Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
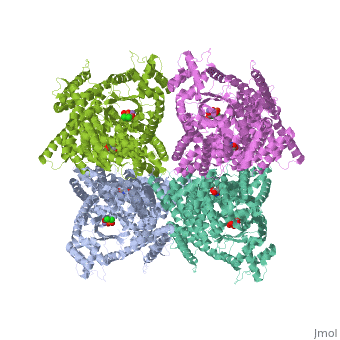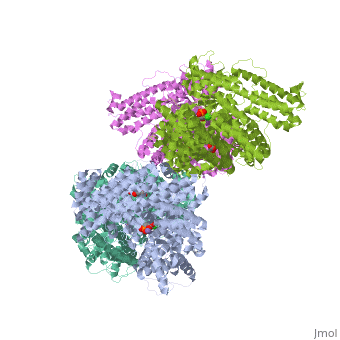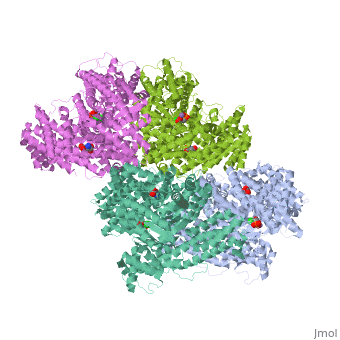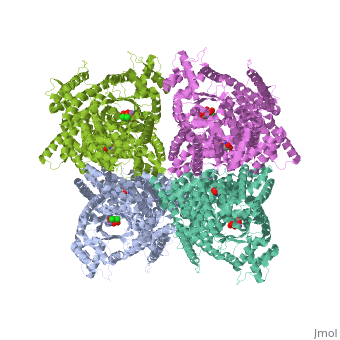
FunctionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) catalyzes the addition of bicarbonate to phosphoenolpyruvate to form oxaloacetate and phosphate. PEPC is part of the carbon fixation process in plants. PEPC is inhibited by aspartate, fumarate and malonate. Structural highlightsMaze PEPC active site contains an Mn+2 ion[1]. |
| ||||||||||
3D structures of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase3D structures of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
Updated on 27-June-2016
3odm – PEPC + malonate – Clostridium perfringens
3zgb, 3zge – PEPC + aspartate – Flaveria pringlei
1fiy, 1qb4 – EcPEPC + aspartate – Escherichia coli
1jqn – EcPEPC + aspartate + PEP analog
1jqo – PEPC – corn
4bxc – FtPEPC + α-D-glucose-6-phosphate – Flaveria trinervia
4bxh – FtPEPC