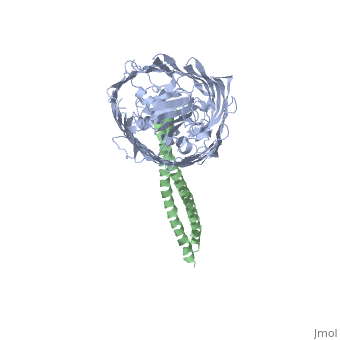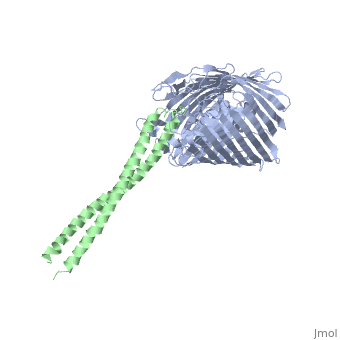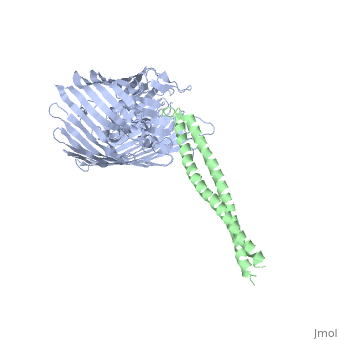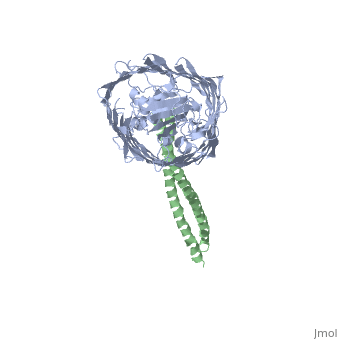
2ysu
Structure of the complex between BtuB and Colicin E2 receptor binding domainStructure of the complex between BtuB and Colicin E2 receptor binding domain
Structural highlights
Function[BTUB_ECOLI] Involved in the active translocation of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) across the outer membrane to the periplasmic space. It derives its energy for transport by interacting with the trans-periplasmic membrane protein TonB. Is also a receptor for bacteriophages BF23 and C1, and for A and E colicins.[HAMAP-Rule:MF_01531] [CEA2_ECOLX] This plasmid-coded bactericidal protein is an endonuclease active on both single- and double-stranded DNA but with undefined specificity. Colicins are polypeptide toxins produced by and active against E.coli and closely related bacteria. Evolutionary ConservationCheck, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe crystal structure of the complex of the BtuB receptor and the 135-residue coiled-coil receptor-binding R-domain of colicin E3 (E3R135) suggested a novel mechanism for import of colicin proteins across the outer membrane. It was proposed that one function of the R-domain, which extends along the outer membrane surface, is to recruit an additional outer membrane protein(s) to form a translocon for passage colicin activity domain. A 3.5-A crystal structure of the complex of E2R135 and BtuB (E2R135-BtuB) was obtained, which revealed E2R135 bound to BtuB in an oblique orientation identical to that previously found for E3R135. The only significant difference between the two structures was that the bound coiled-coil R-domain of colicin E2, compared with that of colicin E3, was extended by two and five residues at the N and C termini, respectively. There was no detectable displacement of the BtuB plug domain in either structure, implying that colicin is not imported through the outer membrane by BtuB alone. It was concluded that the oblique orientation of the R-domain of the nuclease E colicins has a function in the recruitment of another member(s) of an outer membrane translocon. Screening of porin knock-out mutants showed that either OmpF or OmpC can function in such a translocon. Arg(452) at the R/C-domain interface in colicin E2 was found have an essential role at a putative site of protease cleavage, which would liberate the C-terminal activity domain for passage through the outer membrane translocon. Structure of the complex of the colicin E2 R-domain and its BtuB receptor. The outer membrane colicin translocon.,Sharma O, Yamashita E, Zhalnina MV, Zakharov SD, Datsenko KA, Wanner BL, Cramer WA J Biol Chem. 2007 Aug 10;282(32):23163-70. Epub 2007 Jun 4. PMID:17548346[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||