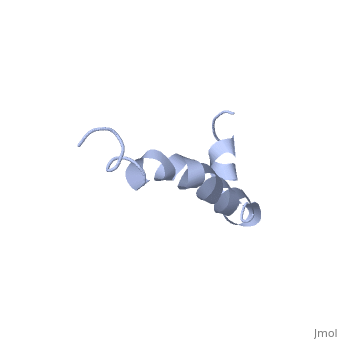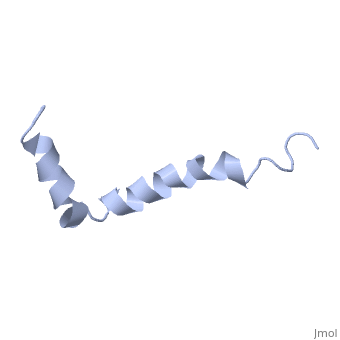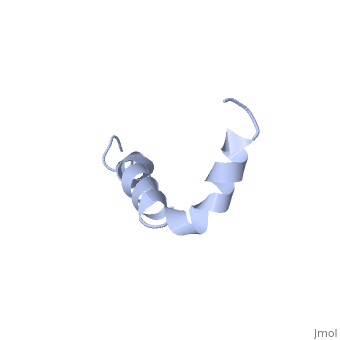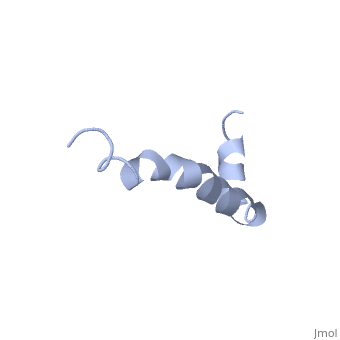
Amyloid beta
IntroductionAlzheimer's disease is characterized by extracellular proteic plaques and intracellular neurofibril tangles.[1] These plaques are collections of beta-amyloid of beta-sheets. The fibrils form when normally soluble amyloid beta proteins reach a critical concentration and become insoluble, misfold, and aggregate.[2] When amyloid beta comes into contact with metal ions and oxygen the result is the production of reactive oxygen species (especially hydrogen peroxide) without oxygen and metal ions amyloid beta ca induce pore formation in neuronal and endothelial cells, triggering cell death.[1][3] Yet another source of amyloid beta toxicity stems from its ability to induce endothelial cell damage through the production of superoxide, though the mechanism of such induction is unclear.[3] While the presence of the fibril plaques remains a marker for Alzheimer's disease recent studies have suggested that alymoild beta oligomers most devestating effect is the impairment of long-term potentiation which decreases dendritic spine density in the hippocampal brain and impairs memory.[4] StructureAmyoloid beta is actually the of the which is a type I membrane-spanning glycoprotein encoded on chromosome 21 [APP].[3] Amyloid beta results from an abnormal cleavage by beta-secretase at the N-terminal and gamma-secretase at the C-terminal[[1]]. The cleavage is nonspecific and results in peptides 39-43 amino acids in length, with 42 being the most common. Such cleavages occur most commonly in the plasma membrane though it can also occur in neuronal membranes.[3] The first 16 residues, Asp-Ala-Glu-Phe-Arg-His-Asp-Ser-Gly-Tyr-Glu--Val-His-His-Gln-Lys, are mostly hydrophobic with acting as a binding domain for Cu(II). Residues function as the self recognition region allowing for the formation of dimers and/or oligomers. This region also serves as the binding site for cholesterol, apolipoproteinE, alpha7nAChr, and amyloid beta-peptide binding alcohol dehydrogenase.[3] The most reasonable structure determined structure consists of ; the first helix (residues 8-25) is well defined and has an RMSD of 0.38 angstroms and the second (residues 28-38) is interrupted at the Ile32-Gly33 connection. The second helix corresponds to the trans-membrane region of APP and thus contains multiple small and hydrophobic amino acids. The two helices are connected by a (residues 26 and 27).[1] The toxicity of amyloid beta is due to the formation of aggregates and oligomers. The actual structures of these oligomers is unknown but is likely similar to that of amyloid beta in mature plaques.[1]
|
| ||||||||||
NeurotoxicityNeurotoxicity
Generation of Radicals
Amyloid beta produces reactive oxygen species, which induces oxidative stress and inflammation.[3]
Pore Formation
Amyloid beta can adhere to endothelial cell walls and create lesions, eventually a large deposit will cause cerebral hemorrhage. The pores cause loss of calcium homeostasis and an influx of Ca2+ into neurons.[3]
Interaction with tau
Tau proteins function to stabilize microtubules [[2]]. Association between Tau proteins and amyloid beta results in dissociation of tau from microtubules which collapses the axonal structure leading to the death of neurons.[3]
Binding ApoE
