Molecular Playground/Alginate
One of the CBI Molecules being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst and on display at the Molecular Playground.
Alginate is a linear, organic polymer isolated from bacteria and algae. It has been shown to be biocompatible (non-toxic to human cells) and has thus found numerous applications as a thickener in food processing and biomaterial for tissue engineering. Owing to its unique physical properties, alginate hydrogels have been used as a scaffold material for building artificial organs, as a dressing for ulcerous wounds and as a vector for the targeted delivery of anti-cancer drugs.
|
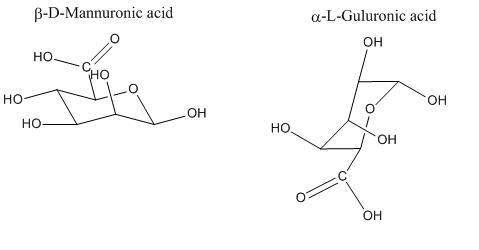
Alginate is composed of a random sequence of mannuronic acid (M) and guluronic acid (G). Exposure to divalent cations (e.g. calcium, barium, etc.) causes the guluronic acid residues to chemically cross-link, and the ensuing entanglements cause the alginate solution to form a hydrogel. Alginate can vary widely in length, monomeric sequence and G/M ratio depending on the source and native climate. The ratio of G/M in the chain influences the strength of alginate hydrogels and can be tuned by combining alginate obtained from different organisms. The rotating molecule to the right is an example of a short chain of sodium alginate.
Molecular Playground banner: A short, linear chain of sodium alginate.
