DNA-binding affinity and altered specificity observed for posterior HOX proteins when compared with anterior HOX proteins. DNA-binding studies of wild-type and mutant HoxA9 and HoxB1 show residues in the N-terminal arm of the homeodomains are critical for proper DNA sequence recognition despite lack of direct contact by these residues to the DNA bases. These results help shed light on the mechanism of transcriptional regulation by HOX proteins and show how DNA-binding proteins may use indirect contacts to determine sequence specificity.
Structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 bound to DNA: Hox hexapeptide and DNA recognition anterior to posterior., LaRonde-LeBlanc NA, Wolberger C, Genes Dev. 2003 Aug 15;17(16):2060-72. PMID:12923056
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
About this StructureAbout this Structure
1puf is a 4 chain structure with sequence from Homo sapiens and Mus musculus. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
See AlsoSee Also
- Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing
- User:Wayne Decatur/Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing
ReferenceReference
- ↑ LaRonde-LeBlanc NA, Wolberger C. Structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 bound to DNA: Hox hexapeptide and DNA recognition anterior to posterior. Genes Dev. 2003 Aug 15;17(16):2060-72. PMID:12923056 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.1103303