1ext
EXTRACELLULAR DOMAIN OF THE 55KDA TUMOR NECROSIS FACTOR RECEPTOR. CRYSTALLIZED AT PH3.7 IN P 21 21 21.
|
OverviewOverview
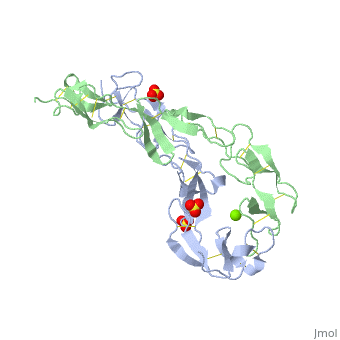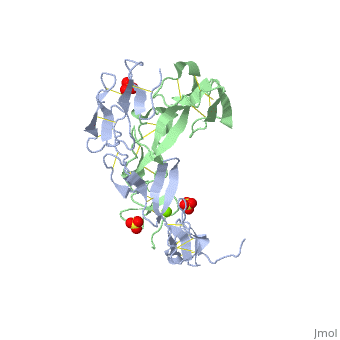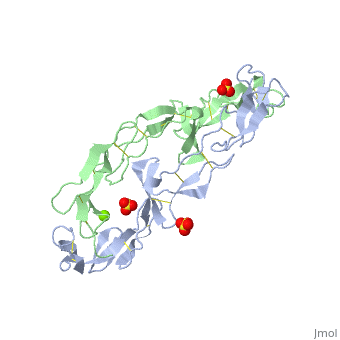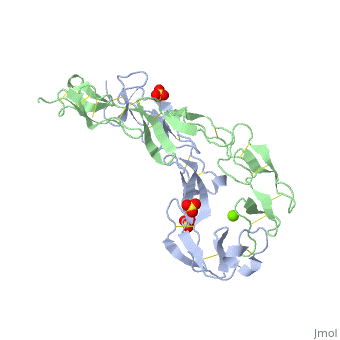
BACKGROUND: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a powerful cytokine that is, involved in immune and pro-inflammatory responses. Two TNF receptors that, belong to the cysteine-rich low affinity nerve growth factor receptor, family (TNF-R1 and TNF-R2) are the sole mediators of TNF signalling., Signalling is thought to occur when a trimer of TNF binds to the, extracellular domains of two or three receptor molecules, which permits, aggregation and activation of the cytoplasmic domains. The complex is then, internalized within an endocytic vesicle, whereupon it dissociates at low, pH. Structure of the soluble extracellular domain of the receptor, (sTNF-R1) both in the unliganded and TNF-bound state have previously been, determined. In both instances, the fourth subdomain of the receptor was, found to be partly disordered. In the unliganded state at pH 7.5, the, extracellular domain forms two distinct types of dimer, parallel and, antiparallel; the antiparallel dimer occludes the TNF-binding. RESULTS: We, have determined the structure of sTNF-R1 in two crystal forms in high salt, at pH 3.7. The orthorhombic crystals diffract to 1.85 and the entire, polypeptide is well ordered. In contrast, the C-terminal 32 residues are, disordered in the hexagonal crystals. In the orthorhombic form, these, residues exhibit a topology and disulphide connectivity that differs from, the other three cysteine-rich domains in the molecule. In both forms, the, interface is considerably more extensive than that used in complex, formation with LTalpha. This 'low pH' dimer is different from both of the, dimers observed in crystals grown at pH 7.5. CONCLUSIONS: The occurrence, of the antiparallel dimers in both low pH crystal forms suggest that they, are not an artefact of crystal packing. Such dimers may form in the low pH, environment of the endosome. Because the dimer contact surface occludes, the TNF-binding site, formation of this dimer would dissociate the, TNF-receptor complex within the endosome. Three of the four cysteine-rich, domains of TNF-R1 are constructed from two distinct structural modules, termed A1 and B2. The fourth subdomain comprises an A1 module followed by, an unusual C2 module. Although the orientation of these modules with, respect to each other is sensitive to crystal packing, ligand binding, pH, and ionic strength, the modules are structurally well conserved between, and within the known sTNF-R1 structures.
DiseaseDisease
Known diseases associated with this structure: Periodic fever, familial OMIM:[191190]
About this StructureAbout this Structure
1EXT is a Single protein structure of sequence from Homo sapiens with SO4 and MG as ligands. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
Structures of the extracellular domain of the type I tumor necrosis factor receptor., Naismith JH, Devine TQ, Kohno T, Sprang SR, Structure. 1996 Nov 15;4(11):1251-62. PMID:8939750
Page seeded by OCA on Mon Nov 12 16:47:27 2007