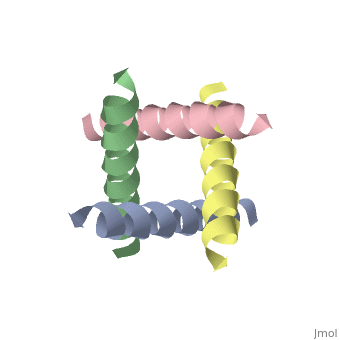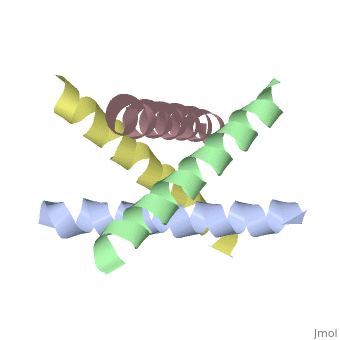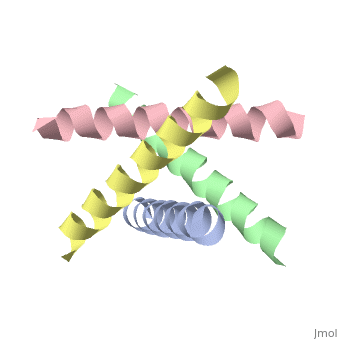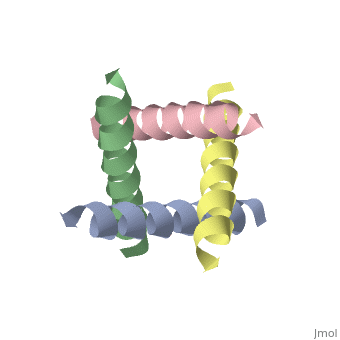M2 Proton Channel from Influenza A VirusM2 Proton Channel from Influenza A Virus
BackgroundBackground
The M2 proton channel is a key protein that leads to viral infection [Takeuchi et al]. The M2 proton channel acidifies the viron which allows the viral matrix protein (M1) to disassociate from the ribonucleoprotein (RNP) [wu et al]. This allows the RNP to be transported to the nucleus of the cell [wu et al]. Several recent studies have looked at the effects of [1] and [Schnell et al] on inhibiting the transfer of protons through the M2 channel [2]. It has been found that M2 is resistant to these two drugs in 90% of humans, birds and pigs [3]. Understanding the structure and function of this proton channel is necessary in solving the resistance problem [2].
StructureStructure
The M2 proton channel from influenza A is 97 amino acid residues and forms a 24-residue N-terminal extracellular domain, a 19-residue trans-membrane domain, and a 54-residue C-terminal cytoplasmic domain [wu et al]. The 19-residue TM domain forms the highly selective proton channel [Takashi et al]. Circular dichroism spectra has shown the TM domain to form one α-helix that spans the membrane [wu et al]. By analytical ultracentrifugation, the TM domain is found to form [takeuchi et al]. This tetrameric bundle of the TM domain is found by NMR to be tilted by 25-38° from the channel axis [takeuchi et al]. The trameric helices form a left-handed bundle that resembles a truncated cone [2]. The TM helicies are arranged around the channel pore with an approximate fourfold rotational symmetry [takeuchi et al].
Central CavityCentral Cavity
pH GatingpH Gating
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Nishimura K, Kim S, Zhang L, Cross TA. The closed state of a H+ channel helical bundle combining precise orientational and distance restraints from solid state NMR. Biochemistry. 2002 Nov 5;41(44):13170-7. PMID:12403618
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Cite error: Invalid
<ref> tag; no text was provided for refs named Stouffer
- ↑ Nishimura K, Kim S, Zhang L, Cross TA. The closed state of a H+ channel helical bundle combining precise orientational and distance restraints from solid state NMR. Biochemistry. 2002 Nov 5;41(44):13170-7. PMID:12403618
proteopedia link