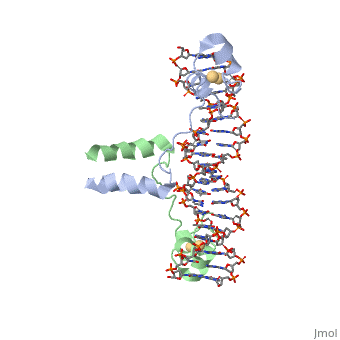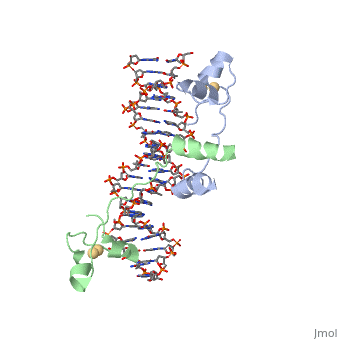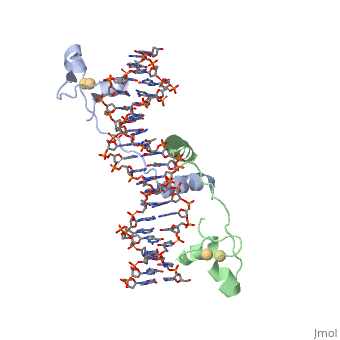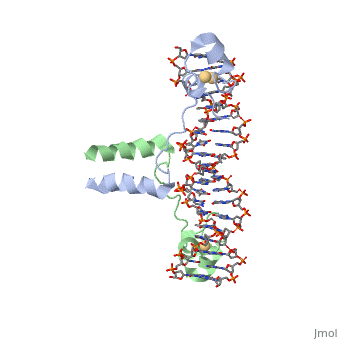
DNA-protein interactions
DNA-Protein interactionsDNA-Protein interactions
While DNA contains all the genetic material in a cell, proteins play an important role in regulating the transcription of DNA to RNA, not to mention replication, repair and packaging.. The interactions between DNA and proteins are important in this process. Most sequence specific interactions occur in the , as the in this groove. In contrast, the contains more of the of DNA.
Helix-Turn-Helix Interactions with DNAThe first DNA binding domain characterized was the helix-turn-helix. In helix-turn-helix protein, two α helices are joined by a turn. In most cases, such as in the Cro repressor, the C terminal helix contributes most to DNA recognition, and hence it is often called the "recognition helix". It binds to the major groove of DNA through a series of hydrogen bonds and various Van der Waals interactions with exposed bases.The N-terminal alpha helix stabilizes the interaction between the interaction between protein and DNA, but does not play a particularly strong role in its recognition.[2] The recognition helix and its preceding helix always have the same relative orientation.[ Leucine zippersZinc fingers |
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
This text shows how to insert references: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644