1tyf
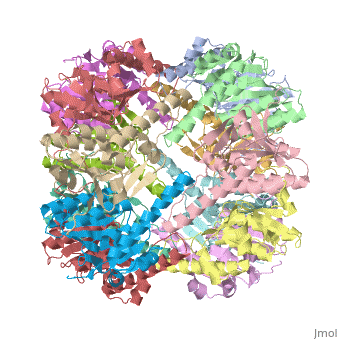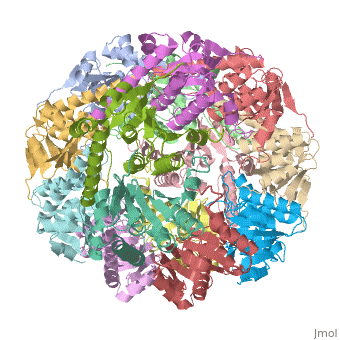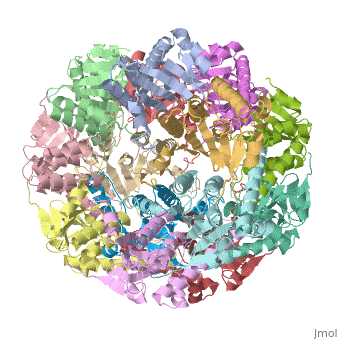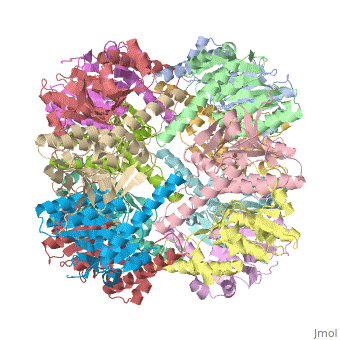
THE STRUCTURE OF CLPP AT 2.3 ANGSTROM RESOLUTION SUGGESTS A MODEL FOR ATP-DEPENDENT PROTEOLYSISTHE STRUCTURE OF CLPP AT 2.3 ANGSTROM RESOLUTION SUGGESTS A MODEL FOR ATP-DEPENDENT PROTEOLYSIS
Structural highlights
Function[CLPP_ECOLI] Cleaves peptides in various proteins in a process that requires ATP hydrolysis. Has a chymotrypsin-like activity. Plays a major role in the degradation of misfolded proteins. May play the role of a master protease which is attracted to different substrates by different specificity factors such as ClpA or ClpX. Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedWe have determined the crystal structure of the proteolytic component of the caseinolytic Clp protease (ClpP) from E. coli at 2.3 A resolution using an ab initio phasing procedure that exploits the internal 14-fold symmetry of the oligomer. The structure of a ClpP monomer has a distinct fold that defines a fifth structural family of serine proteases but a conserved catalytic apparatus. The active protease resembles a hollow, solid-walled cylinder composed of two 7-fold symmetric rings stacked back-to-back. Its 14 proteolytic active sites are located within a central, roughly spherical chamber approximately 51 A in diameter. Access to the proteolytic chamber is controlled by two axial pores, each having a minimum diameter of approximately 10 A. From the structural features of ClpP, we suggest a model for its action in degrading proteins. The structure of ClpP at 2.3 A resolution suggests a model for ATP-dependent proteolysis.,Wang J, Hartling JA, Flanagan JM Cell. 1997 Nov 14;91(4):447-56. PMID:9390554[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences |
| ||||||||||||||||