Apolipoprotein E is normally involved in lipoprotein metabolism and transfer but it has been shown to play a role in the development of Alzheimer's. ApoE4 has the most affinity for amyloid beta and uses the low-density lipoprotein-related protein receptor to internalize amyloid beta into neurons it also promotes the production od amyloid beta by stimulating APP recycling. It is also theorized that apolipoproteins promote the aggregation of amyloid beta into toxic oligomers.[3]
Binding ABAD
Amyloid beta-peptide binding alcohol dehydrogenase (ABAD) is an enzyme belonging to a family of short chain dehyndrogenase/reductases.[5] When amyloid beta binds to ABAD in the mitochondria there is increased mitochondrial dysfunction, increased reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress.[3] It has been found that by inhibiting amyloid beta from binding ADAB, using a decoy peptide, oxygen consumption is increased and the toxic effect are decreased. [6]
Binding Catalase
Catalase normally functions to convert hydrogen peroxide to hydrogen and water. If amyloid beta complexes with catalase at residues 31-35 catalase can no longer breakdown the toxic molecule. Is it thought that the inactivation of catalase is due to the insertion of the sulfur side chain of methionine into the catalytic site.[3]
Prevention and TreatmentPrevention and Treatment
Two major approaches have been taken to treating Alzheimer's; inhibiting the formation of APP and reducing the neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta itself. The most promising treatment the prevention of the enzymes responsible for creating APP, AF267B, which is a muscarinic receptor that activates aplha-secretase and reduces tau pathology.[3] Very recently is was discovered the loss of active JNK associated with the absence of both MKK4 and MKK7 protects neurons against amyloid beta-induced toxicity
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Crescenzi O, Tomaselli S, Guerrini R, Salvadori S, D'Ursi AM, Temussi PA, Picone D. Solution structure of the Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide (1-42) in an apolar microenvironment. Similarity with a virus fusion domain. Eur J Biochem. 2002 Nov;269(22):5642-8. PMID:12423364
- ↑ Vlassenko AG, Benzinger TL, Morris JC. PET amyloid-beta imaging in preclinical Alzheimer's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov 12. PMID:22108203 doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.11.005
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 Rauk A. Why is the amyloid beta peptide of Alzheimer's disease neurotoxic? Dalton Trans. 2008 Mar 14;(10):1273-82. Epub 2008 Feb 12. PMID:18305836 doi:10.1039/b718601k
- ↑ Funke SA. Detection of Soluble Amyloid-beta Oligomers and Insoluble High-Molecular-Weight Particles in CSF: Development of Methods with Potential for Diagnosis and Therapy Monitoring of Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;2011:151645. Epub 2011 Nov 2. PMID:22114742 doi:10.4061/2011/151645
- ↑ Amyloid β-Peptide-binding Alcohol Dehydrogenase Is a Component of the Cellular Response to Nutritional Stress: Yan, Shi Du et al. (2000). DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M000055200
- ↑ Inhibition of Amyloid-beta (A beta) peptide-binding alcohol dehydrogenase-A beta interaction reduces A beta accumulation and improves mitochondrial function in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease: Yao, Jen et al. (2006). [1]