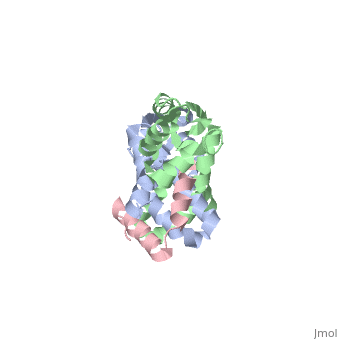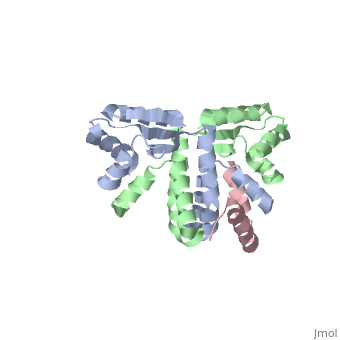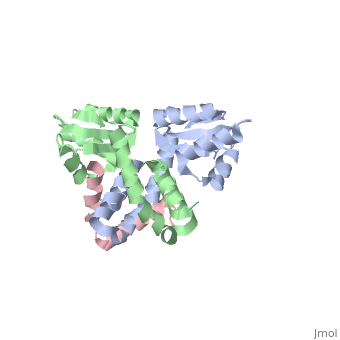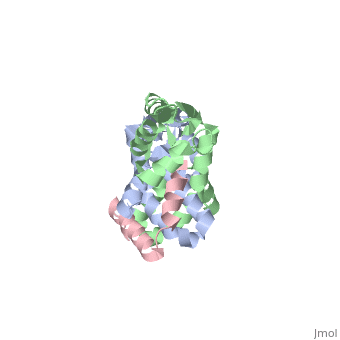1dd3
|
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN L12 FROM THERMOTOGA MARITIMA
OverviewOverview
Protein L12, the only multicopy component of the ribosome, is presumed to, be involved in the binding of translation factors, stimulating, factor-dependent GTP hydrolysis. Crystal structures of L12 from, Thermotogamaritima have been solved in two space groups by the multiple, anomalous dispersion method and refined at 2.4 and 2.0 A resolution. In, both crystal forms, an asymmetric unit comprises two full-length L12, molecules and two N-terminal L12 fragments that are associated in a, specific, hetero-tetrameric complex with one non-crystallographic 2-fold, axis. The two full-length proteins form a tight, symmetric, parallel, dimer, mainly through their N-terminal domains. Each monomer of this, central dimer additionally associates in a different way with an, N-terminal L12 fragment. Both dimerization modes are unlike models, proposed previously and suggest that similar complexes may occur in vivo, and in situ. The structures also display different L12 monomer, conformations, in accord with the suggested dynamic role of the protein in, the ribosomal translocation process. The structures have been submitted to, the Protein Databank (http://www.rcsb.org/pdb) under accession numbers, 1DD3 and 1DD4.
About this StructureAbout this Structure
1DD3 is a Protein complex structure of sequences from Thermotoga maritima. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
Flexibility, conformational diversity and two dimerization modes in complexes of ribosomal protein L12., Wahl MC, Bourenkov GP, Bartunik HD, Huber R, EMBO J. 2000 Jan 17;19(2):174-86. PMID:10637222
Page seeded by OCA on Tue Nov 20 13:11:03 2007