G18secL03Tpc4
|
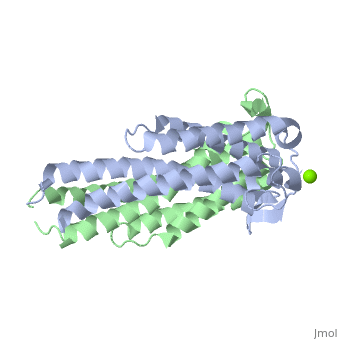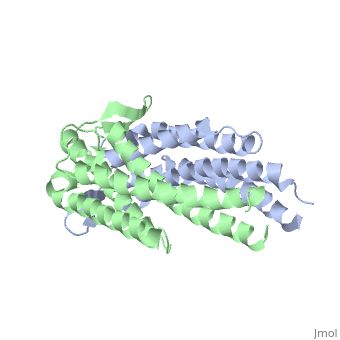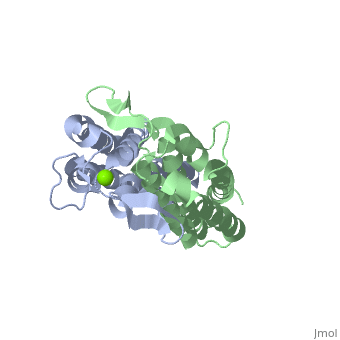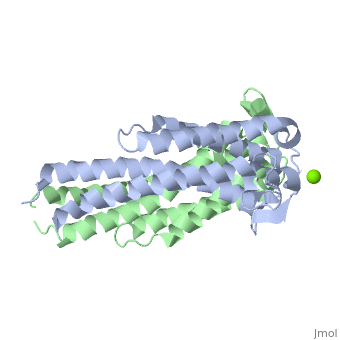
Outer surface protein C (OspC) of Borrelia burgdorferiOuter surface protein C (OspC) of Borrelia burgdorferi
Outer surface protein C (OspC) is one of the major antigens on the surface of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. It greatly differs from other outer surface proteins, such as OspA and OspB in both structure and function. The uniqueness of OspC is that it comes into play when the pathogen is being transmitted to humans or other mammals. OspC is being produced by Borrelia burgdorferi when infected ticks feed, but its synthesis is known to slow down greatly after transmission to a mammalian host. It was demonstrated that those spirochetes that lack OspC are capable to replicate inside and migrate to the salivary glands of the tick vector but do not infect mammals [1]
</ref>. Therefore, OspC is believed to determine virulence of the spirochete to mammals, including humans.