Ketol-acid reductoisomerase
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
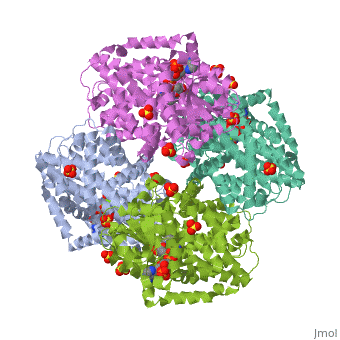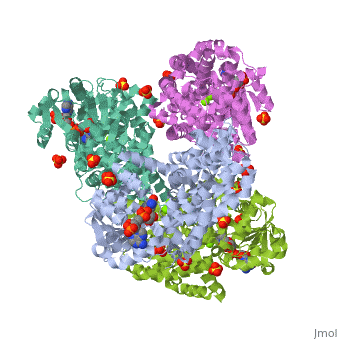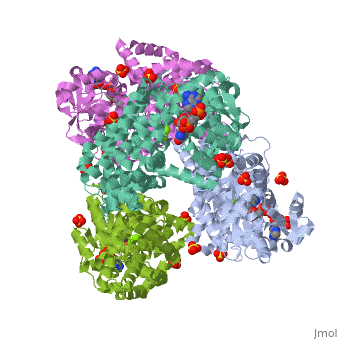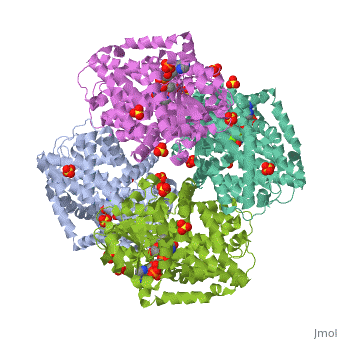
FunctionKetol-acid reductoisomerase (KARI) is a bifunctional enzyme which catalizes two steps in the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids. KARI catalyzes the isomerization of alkyls and the NADPH-dependent reduction of a 2-ketoacid[1]. There are two forms of KARI. A short form – Class I – found in fungi and most bacteria and a long form. For the active site see Arnold lab: coenzyme specificity – Class II – found in plants. 3D Structures of Ketol-acid reductoisomeraseKetol-acid reductoisomerase 3D structures
|
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Tyagi R, Lee YT, Guddat LW, Duggleby RG. Probing the mechanism of the bifunctional enzyme ketol-acid reductoisomerase by site-directed mutagenesis of the active site. FEBS J. 2005 Jan;272(2):593-602. PMID:15654896 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2004.04506.x