2djh
|
Crystal structure of the carboxy-terminal ribonuclease domain of Colicin E5
OverviewOverview
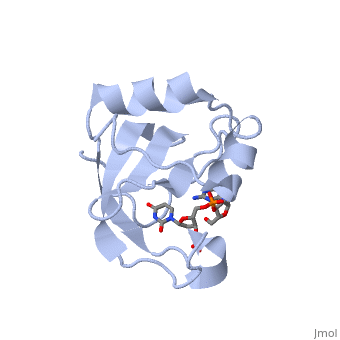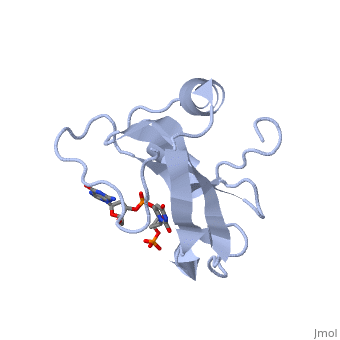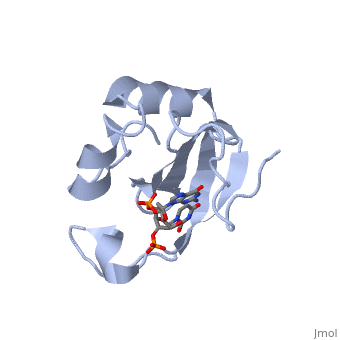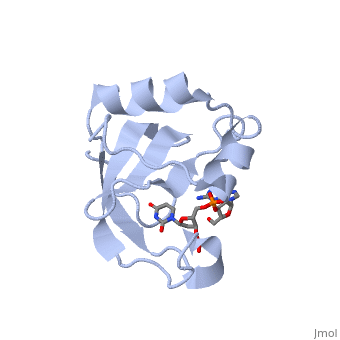
Colicin E5--a tRNase toxin--specifically cleaves QUN (Q: queuosine), anticodons of the Escherichia coli tRNAs for Tyr, His, Asn and Asp. Here, we report the crystal structure of the C-terminal ribonuclease domain, (CRD) of E5 complexed with a substrate analog, namely, dGpdUp, at a, resolution of 1.9 A. Thisstructure is the first to reveal the substrate, recognition mechanism of sequence-specific ribonucleases. E5-CRD realized, the strict recognition for both the guanine and uracil bases of dGpdUp, forming Watson-Crick-type hydrogen bonds and ring stacking interactions, thus mimicking the codons of mRNAs to bind to tRNA anticodons. The docking, model of E5-CRD with tRNA also suggests its substrate preference for tRNA, over ssRNA. In addition, the structure of E5-CRD/dGpdUp along with the, mutational analysis suggests that Arg33 may play an important role in the, catalytic activity, and Lys25/Lys60 may also be involved without His in, E5-CRD. Finally, the comparison of the structures of E5-CRD/dGpdUp and, E5-CRD/ImmE5 (an inhibitor protein) complexes suggests that the binding, mode of E5-CRD and ImmE5 mimics that of mRNA and tRNA; this may represent, the evolutionary pathway of these proteins from the RNA-RNA interaction, through the RNA-protein interaction of tRNA/E5-CRD.
About this StructureAbout this Structure
2DJH is a Single protein structure of sequence from Escherichia coli with 3PD as ligand. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
Structural basis for sequence-dependent recognition of colicin E5 tRNase by mimicking the mRNA-tRNA interaction., Yajima S, Inoue S, Ogawa T, Nonaka T, Ohsawa K, Masaki H, Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(21):6074-82. Epub 2006 Nov 11. PMID:17099236
Page seeded by OCA on Wed Nov 21 09:38:01 2007