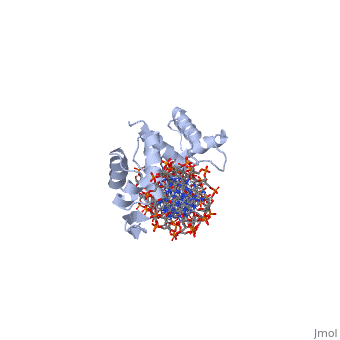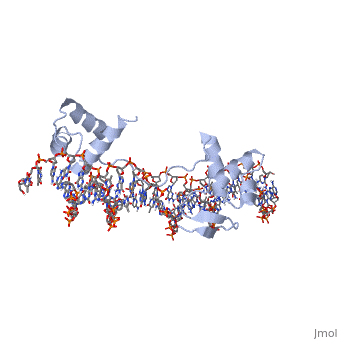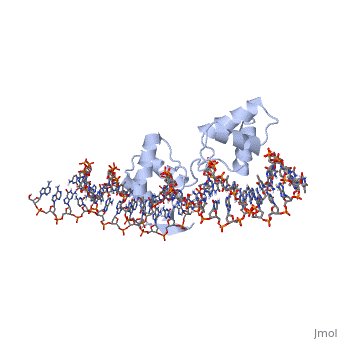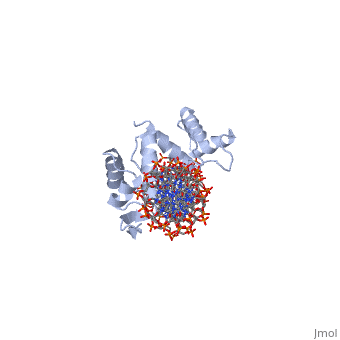
Paired box protein
FunctionPaired box protein (PAX) are transcription factors which contain paired box domain and a paired-type homeodomain (60 amino acid helix-turn-helix). • PAX-6 contain 2 DNA-binding domains. It is a regulatory factor in eye and brain development. • PAX-5 is associated with B-cell differentiation.
DiseaseMutations in PAX-6 are associated with aniridia and Peter’s anomaly. Mutations in PAX-3 are associated with Waardenburg syndrome, craniofacial-deafness-hand syndrome and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. RelevanceStructural highlights |
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of paired box protein3D Structures of paired box protein
Updated on 14-June-2016
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Thompson KW, Joshi P, Dymond JS, Gorrepati L, Smith HE, Krause MW, Eisenmann DM. The Paired-box protein PAX-3 regulates the choice between lateral and ventral epidermal cell fates in C. elegans. Dev Biol. 2016 Apr 15;412(2):191-207. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.03.002. Epub 2016, Mar 4. PMID:26953187 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.03.002