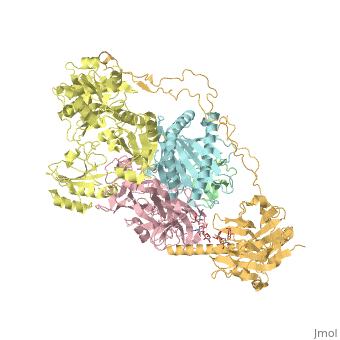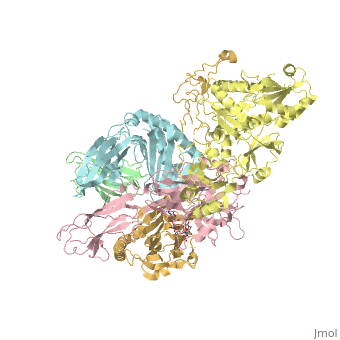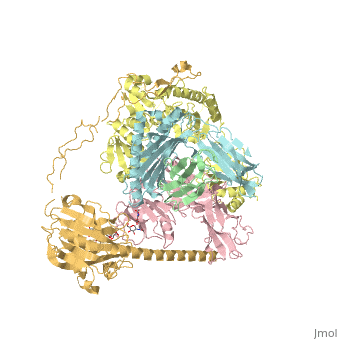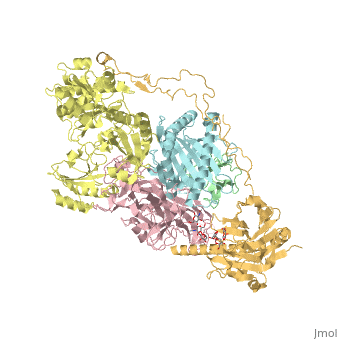
Calreticulin
FunctionCalreticulin (CALR) is a multifunction calcium-binding chaperone. CALR is a molecular chaperone, an extracellular lectin, an intracellular mediator of integrin function, an inhibitor of steroid hormone-regulated gene expression and a C1q-binding protein[1]. DiseaseMost patients with essential thrombocythemia or primary myelofibrosis not associated with JAK2 or MPL mutation have CALR mutation[2]. RelevanceCALR is active in regulating intracellular Ca+2 homeostasis[3]. Structural highlightsCALR structure consists of 3 domains: N-terminal globular domain which has chaperone function; P-domain which is proline-rich, binds Ca+2 with high affinity and possesses a lectin-like chaperone function; C-terminal domain containing an ER retention signal.
|
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of calreticulin3D Structures of calreticulin
Updated on 19-December-2017
1hhn, 1k91, 1k9c – CALR P domain 189-288 – rat - NMR
6eny – hCALR + β-microglobulin + tapasin + protein disulfide-isomerase + MHC class I antigen – human
5v90 – hCALR P domain 238-273 + ERP29
3o0v, 3o0w, 3o0x, 3rg0 – CALR lectin domain 18-206 301-368 (mutant) – mouse
3pos, 3pow – hCALR lectin domain 18-206 301-368
5lk5 – hCALR lectin domain 18-206 301-368 (mutant)
5hca, 5hcb – CALR lectin domain 18-206 301-368 + glucose – Entamoeba histolytica
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Coppolino MG, Dedhar S. Calreticulin. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1998 May;30(5):553-8. PMID:9693955
- ↑ Klampfl T, Gisslinger H, Harutyunyan AS, Nivarthi H, Rumi E, Milosevic JD, Them NC, Berg T, Gisslinger B, Pietra D, Chen D, Vladimer GI, Bagienski K, Milanesi C, Casetti IC, Sant'Antonio E, Ferretti V, Elena C, Schischlik F, Cleary C, Six M, Schalling M, Schonegger A, Bock C, Malcovati L, Pascutto C, Superti-Furga G, Cazzola M, Kralovics R. Somatic mutations of calreticulin in myeloproliferative neoplasms. N Engl J Med. 2013 Dec 19;369(25):2379-90. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1311347. Epub 2013 , Dec 10. PMID:24325356 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1311347
- ↑ Wang WA, Groenendyk J, Michalak M. Calreticulin signaling in health and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Jun;44(6):842-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.02.009., Epub 2012 Feb 21. PMID:22373697 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2012.02.009