Molecular Playground/FAK
(FAK) Focal Adhesion Kinase
|
|
BackgroundBackground
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a protein tyrosine kinase which is recruited at an early stage to focal adhesions and which mediates many of the downstream responses. FAK plays a very important role in integrin-mediated signaling and in modulating such processes as cell growth, differentiation, wound healing, and tumor metastasis.
StructureStructure
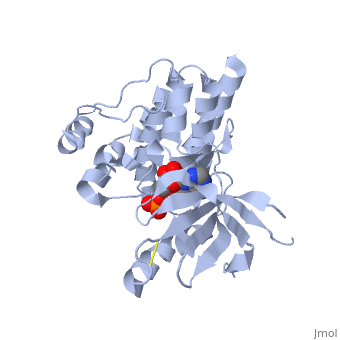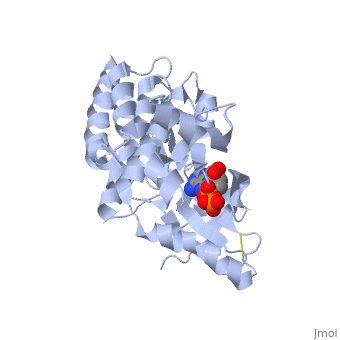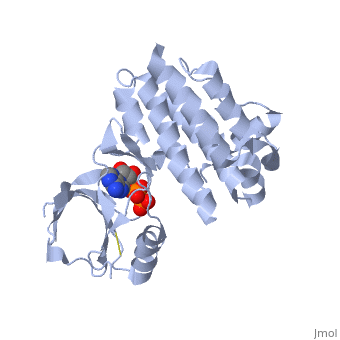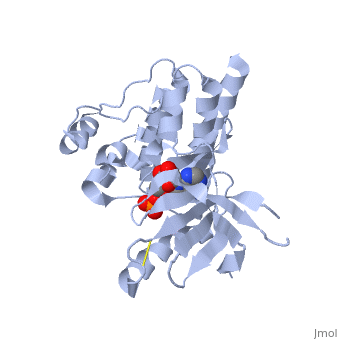
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation by phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2)-induced conformational change. In the inactive state, FAK adopts a closed, auto-inhibited conformation through interactions between its four-point-one, ezrin, radixin, moesin (FERM) and kinase domains.
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) contains a FERM (protein 4.1, ezrin, radixin and moesin homology) domain, a kinase domain and a focal adhesion targeting (FAT) domain. The FAT domain recruits FAK to focal contacts by associating with integrin-associated proteins such as talin and paxillin. It also links FAK to the activation of Rho GTPases by binding to guanine nucleotide-exchange factors (GEFs) such as p190 RhoGEF. FAK contains three proline-rich regions (PRR1–3), which bind Src-homology-3 (SH3) domain-containing proteins such as p130Cas, the GTPase regulator associated with FAK (GRAF) and the Arf-GTPase-activating protein ASAP1. FAK is phosphorylated (P) on several tyrosine residues, including Tyr397, 407, 576, 577, 861 and 925. Tyrosine phosphorylation on Tyr397 creates a Src-homology-2 (SH2) binding site for Src, phospholipase Cgamma (PLCgamma), suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS), growth-factor-receptor-bound protein 7 (GRB7), the Shc adaptor protein, p120 RasGAP and the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). Phosphorylation of Tyr576 and Tyr577 within the kinase domain is required for maximal FAK catalytic activity, whereas the binding of FAK-family interacting protein of 200 kDa (FIP200) to the kinase region inhibits FAK catalytic activity. FAK phosphorylation at Tyr925 creates a binding site for GRB2.
ReferencesReferences
1. Noble, Molecular Biophysics, 2001
2. Satyajit K. Mitra. Nature Reviews, 2005
3. Margaret C. Frame. Nature Reviews, 2010