1puf
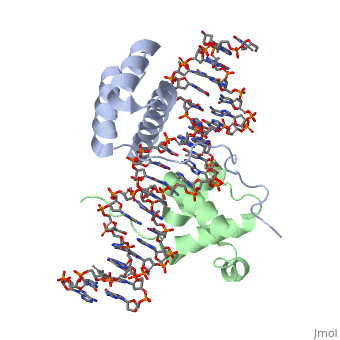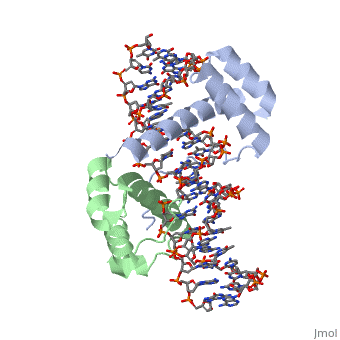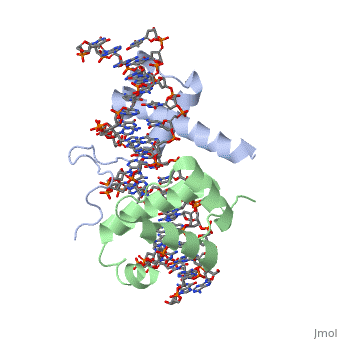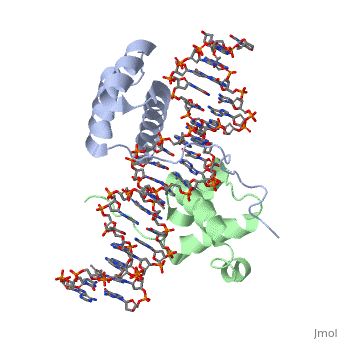
Crystal Structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 homeodomains bound to DNACrystal Structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 homeodomains bound to DNA
The HOX/HOM superfamily of homeodomain proteins controls cell fate and segmental embryonic patterning by a mechanism that is conserved in all metazoans. The linear arrangement of the Hox genes on the chromosome correlates with the spatial distribution of HOX protein expression along the anterior-posterior axis of the embryo. Most HOX proteins bind DNA cooperatively with members of the PBC family of TALE-type homeodomain proteins, which includes human Pbx1. Cooperative DNA binding between HOX and PBC proteins requires a residue N-terminal to the HOX homeodomain termed the hexapeptide, which differs significantly in sequence between anterior- and posterior-regulating HOX proteins. We report here the 1.9-A-resolution structure of a posterior HOX protein, HoxA9, complexed with Pbx1 and DNA, which reveals that the posterior Hox hexapeptide adopts an altered conformation as compared with that seen in previously determined anterior HOX/PBC structures. The additional nonspecific interactions and altered DNA conformation in this structure account for the stronger DNA-binding affinity and altered specificity observed for posterior HOX proteins when compared with anterior HOX proteins. DNA-binding studies of wild-type and mutant HoxA9 and HoxB1 show residues in the N-terminal arm of the homeodomains are critical for proper DNA sequence recognition despite lack of direct contact by these residues to the DNA bases. These results help shed light on the mechanism of transcriptional regulation by HOX proteins and show how DNA-binding proteins may use indirect contacts to determine sequence specificity.
Structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 bound to DNA: Hox hexapeptide and DNA recognition anterior to posterior., LaRonde-LeBlanc NA, Wolberger C, Genes Dev. 2003 Aug 15;17(16):2060-72. PMID:12923056
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
DiseaseDisease
[PBX1_HUMAN] Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PBX1 is a cause of pre-B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). Translocation t(1;19)(q23;p13.3) with TCF3. TCF3-PBX1 transforms cells by constitutively activating transcription of genes regulated by PBX1 or by other members of the PBX protein family.
FunctionFunction
[PBX1_HUMAN] Binds the sequence 5'-ATCAATCAA-3'. Acts as a transcriptional activator of PF4 in complex with MEIS1. Converted into a potent transcriptional activator by the (1;19) translocation. May have a role in steroidogenesis and, subsequently, sexual development and differentiation. Isoform PBX1b as part of a PDX1:PBX1b:MEIS2b complex in pancreatic acinar cells is involved in the transcriptional activation of the ELA1 enhancer; the complex binds to the enhancer B element and cooperates with the transcription factor 1 complex (PTF1) bound to the enhancer A element. Probably in complex with MEIS2, is involved in transcriptional regulation by KLF4.[1][2] [HXA9_MOUSE] Sequence-specific transcription factor which is part of a developmental regulatory system that provides cells with specific positional identities on the anterior-posterior axis. Required for induction of E-selectin and VCAM-1, on the endothelial cells surface at sites of inflammation (By similarity).
About this StructureAbout this Structure
1puf is a 4 chain structure with sequence from Homo sapiens and Mus musculus. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
See AlsoSee Also
ReferenceReference
- ↑ LaRonde-LeBlanc NA, Wolberger C. Structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 bound to DNA: Hox hexapeptide and DNA recognition anterior to posterior. Genes Dev. 2003 Aug 15;17(16):2060-72. PMID:12923056 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.1103303
- ↑ Okada Y, Nagai R, Sato T, Matsuura E, Minami T, Morita I, Doi T. Homeodomain proteins MEIS1 and PBXs regulate the lineage-specific transcription of the platelet factor 4 gene. Blood. 2003 Jun 15;101(12):4748-56. Epub 2003 Feb 27. PMID:12609849 doi:10.1182/blood-2002-02-0380
- ↑ Bjerke GA, Hyman-Walsh C, Wotton D. Cooperative transcriptional activation by Klf4, Meis2, and Pbx1. Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Sep;31(18):3723-33. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01456-10. Epub 2011 Jul , 11. PMID:21746878 doi:10.1128/MCB.01456-10