Succinyl-CoA synthetase
|
Succinyl-Coa synthetase catalyzes the reversible reaction of succinyl-CoA + NDP + Pi <-> succinate + CoA + NTP (where N is either adenosine or guanosine. It can be found in Escherichia coli.
StructureStructure
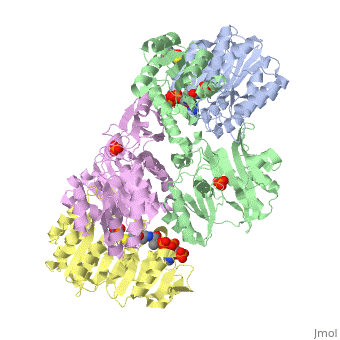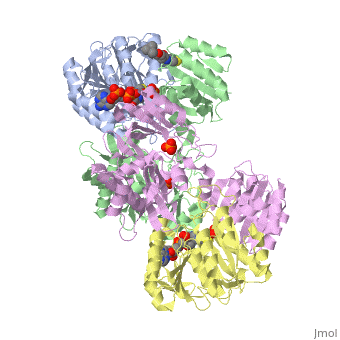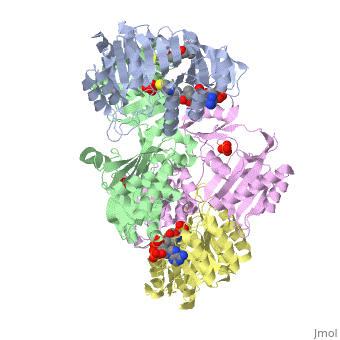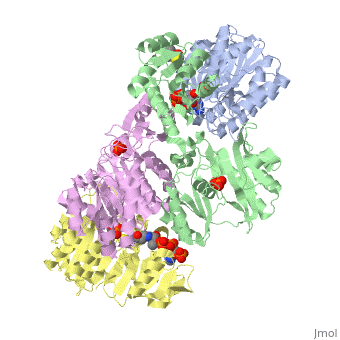
Succinyl-CoA synthetase is a tetramer with an active site on each subunit. This can be seen in the Jmol representation (the PDB code is 1CQJ). The two subunits are denoted alpha and beta. A phosphorylated histidine intermediate is responsible for the dephosphorylation of ATP and it is suspected that there is another active site on the beta subunit that is responsible for the continued catalysis of the reaction. There is a suspected nucleotide binding site on the N-terminal of the beta subunit which would imply that there are two active sites roughly 35 A apart from each other and that the HIS 246 alpha loop moves between them during catalysis. A cooperative binding catalysis mechanism has been proposed and it has been shown that binding of ATP at one catalytic site promotes catalytic activity at another catalysis site. On the alpha subunit it has been shown that interacts with the active HIS 246 alpha residue in the phosphorylated and dephosphorylated enzyme and it is supposed that GLU 197 beta serves a similar purpose on the beta subunit.
Bound Form of Succinyl-CoA synthetaseBound Form of Succinyl-CoA synthetase
|
The form of succinyl-CoA synthetase shown here (PDB code 1CQI) is the bound form with two (the ADP is highlighted and the Mg is in green). As seen here, the residues on both the alpha and beta subunits are present and interacting with the lone Pi group while the ADP group is bound elsewhere on the subunit.